More expensive modifications of networking equipment use the MIMO scheme. This means that data is transmitted in several streams at once. With this technology, data packets are split into chunks and sent one after another at high speed to the receiver. It is important that the receiving side also supports this technology.

- 5 GHz or 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi: advantages of which bandwidth to choose
- Both frequencies on the same router
- What frequency does the wi-fi work on
- 2.4 GHz
- How frequency bands differ from each other
- Today's generation: 802.11ac Wi-Fi
- What parameters will the next generation have
- What classes of Wi-Fi exist
- Why change the wireless mode
- How to configure the b/g/n Wi-Fi router mode
- History
- Characteristics of the protocols
- Standard a
- 802.11b
- WiFi data encryption and types of authentication
- What is WEP wifi security?
- What is a WPA key or password?
- What is WPA2-PSK – Personal or Enterprise?
- What is WPA3-PSK?
- WPA Encryption Type – TKIP or AES?
- Comparison of speeds in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands
- Actual Wi-Fi speed: 2.4 GHz (802.11n)
- Advantages and disadvantages of Wi-Fi protocols
- 802.11а
- 802.11b
- 802.11g
- 802.11n
- What mode to choose on the Wi-Fi router
- How to find out what frequency your wi-fi router works on
- Which one is better, how to change the settings
- 2.4 or 5 GHz
- Choosing between 20 and 40 MHz
5 GHz or 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi: advantages of which bandwidth to choose
Today's Wi-Fi can operate in two different radio frequency "bands": 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz. 5 GHz Wi-Fi has become widespread thanks to the 802.11n standard – now known as Wi-Fi 4 – which was introduced back in 2009. Prior to that, the standard frequency for Wi-Fi was 2.4 GHz. This was a big upgrade! 5 GHz uses shorter radio waves, which provides higher speeds.
WiGig goes further and operates in the 60 GHz band. This means even shorter radio waves, resulting in even faster speeds, but over a much shorter distance.
5 GHz has also provided a more reliable wireless connection, especially in dense areas with many networks and devices. Traditional cordless phones and wireless baby monitors also operate at 2.4 GHz. This means that they only affect 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi, not 5 GHz Wi-Fi.

Thus, 5 GHz is faster and provides a more reliable connection. It's a newer technology, and it's tempting to use 5 GHz all the time and scrap the 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi. But the shorter radio waves of 5 GHz Wi-Fi mean that it can cover a shorter distance and doesn't penetrate hard objects as well as 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi. In other words, 2.4 GHz can cover a larger area and pass through walls better.
Both frequencies on the same router
Today's routers tend to be dual-band and can handle separate 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi networks simultaneously. Some are "tri-band," which can provide a 2.4 GHz signal along with two separate 5 GHz signals to reduce congestion among 5 GHz Wi-Fi devices.
This isn't just a compatibility feature for older devices that only support 2.4GHz Wi-Fi. At times, you'll need 2.4GHz Wi-Fi even with a modern device that supports 5GHz.
Routers can be set up in one of two ways: they can hide the difference between 2.4GHz and 5GHz networks or reveal it. It all depends on how you name the two separate Wi-Fi networks. For example, you could name both networks "MyWiFi" and give them the same password. In theory, your devices will automatically choose the best network at any given time. But this doesn't always work correctly and you might get devices connected to a 2.4 GHz network when they should be using 5 GHz or vice versa.
So instead, you might call one network "MyWiFi – 2.4 GHz" and another "MyWiFi – 5 GHz". The names don't have to be related to each other or include frequency – you can call one "peanut" and the other "apple" if you want. With two different names, you can choose between networks on the device. Of course, you can still give them the same password.
What frequency does the wi-fi work on
Many users wonder how to find out what frequency Wi-Fi is running on. At the moment, network equipment operates in only two bands – 2.4 and 5.
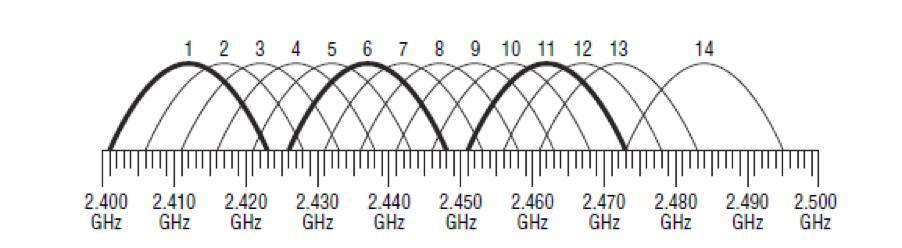
In the vast majority of cases, the 2.4 GHz frequency is used, because it appeared first. Each remote access point on this frequency operates on channels one through thirteen inclusive.
As a rule, problems with the Internet connection occur if there is a working router nearby. Thus, on the same channel they simply share the speed between them. By default, network equipment automatically connects to the most free channel, so in case of Internet problems it is recommended to reboot the router.
Please note! Such manipulation is not able to unload the range even a little bit. That is why experts strongly recommend buying dual-band routers, which will allow you to use the second wave length of 5 GHz, which is more free because it is new.
Now it is worth familiarizing yourself with the principle of setting a particular frequency when operating network equipment.
2.4 GHz
The frequency of Wi-Fi signal is set quite simply, it is done in the router's web-shell. After logging into the system, the user should go to the "Wireless 2.4 GHz" section. Then the sequence of actions looks as follows:
- Go to "Wireless Setting" and specify the name of the wireless network.
- Among available parameters it is necessary to pay attention to the used channel, by default it should be set to "Auto" mode.
- Set Mode 11 b/g/n mixed.
- Set the channel width to "Auto".
- For the changes to take effect, you must "Save" them.
How frequency bands differ from each other
Each frequency band has its own individual characteristics, as well as advantages and disadvantages. Perhaps the most significant differences between the 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi channels are the data transfer rate and coverage area.
- The 2.4 GHz frequency provides a larger coverage area, which implies a wider signal coverage and range compared to the 5 GHz band.
- As for the 5 GHz band, it provides a smaller coverage area, but a higher data rate.
These features of the frequency ranges are due to the characteristics of electromagnetic waves. The fact is that the higher the frequency, the radio waves attenuate more, becoming more susceptible to obstacles in the form of walls, ceilings, doors, furniture and household appliances.
A noticeable reduction in coverage area is especially noticeable in multi-room offices and apartment buildings. For example, a door made of wood reduces the signal level at 5 GHz by almost 1.5 times compared to a lower frequency. The high data rate at 5 GHz is due to the extended bandwidth of 80 mHz.
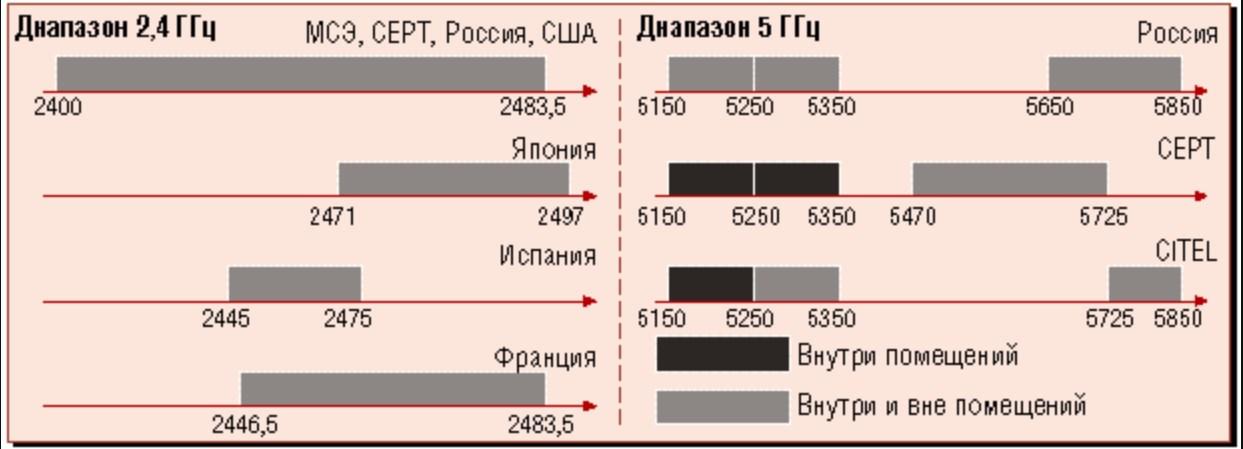
Please note! Another significant difference between the frequency bands that affects the speed of the Internet is the less congestion on the 5 GHz frequency, therefore, the user has the opportunity to use a greater number of channels in operation. This inevitably leads to faster and more stable wireless connections.
Today's generation: 802.11ac Wi-Fi
Technology does not stand still and wi-fi is improving all the time. Another Wi-Fi .11ac protocol has now been released. It happened in 2014. It is the latest approved wireless standard.
The data transfer speed is amazing – 6.7 Gbps, but it can be developed only on a special device with eight antennas. IEEE 802.11ac operates at 5 GHz, making it backward compatible with IEEE 802.11n in that band and IEEE 802.11a. The official name is "Wi-Fi 5."

What parameters will the next generation have
The plan is to replace 802.11ac by 2020 with the latest IEEE 802.11ax standard, which is being developed and refined by the Alliance. It will operate on the 2.4 and 5 GHz frequency bands, but will be able to use additional bands from 1 to 7 GHz. The speeds demonstrated by the devices at the presentation of the standard were up to 11 Gbps.
What classes of Wi-Fi exist
In the description of some network devices you can notice such a parameter as "Wi-Fi Class". It is necessary to understand what this means. A list of possible classes is presented below:
- "AC" means that the wireless network access point works on one of the most modern and fastest protocols IEEE 802.11ac. This, in turn, characterizes the device with a 5 GHz frequency range. You can connect to it from phones and tablets that support .11a/b/g/n/ac.
- "N". Obviously, this marking shows that the device works with IEEE 802.11n technology. It is backward compatible with previous Wi-Fi standards: b, g, n. The letter may be followed by numbers showing the rounded summation values of the maximum channel speeds.
- "AC2600 Wave 2". Maximum speed of 1733 Mbit/s at 5 GHz and 800 Mbit/s at 2.4 GHz. We recommend using devices that support the standard .11aс to develop such characteristics.
Important! There are a number of other classes of Wi-Fi, which are designated approximately the same. That is, the name uses a set of protocols used for data transmission, and the total speed by frequency, if there is support for multiple bands.
The Driver Pack program allows you to find the best driver for your adapter
Why change the wireless mode
Wi-Fi modules built into devices support certain standards. New TVs, computers, phones, etc. connect to wi-fi mode b/g/n/ac, frequency bands use 2.4 and 5 MHz. Not all models support the ac standard. As a rule, these are low-priced products.
Technics with wi-fi reception of earlier years of release assumes support for b/g. Accordingly, when you need to access the Internet, and Wi-Fi works in n mode, you will not be able to connect to the Internet.
When you try to connect, the device displays one of the error statuses about the inability to connect to the network.
Pay attention! To solve the issue, you need to configure the automatic mode of Wi-Fi 11n g b.
How to configure the b/g/n Wi-Fi router mode
To select the desired settings of Wi-Fi mode, you need to go into the settings of the router. To do this, you need to go to the IP address that is listed on the back of the device (TP-Link example TL-MR3220 control panel).
The task is to set the combined mode. This configuration option will allow the device to select the desired mode independently.
When the settings are made, the router is connected to a laptop. For this purpose, a network cable is provided with the router. Upon completion of the setup, the cable is disconnected.
Pay attention! It is recommended to fix the parameters of the settings to be changed. This will help you to return the data to their original state if necessary.
- On the left, as shown in the figure below, is the Wireless tab, you should go to the Wireless Settings page.
- The third item on the list is Mode. Next to it is a drop-down list where you can select the desired mode. The standard setting is 11bgn mixed.
- Press Save button to save your changes. The option Save.
- Restart the device.
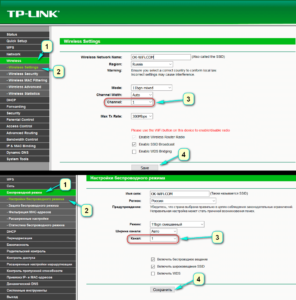
For early models of computers and laptops, when this setting is not successful, you should set 11bg mixed or 11g only.
In the control panel of other router models, the algorithm is the same. The names of the options may be different.
For example, in the menu of ASUS device in the general settings on the right side you need to find the section "Wireless Network" and on the left side in the item "Wireless Network Mode" select the desired option.
Zyxel router settings menu will offer its own menu visualization. Here you should go to the "Access point" section on the top panel, then select the mode from the drop-down list in the item "Standard". To save the data use the "Apply" button.
Pay attention! The mode settings are configured in the same way in all the routers. The difference is in the menu interface. Change the standard in the section with the names: Wireless, "Wireless Network", Wi-Fi.
History
In the heyday of Wifi, the data transfer rate was quite low. A radio link was used, with speeds not exceeding one Megabit per second, sometimes as high as two. The first high frequency format for a wireless connection was called IEEE 802.11a. It had speeds up to 54 Megabits per second, which was considered very fast. The frequency of operation corresponded to five GHz.
In 1999 a new type of Wifi came out, which was not the expected continuation, but a new technology. Its name is IEEE 802.11b. HR-DSSS technology was used and provided for the use of the unlicensed 2.4 GHz frequency band. The transmission speed was up to eleven Megabits per second.
Important. All Wifi specifications, standard encryption parameters and other features are tested for compatibility and certified by a special organization called the Wi-Fi Alliance.

For a long time 802.11b was the most common and popular type used to build a multitude of networks based on wireless technology. Now, it has been replaced by g, which is also gradually giving way to the Wifi n standard, which is fast enough.
802.11g came out back in 2002, is a 2.4 Gigahertz frequency with a Wifi data rate of 54 Megabits per second. Wifi speeds from a to b, g, n, have steadily increased. It has also been increasing with the release of new drivers.
The latest versions have backward compatibility with 802.11b. For example, 802.11g backward compatibility can be done in the DSSS modulation technique. In this case the speed of connection will be limited to 11 Mbit/s, or in OFDM modulation techniques, where the speed will be 54 Megabits per second. It turns out that this standard is the most optimal in the connections of this type.
Characteristics of the protocols
Each of the protocols at the time of its release was considered the most modern and advanced, has personal characteristics and capabilities.
Standard a
Despite the fact that the date of its adoption is considered to be 1999, in practical application it has become only at the beginning of the noughties. Used in technologically advanced countries, such as Japan and America. In domestic conditions has not reached a sufficiently large popularity. It uses a signal modulation scheme that works on the principle of multiplexing with separation according to orthogonal frequencies.
Note! A large mass of information is divided into parallel sub-streams with low bit rate, subsequently, a certain number of carriers is used for modulation.
The protocol establishes three mandatory information exchange rates, at six, twelve and twenty-four Megabits per second, as well as as as many as five additional ones. It is possible to use two channels at the same time and the speed of data exchange increases several times.
802.11b
In this particular case, the method of broadband modulation and direct spectrum expansion is used. The range of operation is fourteen channels, which are distributed in increments of 25 megahertz. This is to ensure that there is no interference or signal overlap. When one channel works, information is not transmitted through the others. Three channels can be applied at the same time.
The maximum Wi-Fi speed will depend on the amount of interference and the distance between the devices.
The protocol introduces the highest possible transmission speed of 11 Megabits per second, which is comparable to a 10 BaseT Ethernet wired network. Such performance takes place only when information is transmitted by a single WLAN device. If an increased number of subscriber stations are used at one time, the data is distributed evenly among subscribers, resulting in lower speeds for a particular device.
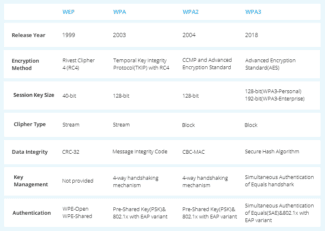
WiFi data encryption and types of authentication
So, we have seen the need for wifi network encryption, now let's see what types there are:
What is WEP wifi security?
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is the very first standard that appeared, which in terms of reliability no longer meets modern requirements. All programs set up to break into the wifi network by brute forcing are mainly aimed at finding the WEP encryption key.
What is a WPA key or password?
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) is a more modern standard of authentication that allows you to reliably protect your local network and the Internet from illegal intrusions.
What is WPA2-PSK – Personal or Enterprise?

There are two other security standards for WiFi WPA2 and WPA:
- Personal, referred to as WPA/PSK or WPA2/PSK. This type is the most widely used and is best for most purposes – at home or in the office. With WPA2/PSK, we set a password of at least 8 characters, which is stored in the memory of the device that we connect to the router.
- Enterprise is a more complex configuration that requires RADIUS enabled on the router. It works like a DHCP server, i.e. a separate password is assigned for each individual connected gadget.

What is WPA3-PSK?
The standard of WPA3-PSK encryption has appeared quite recently and has come to the replacement of WPA2. Although WPA2 is known for its high security features, WPA3 is not vulnerable to being hacked. All modern devices already support this type – routers, access points, wifi adapters, and others.
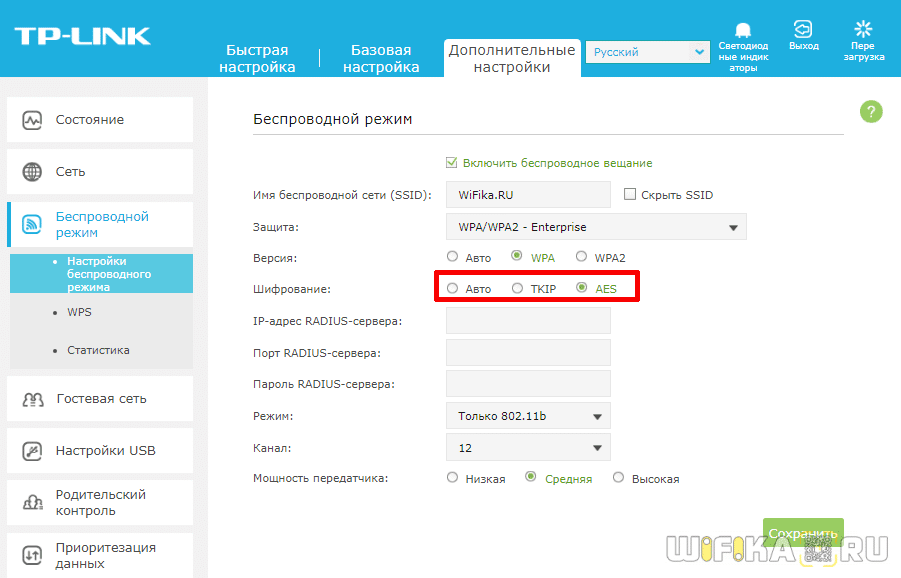
WPA Encryption Type – TKIP or AES?
So, we have decided that WPA2/PSK (Personal) is the best choice for network security, but it has two other types of encryption for authentication.
- TKIP – this is an obsolete type today, but it is still widely used because many devices for a number of years now only support it. Does not work with WPA2/PSK and does not support 802.11n WiFi.
- AES is the latest and most secure type of WiFi encryption.
Comparison of speeds in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands
Before checking the speeds via Wi-Fi, I decided to measure them via network cable. Here are the results:
- The speeds directly from the ISP network cable into the laptop (without the router):
 I expected to see about 100 Mbps (that's the speed according to the tariff) . Perhaps the problem is in the network card of the laptop (the laptop is not very new) . For some reason, I immediately thought that the provider does not give the advertised speed. But as it turned out later, the speed via Wi-Fi in the range of 5 GHz was under 100 Mbps.
I expected to see about 100 Mbps (that's the speed according to the tariff) . Perhaps the problem is in the network card of the laptop (the laptop is not very new) . For some reason, I immediately thought that the provider does not give the advertised speed. But as it turned out later, the speed via Wi-Fi in the range of 5 GHz was under 100 Mbps. - By cable, but from the router, the speed was about the same:
 I think the problem is in the network card of the laptop. Probably in the driver. Too bad, I didn't have another computer handy. But the cable speeds are not of much interest to us. This is just a general picture of what's going on.
I think the problem is in the network card of the laptop. Probably in the driver. Too bad, I didn't have another computer handy. But the cable speeds are not of much interest to us. This is just a general picture of what's going on.
Since when the signal level drops, the Internet speed also drops, I measured in two places. Closer to the router and further away. In this article I will also show the actual Wi-Fi speed in two variants:
- At a distance of about 6 meters from the router. No line of sight. In the way one wall with a closet (closet) .
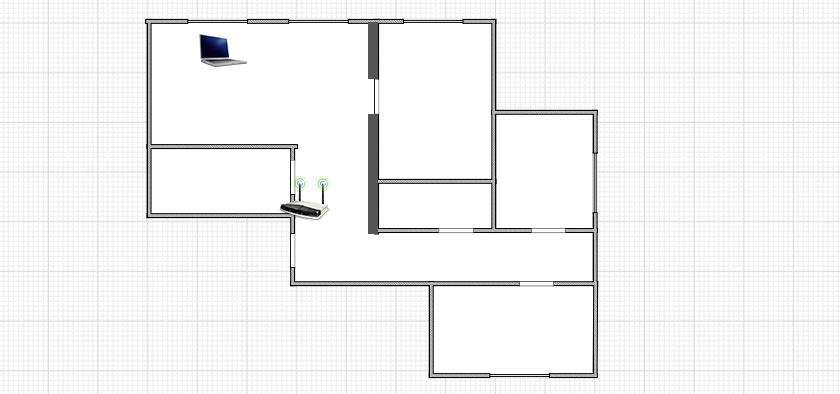
- Then I moved further away from the router. The signal went through 2-3 walls (one of them load-bearing) . The signal level on the laptop was no longer maximal. Especially in the 5 GHz band.

Actual Wi-Fi speed: 2.4 GHz (802.11n)
1 First, I connected to a Wi-Fi network in the 2.4 GHz band. The signal is good (all the divisions on the laptop) . This is the speed on the 2.4 GHz band near the router:

Even for the 2.4 GHz band, that's low speed. Especially since my router is not a budget router. I used to get up to 50 Mbps. But rarely. I think the 15 neighboring Wi-Fi networks in the same range are doing their job (creating interference).
2 Move away from the router and check the speed. On the same 2.4 GHz band. As you can see, the speed has dropped a bit. The ping is up. The signal level has also dropped a little bit. The screenshot shows the maximum signal, but sometimes one division was missing. Note the network level in the 5 GHz band (Marsik_5G) in the screenshot below. The signal is almost nonexistent.

Along with the Wi-Fi signal level, the connection speed is dropping.
The speed of the Wi-Fi network in the range of 2.4 GHz is not very good. Basically, the normal speed in this range is somewhere between 40 Mbps and 70 Mbps. It can be less, or more (very rare) . It all depends on the equipment (router and client) , settings, interference, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages of Wi-Fi protocols
Each subsequent Wi-Fi technology has its own advantages and disadvantages. Developers are constantly improving the initial parameters, trying to speed up the performance and stability of the line.
802.11а
Refers to the first certified variants developed in 1999. It functions based on the method of broadband modulation with direct spectral expansion. Characterized by:
Important. The standard band is subdivided into 3 independent channels providing operation of three grids. Products released in this class are certified by WECA (an international organization).
802.11b
Started to be used in 2001, is used in the U.S. and Japan, in European countries and Russia has not spread. When creating it the main accent was made on clock frequency and the level of throughput. Modifications allowed to eliminate the influence of other equipment on the quality characteristics of the signal.
The device has a higher cost, the coding is by the "Convoltion Coding" system.

802.11g
This version is popular due to its compatibility with the 802.11b standard and its data transfer rate. It first appeared in 2002, now it is less common. Its advantages include:
The device operates at a frequency of 2.4 GHz, with a speed of 54 Mbps.
802.11n
The latest generation of the standard, registered in 2009. It is an improvement on 802.11b, operating in the same frequency range. It outperforms its predecessors in terms of speed, showing speeds in tests of about 600 Mbps. Requires the simultaneous use of four antennas for operation.
Important! The new developing technology can cause device conflicts. The problem is associated with different manufacturers of devices and peculiarities of their manufacture.
What mode to choose on the Wi-Fi router
Routers support Wi-Fi protocols b, g, n. Dual-band devices can function under the as standard. Modern mobile devices, laptops operate in Wi-Fi bgn mode under different bands – from 2.4 to 5 GHz.
Important! Outdated hardware can not support the types of "as" and Wi-Fi n. If the router has one of the specified, the device will not be able to connect to the connection.
The optimal solution when selecting the mode is considered a mixture of Wi-Fi standards from b, g, n. In this case, the newest and older devices will function on the line. This mode is preinstalled on most adapters. If there is no outdated equipment, then experts recommend setting the range to 2.4 GHz – this approach will increase the speed of the Internet.

How to find out what frequency your wi-fi router works on
Before making adjustments to the modem, it is necessary to review the current settings. How to find out the frequency of the Wi-Fi router through the settings:

- Open the browser.
- Login to the panel as administrator: in the search box write 192.168.0.1.
- Enter login, password. Standard ones often have the same appearance – Admin.
- Go to Wireless mode. The box will indicate the frequency and other operating parameters.
Also the range can be found via WiFiInfoView utility. With it you can not only determine the frequency, but also change the settings:
- Download a small program.
- If the utility is in an archive, then unzip it.
- Run the exe file. Installation on the device is not required.
- The screen shows the information about the current channel and frequency. There is no need to open any additional parameters of the modem.
Which one is better, how to change the settings
Almost all adapter settings are made in the web interface. Different routers may have different instructions on how to change the settings. Here's an example of how to work with TP-Link:
- Open your browser. Enter the standard 192.168.1.1 (or 0.1) number set.
- Click on Settings.
- In the login and password fields, write admin. Sometimes the default may be another word – user.
- Go to the menu, in the left column will be the item Wireless mode.
- There you will find the Bandwidth, choose the frequency.
- Save. Reset the network adapter.
2.4 or 5 GHz
Conclusion: Each frequency has advantages and limitations depending on local conditions and individual tasks. Users living in a regular apartment can have a high-speed connection at 2.4 GHz as long as the network is not too congested. When you need to broadcast the signal over long distances or to reduce serious interference, the 5 GHz is a priority.
Important! Older router models may not support the 5 GHz transition. Usually the marking is indicated on the body of the device.

Choosing between 20 and 40 MHz
Within the 2.4 GHz frequency, you can also vary the bandwidth: 20 or 40 MHz. At first glance, the larger width is preferable, but it is worth examining their characteristics in more detail:
- The 20 MHz width has three non-intersecting channels. They are independent, so there will be no interference even when 2-3 devices are connected.
- The 40 MHz band has one free channel. To have a good connection speed, it is possible to activate Wi-Fi on only 1 device.
- Setting clear modes on older hardware provokes incompatibility of devices.
Consequently, the 40 MHz indicator passes the pulse well, but negatively affects the quality of neighboring connections, that is, the risk of conflict is higher if the band becomes wider. And on the practical side it is recommended:
Read More: