Wireless networks have greatly simplified human life. Today it is not necessary to pull wires everywhere, it is enough to put a single router, which will provide wireless connection to the entire apartment or house. Not everyone can understand the principles of these devices, especially when the interface configuration of the router is opened by a person for the first time. Very often people stumble upon such a parameter as Wi-Fi channel width and don't understand what this item of wireless connection settings can mean and how it affects the network created by the router. In today's article, we will look at what 20 or 40 MHz Wi-Fi channel width is, which is better and how they differ.
- 5 GHz Wifi Channels – increase the speed of the Internet with the right channel
- Comparison of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz wifi data transmission standards
- Different Channel Widths and Features
- How to set the channel width on your router
- Tuning your equipment
- How to increase the speed of your WiFi network?!
- 1. Choosing the fastest standard – 802.11N
- How to change the channel on a particular router: step-by-step instructions
- TP-Link
- ASUS
- Useful recommendations
- Wi-fi Channel Width: What It Is and What It Affects
- Which mode to choose
- What's the difference between a Wi-Fi channel width of 20 and 40
- What is the best channel width to choose
- What frequency does wi-fi work on
- 2.4 GHz
- How frequency bands differ from each other
- The dangers of radiation from a WiFi router
- Protection technologies against electromagnetic smog
- What is the difference in practice
- 20
- 40
- How to adjust the bandwidth on the router
- Tp-link
- Asus
5 GHz Wifi Channels – increase the speed of the Internet with the right channel
Sometimes with a WiFi connection, you may experience connectivity problems due to the fact that the wrong channel is chosen to work. In this case, restarting the router may help. However, in some cases this does not help. To establish a wireless connection, you need to figure out what happens, which channel to choose for WiFi, 5 GHz or 2.4 GHz, and what you need to do to specify it in the settings. How to do this correctly will be explained in more detail in this article.
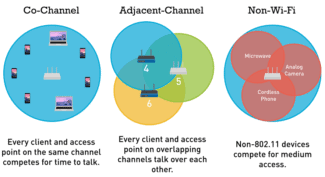
The router, when transmitting a wireless signal, works using certain frequencies. The entire frequency band is divided into several channels, each of which represents a portion of the original gap. The router uses one of the options available to it when operating. It is possible that one of them is used by several people. In this case, they will interfere with each other.

Important! Different channels can partially overlap each other. In this case, at any given time on each of them can transmit a signal only one source. In this case, the connection speed will be significantly lower.
Routers use two bands: 2.4 and 5 GHz. In the first case, according to European and Russian standards there are 13 channels, of which 3 have no common frequencies. Each of them has a width of 20 MHz. The second case uses 33 frequency bands, of which 19 do not overlap.
Comparison of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz wifi data transmission standards
Wireless operation is defined by a group of 802.11 standards. The names use a numerical code with a letter index: a, b, g, n, ac. The first four of these are the most common. The 802.11ac standard is the newest of these. It only works with the 5 GHz band.
Standards with the codes b, g, n work only with the 2.4 GHz frequency band. They are more popular and affordable. Household appliances that can be connected to WiFi also work in this frequency range.
The 5 GHz frequency is rarely used. It improves the quality of communication, but is not yet widespread enough. Routers of this type are backward compatible and can operate in both bands. There are 19 non-intersecting channels in this band, while there are only 3 channels in 2.4 GHz.
The range of this communication is smaller, and objects and walls create more interference than for 2.4 GHz. Not all gadgets are capable of working in this range.
Different Channel Widths and Features
Channel widths can vary, including 20, 40, 80 and 160 MHz. Often routers operate on two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. 2.4 GHz typically uses 20 and 40 MHz wide channels, and 5 GHz uses 40, 80 and 160 MHz wide channels.
Choosing the optimal channel width depends on a number of factors, such as the number of devices on the network, their location, types of applications, and possible sources of interference. In general:
- For 2.4 GHz, 20 MHz is recommended because it reduces the chance of overlap with other networks and provides good compatibility with various devices.
- For 5 GHz, you can use wide channels (80 or 160 MHz) for maximum speed if your home does not have many other networks that might cause interference.
How to set the channel width on your router
You'll need to access your router's administrative interface to set the Wi-Fi channel width. The steps may vary slightly depending on the router manufacturer and model, but the process is usually as follows:
- Enter the IP address of the router in the address bar of your browser. This is usually 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1.
- Enter your username and password to access the router's settings. If you haven't changed them before, look for the information on the router label or in your documentation.
- In the router settings menu, find the section relating to wireless settings (Wireless Settings).
- Select the desired channel width for each band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz).
- Save your changes and reboot your router if necessary.
- Resolve Wi-Fi Channel Width Problems
Clear instruction, using a TP-Link router as an example:
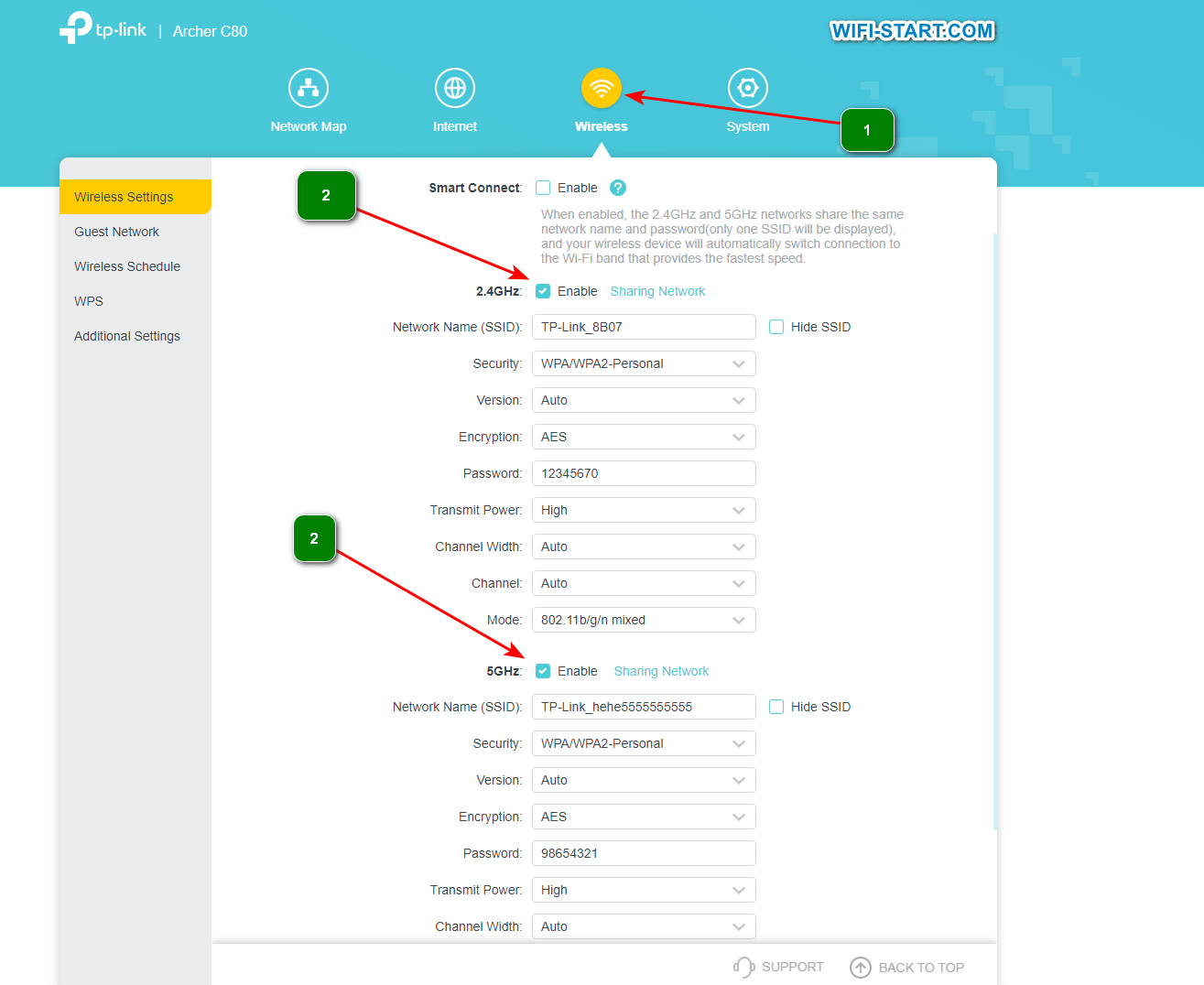
If you encounter problems such as slow speeds, signal loss, or device compatibility, try changing the channel width. Start with the smallest width and gradually increase it, observing signal quality and network performance. You may have to experiment with different channel widths to find the best option for your situation.
Tuning your equipment


The other day a man came to me who was angry about his home router and really wanted to change it. The main complaint about the work was the following – "The router cuts the speed when working via WiFi": when connected via cable it pumps an average of 60-70 megabits, and over a wireless network – no more than 20. And no matter what arguments the subscriber did not want to pay attention, but just stupidly demanded an exchange. Of course, we met him and exchanged one fully working device for another. So in the near future expect it to appear again. To you, my readers, I want to explain in detail the examples of why the router can limit the speed of the Wi-Fi and how you can make this difference, if not completely eliminate, then at least partially leveled for the better.
Before we proceed to active operations, I will give a few facts that you should always take into account if you use Wi-Fi.
Firstly, network equipment manufacturers usually specify the theoretically achievable speed in the technical specifications. That is, if you see Wireless N150 on the router, it means that the maximum speed of the wireless module of the device can theoretically reach 150 mb/s. Correspondingly N300 – up to 300 mb/s. Pay attention to the word theoretically. With the one that you will actually have, it is not that it will not coincide, but it will differ significantly in a smaller way. With this we encountered a few years ago when the standard was actively used 802.11G with a maximum theoretical speed of up to 54 mb/s, which in practice was rarely higher than 20 mb/s. With faster and more modern standards everything is completely identical.
Secondly, if you have problems with WiFi speed, the first thing to do is to update the router's firmware, since it affects the operation of all of its components. You can get it from the official server of the manufacturer. For example, for D-Link devices this server is ftp.dlink.ru..
Pay attention to the firmware versions:
How to increase the speed of your WiFi network?!
Below I will list the main reasons for the decrease in wireless network bandwidth and possible ways to fix them, which will help 90% of the time.
1. Choosing the fastest standard – 802.11N
Currently in the 2.4 GHz band the fastest wireless standard is 802.11N. All wireless routers manufactured since 2010 are marked as Wireless N150 and Wireless N300, which means that they support this standard and the maximum achievable speed. But here the access device's universal settings play a nasty trick on the user. The thing is that in most cases the standard used is mixed, i.e. 802.11 B/G/N mixed. This is correct, but… the way that a wireless network works is that all devices work with the standard that they support. Take a look at this table here:
In other words, if you connect an old laptop with a G-standard adapter and actively receive and transmit data, then the speed of other devices will also decrease. In some cases even by 60-80%. The way out is either not to connect such devices, or, if possible, connect them via cable.
To achieve maximum speed indicators, all adapters in your home network must work on the Don standard. Therefore, if you have all devices modern and support 802.11 N mode, it is desirable to switch the whole WiFi network to it forcibly. In most cases, this is done using the router's configuration settings in the basic WiFi settings section.
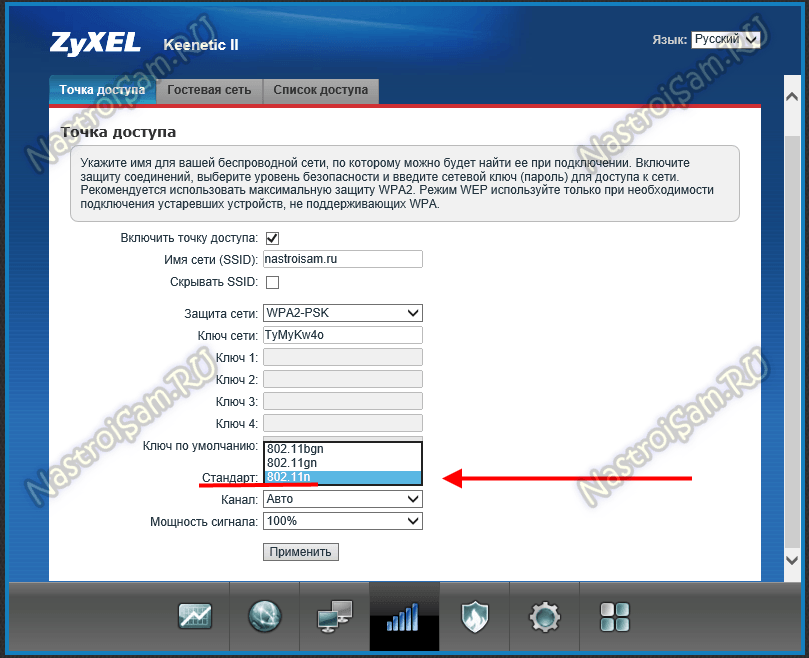
Here is an example for Zyxel Keenetic II:
And here is an example for D-Link DIR-300 on the latest firmware versions:
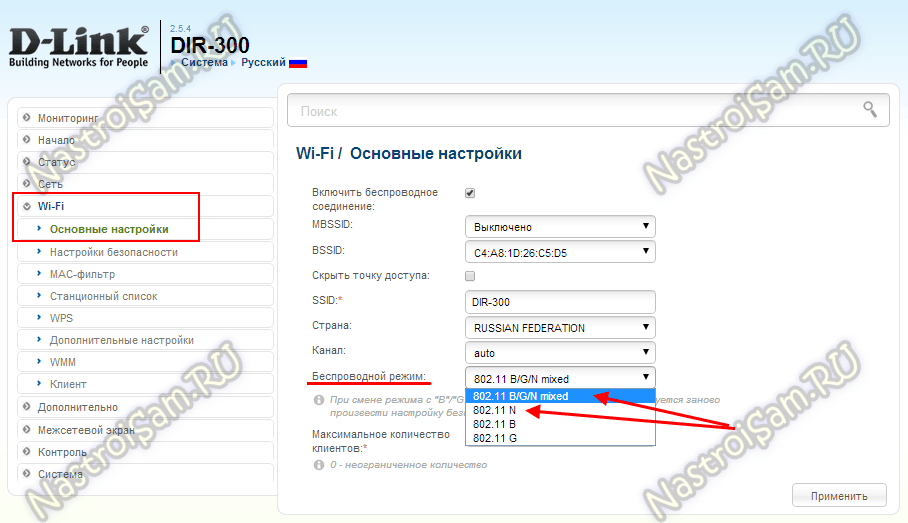
Here you can change the mixed mode to any of the separately supported modes.
On Sagemcom 2804 from Rostelecom, instead of selecting a mode, there is an option to support only 802.11N clients:
How to change the channel on a particular router: step-by-step instructions
Regardless of the type of hardware used, debugging the free bandwidth is performed according to a conventionally uniform algorithm. At the same time, the user must know the IP address of the device and its password in advance.
TP-Link
The devices are widespread in the country, but their interface for the inexperienced user looks complicated and confusing. Which channel on this router is better to choose for Wi-Fi:
- After going into the settings of the device, open the tab "additional adjustment", located at the top of the display.
- Among the information find the block "wireless mode", open the subsection "debugging".
- In the window that appears on the screen look for the parameter "Wi-Fi channel", select one of the proposed slots.
- Complete the adjustment with the "save" button – then the changes will take effect.
Older routers require a slightly different approach. The algorithm includes:
Important! Any changes made to the hardware interface must be saved. Otherwise the user will have to go through all the steps again.

ASUS
Adjustment of the specified type of devices practically does not differ from the work with the equipment that has a standard debugging design. There are no problems with changing the working slot, even for beginners.
- After going to the adjustment subsection, find the inscription "additional debugging" on the left side of the screen.
- Open the sub-item "wireless connections".
- In the opened properties search for "channels" and select an unoccupied slot.
Confirm the changes made by pressing the "apply" button. The system will automatically save the settings entered by the user.

Useful recommendations
Most of the problems users have are due to the inability to log into the interface of the hardware. Standard data for all devices (login and password) is "admin". If the owner has changed the factory settings and forgotten the values, the issue is solved by hardware restart of the router. After that it will go back to the original values.
Trying to study the hardware leads to questions: short gi Wi-Fi what is it and what is it for. The short security interval refers to the interval between data packet transmission (from the device and back to it). So it is sgi Wi-Fi: routers function at the standard values of 800 ns. When the functionality is activated, the interval between Wi-Fi signals is halved and information is transmitted faster. So it sounds in theory, but in practice the speed figures fall due to possible failures and interference on the line.
Important! Interference and signal attenuation are caused by other radio frequency sources, including neighboring routers.
To regulate the operation of the equipment (search for non-intersecting broadcast bands) you need to do some experiments, turn on the specified function and look at the indicators of Internet speed. If they will be extremely low, then the problem lies in the nearby devices and their clogged signal.
The router automatically looks for the fastest options, but does not cope in all situations. Problems arise:
- When the Internet connection speed drops drastically.
- If there are a large number of devices registered on the line. They use randomly matched bands, interfering with each other to function stably.
- When using powerful equipment, but not being able to connect at a distance.
Any of the above options requires manual reconnection of the channel connection. You can use any of the computer utilities or use the analyzer on your mobile device.
Wi-fi Channel Width: What It Is and What It Affects
The width of a wireless channel (other names – Channel Width, Bandwidth) is its bandwidth. Bandwidth affects the speed of the Internet.
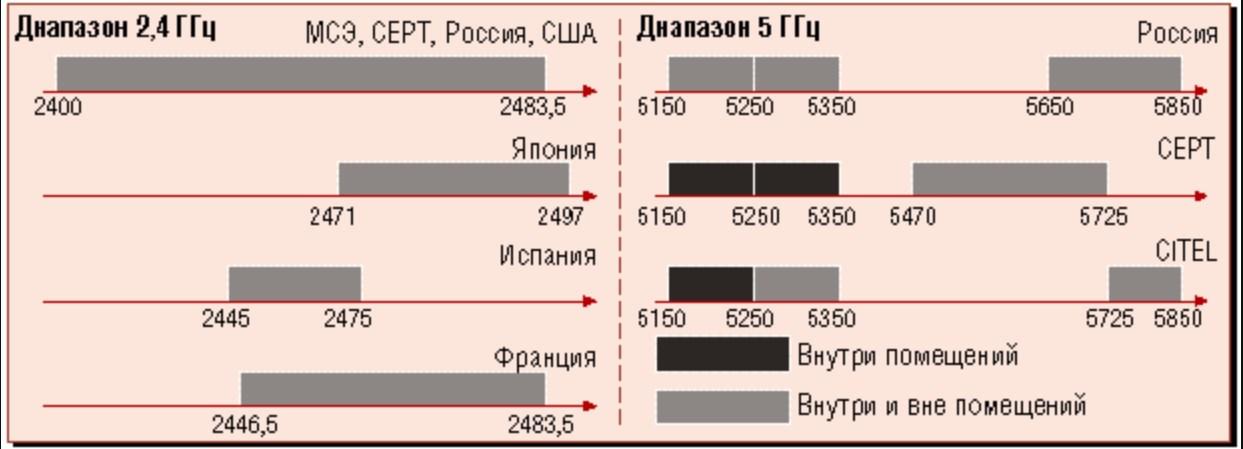
Most modern routers offer a choice of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The advantageous difference of the 5 GHz band is a much larger number of network segments.

These channels are separate frequency bands of the selected band through which the router broadcasts. The bandwidth can be compared to a highway where data "travels" to and from the user. The wider it is, the faster the information is exchanged. For example, the 2.4 GHz frequency band usually allows you to choose a wifi channel width of 20 or 40 MHz.
By dividing the network into such segments, all devices within the coverage area can have a high-quality Internet connection. If two or more devices use the same bandwidth at the same time, it slows down the connection proportionally.
Broadcasting from an identical segment in the area of overlap with the wireless coverage of another router causes noticeable interference and the connection speed drops. You can determine which mode to choose according to the desired bandwidth and channel occupancy.
Which mode to choose
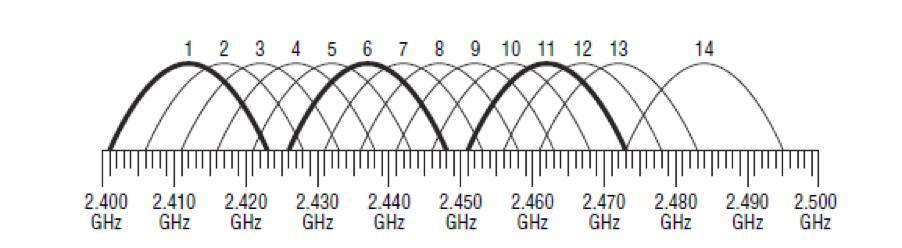
The so-called non-intersecting channels, which have certain numbers, will work best. You can determine them yourself if you look at the broadcast chart, for example, the 2.4 GHz band:
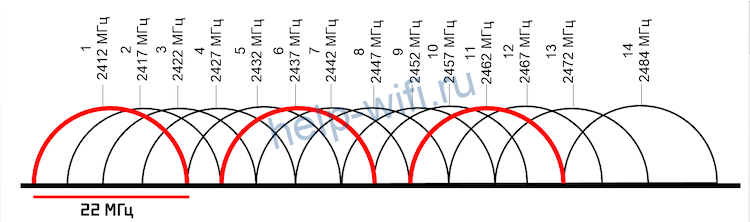
Initially, routers with this frequency mode can broadcast on all 14 channels, but some are reserved for social and government needs. For example, 11 channels are officially used in the U.S. Formally, the laws of the United States do not prohibit citizens to use segments 12 and 13 of the 2.4 GHz band in low-power mode. All channels except 14 are available in Russia and Ukraine. Devices purchased in different countries can see only those frequency band segments, the use of which is approved by the relevant legislation.
Based on the number of 13 channels available to Russians and Ukrainians, channels 1, 6 and 11 will work best. The width of the network segment is also determined by the wireless standard, which is also useful to consider when choosing this parameter.
For example, the minimum conditional channel width of 802.11g and 802.11n specifications is 20 MHz, while its actual value has dropped to 16.25 MHz. This is due to modern signal modulation technologies. The channel spectrum of the 2.4 GHz band with a bandwidth of 16.25 MHz has not 3 but 4 minimally overlapping segments with the numbers 1, 5, 9 and 13.
Broadcasting at 5 GHz provides a much larger number of channels with an identical initial bandwidth. This more advanced wireless technology allows you to choose from 23 non-overlapping segments available depending on the region of use. These channels are usually highlighted in bold in the router's settings.
What's the difference between a Wi-Fi channel width of 20 and 40
Now it's worth sorting out what 20 or 40 MHz Wi-Fi bandwidth is, and which is better. Going back to the previous example with the road and cars, it's worth making a caveat. A wide channel, unlike a freeway, is more negatively affected by external factors. It especially depends on the amount of interference and electromagnetic waves emitted by other home appliances in the house.
Important! So you should keep in mind: the wider the channel, the more it will interfere with other Wi-Fi networks, regardless of the frequency they use. The opposite is also true.
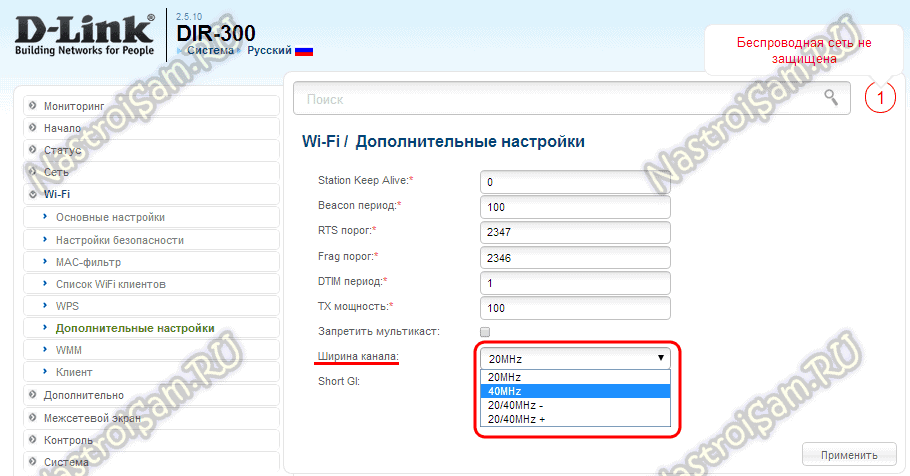
The router's channel settings contain two parameters: 20 MHz and 40 MHz. So what's the difference between them? It is believed that 20 MHz is a narrow channel and 40 MHz is a wide channel. A number of devices allow you to select the parameter automatically. Switching will occur depending on the conditions of use.
This parameter determines not so much the speed of the Internet, but its stability and quality. This is especially true for panel apartment buildings, where up to 4 or more routers can be located on one floor.
Important! If a person is in such a house, it is advisable to choose a width of 20 megahertz. If the user lives in his house, then 40 MHz should be set for maximum efficiency of the device.
For a wifi specification running at 5 GHz, you can even choose a channel width of 80 MHz
What is the best channel width to choose
If you look at the practical side of the issue, using a 40 megahertz channel width in the presence of a large number of wireless networks around is useless. It is enough to take your phone or laptop and look at the list of wireless spots that it can theoretically connect to. The more there are, the less chance the user will feel the difference between 20 and 40 MHz.
Important! The 40 MHz channel will be affected not only by other networks, but also by a number of wireless devices. These include smart watches radio phones microwaves, Bluetooth headphones and so on.
In apartment buildings, a channel width of 20 megahertz works best. Regardless of the fact that it is more limited than 40 MHz, the speed of connection to the WAN at this width is often even higher. It is good if it has an auto-choice channel width function. Activating this option will allow the user not to worry about having the wrong channel selected, because the device itself will adjust to the influence of surrounding factors and switch.
If there is no such function, it is advisable to set it to 20 megahertz. After that, you can test the operation of the device and, if necessary, set another value. There should be no problems with this.
For 2.4 GHz networks often choose a mixed type of channel width
What frequency does wi-fi work on
Many users wonder how to find out what frequency Wi-Fi works. At the moment, network equipment operates in only two bands – 2.4 and 5.
In the vast majority of cases the 2.4 GHz frequency is used, because it appeared first. Each remote access point on this frequency operates on channels from the first to the thirteenth inclusive.
As a rule, problems with Internet connection occur if there is a working router nearby. Thus, on the same channel they simply share the speed between them. By default, network equipment automatically connects to the most free channel, so in case of Internet problems it is recommended to reboot the router.
Please note! Such manipulation is not able to unload the range even a little bit. That is why experts strongly recommend buying dual-band routers, which will allow you to use the second wave length of 5 GHz, which is more free because it is new.
Now it is worth familiarizing yourself with the principle of setting a particular frequency when operating network equipment.
2.4 GHz
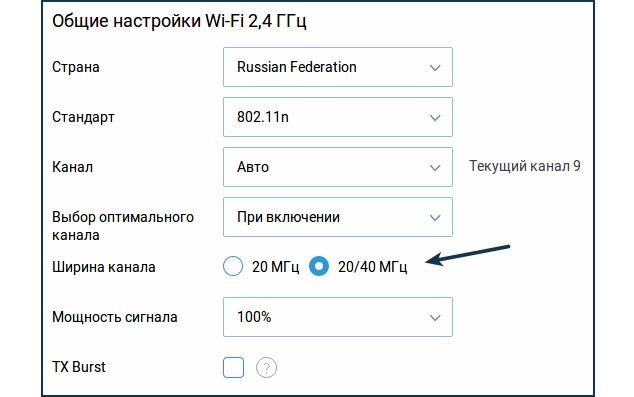
The frequency of Wi-Fi signal is set quite simply, it is done in the router's web-shell. After logging into the system, the user should go to the "Wireless 2.4 GHz" section. Then the sequence of actions looks as follows:
- Go to "Wireless Setting" and specify the name of the wireless network.
- Among available parameters it is necessary to pay attention to the used channel, by default it should be set to "Auto" mode.
- Set Mode 11 b/g/n mixed.
- Set the channel width to "Auto".
- For the changes to take effect, you must "Save" them.
How frequency bands differ from each other
Each frequency band has its own individual characteristics, as well as advantages and disadvantages. Perhaps the most significant differences between the 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi channels are the data transfer rate and coverage area.
- The 2.4 GHz frequency provides a larger coverage area, which implies a wider signal coverage and range compared to the 5 GHz band.
- As for the 5 GHz band, it provides a smaller coverage area, but a higher data rate.
These features of the frequency ranges are due to the characteristics of electromagnetic waves. The fact is that the higher the frequency, the radio waves attenuate more, becoming more susceptible to obstacles in the form of walls, ceilings, doors, furniture and household appliances.
A noticeable reduction in coverage area is especially noticeable in multi-room offices and apartment buildings. For example, a door made of wood reduces the signal level at 5 GHz by almost 1.5 times compared to a lower frequency. The high data rate at 5 GHz is due to the extended bandwidth of 80 mHz.
Please note! Another significant difference between the frequency bands that affects the speed of the Internet is the less congestion on the 5 GHz frequency, therefore, the user has the opportunity to use a greater number of channels in operation. This inevitably results in faster and more stable wireless connections.
The dangers of radiation from a WiFi router
People wonder if WiFi is very dangerous, how long can you stay near it? Some devices have a high frequency and the waves affect the health of the body.
Important A large number of scientists have expressed their opinion that the radiation of the 4G standard affects almost all functions of the brain.

People who are constantly interacting with routers are irritable. The excess signal is reflected in different ways. People sometimes get headaches or complain of poor digestion. It is impossible to fall asleep in the evening, insomnia comes. Constant brain disruption leads to the formation of tumors.
Protection technologies against electromagnetic smog
Electromagnetic smog is rampant in large metropolitan areas. The source is atmospheric electricity, magnetic fields and radio emissions. There are many products freely available to reduce the index. We are talking about shungite-containing and crystalline materials. There are devices like "Neutronics", they create a safe environment for humans.
Above, we talked in detail about the power of the WiFi transmitter. There is data regarding its testing and setting. It is important to remember about safety, to monitor the level of radiation.

Podgornov Ilya Vladimirovich All articles on our site are audited by a technical consultant. If you still have questions you can always ask them on his page.
What is the difference in practice
What does the choice of channel width Wi-Fi 20 or 40 depends on in practice, what is the difference in practice? There is no one-size-fits-all answer to the question of how to choose a lane for a particular setting. It all depends on local conditions, and you can only get the best results by experimenting on the spot. But it doesn't hurt to make a preliminary assessment.
20
If the user lives in an apartment building, it means that in most cases his apartment has several neighboring networks. You can verify this by turning on the network search on the device:
The same picture can be observed in a business center or similar office buildings, where there are many organizations and each tries to organize its own network. In this case you need to focus on the 20 MHz band. It should be understood that in this case the reliability of the network will increase, but the speed may drop if the "localka" includes a large number of devices and the load on the channel is high.
Important! The reliability will also be affected by the use of wireless devices, from headphones to keyboards. The more there are, the narrower the bandwidth is preferable.
40
If the user lives in a private home or there are no other wireless networks in the office, then it makes sense to try increasing the bandwidth to 40 MHz. If there is no interference and the signal strength is sufficient, the bandwidth and speed will increase. You should not forget that the actual connection speed depends on many factors, so in real conditions the choice of bandwidth can only be made according to the results of practical tests.
How to adjust the bandwidth on the router
You can choose the bandwidth in the settings of the router. It is not difficult, but each router manufacturer has slightly different access to the configuration menu.
Please note! Selecting the width of the frequency band is available in many devices, but still not in all devices. There are models where this parameter has a fixed value, or one of two modes can be selected: 20 MHz or auto.
Before proceeding to select the bandwidth value, make sure that the router model you are using has such a setting available.
Tp-link
The easiest way to configure the router is using a browser. To do so you should type 192.168.1.1 (192.168.0.1) in the address bar and enter admin in both fields when prompted for the default login and password. If the login-password pair does not work, you have to look for this information in the documentation of the device. Sometimes this information is written directly on the device.
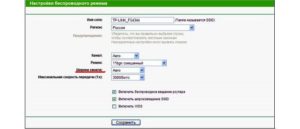
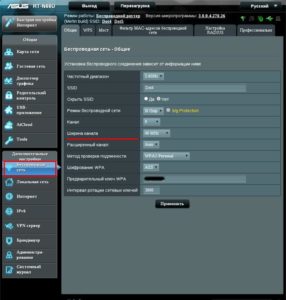
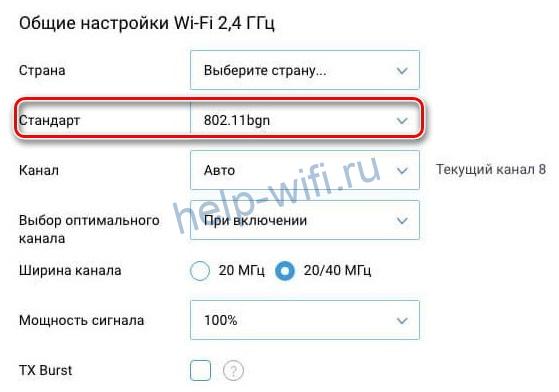
Find "Wireless Mode" – "Wireless Settings" in the menu. On the page that opens, select the item "Channel width", in the list that appears, select the desired value: 20 or 40 MHz Wi-Fi. After pressing the save button, the selected parameter will take effect.
Important! If the router interface does not support the Russian language, then the parameter you are looking for is called Bandwidth (Channel Width) in English terminology.
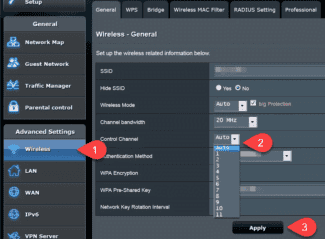
Asus
You can enter the web menu of the router of this manufacturer in the same way as for Tp-Link. In the menu of the Asus router, select "Wireless Network", then "Channel Width". From the drop-down list select and set the required value.