This will reset not only the login data, but also all existing settings.

- IT Technician's Notes
- Wireless Station Modes in Mikrotik
- Setting up the 'Client' mode on D-LINK. Wireless Bridge (WDS).
- D-LINK router as a Wi-Fi network repeater (amplifier)
- Wi-Fi Receiver from a D-LINK router
- Configuring by the example of ZyXEL
- Keenetic V1 router interface
- User complaints and questions
- WISP mode on different routers
- Setting up a TP-Link router as an example
- Preparing to configure
- "Repeater" via cable
- By cable
- How to secure your connection
- Changing your password
- Guest Mode Setting
- How to teach a lesson to fans of free Internet
IT Technician's Notes
Wireless station (client) mode is used in Mikrotik much less frequently than access point mode, but often, when it becomes necessary, administrators are faced with all sorts of difficulties. This is largely due to a lack of understanding of the peculiarities of wireless equipment in this mode. Therefore, in this article we have decided to acquaint readers with the theory and practice of using routers of this manufacturer as a wireless station and to answer frequently asked questions.
Learn how to configure MikroTik from scratch or systematize your existing knowledge at the in-depth MikroTik management course. The author of the course, certified MikroTik trainer Dmitry Skoromnov, personally checks the lab work and monitors the progress of each of his students. Three times as much information as the vendor's MTCNA program, more than 20 hours of practice, and access forever.
To begin with, wireless equipment is far from straightforward. There is a set of standards IEEE 802.11better known as Wi-Fi, which specifies the requirements for wireless data networks and its support guarantees interoperability between devices from different vendors. To put it simply, if your access point and client devices both say that they support 802.11nTo put it simply, if it says that your access point and client devices support the 802.11n standard then they work together, otherwise they don't.
In fact, the devices support more than one standard, and for backward compatibility purposes it is safe to say that any Wi-Fi enabled device that you buy will work with another Wi-Fi enabled device that also supports 802.11 protocols.
But in addition to mandatory support for the standard, many manufacturers implement their own proprietary solutions for wireless devices, and we will not even touch such protocols as Nstream и NV2It should be understood that such features are only supported by hardware from a certain vendor and will not work with other devices. This is neither good nor bad but you should always be clear which of the features provided by the equipment are 802.11 compliant and which are added by the manufacturer.
Wireless Station Modes in Mikrotik
Mikrotik equipment provides a fairly rich set of modes for the wireless station, some of them are standard, the other part contains proprietary extensions, so we have prepared a small compatibility table that allows you to quickly assess the applicability of one or another mode.
The 802.11 column shows the ability of the wireless station to work with the standard equipment from other vendors, RouterOS shows the compatibility with Mikrotik access points in normal mode, and CAPsMAN shows the compatibility with the software controller mode. Compatibility with Nstream and NV2 protocols is not covered by us, as it is far beyond the scope of this article.
Setting up the 'Client' mode on D-LINK. Wireless Bridge (WDS).
First, it is desirable to do a reset on your D-LINK router. Then you have to go into the settings of your router. If you don't know how to do this, see the instructions: how do I enter the settings of my D-Link router? Go to 192.168.0.1. Your control panel may be different. I'll show you an example of my DIR-615. And you, if you don't have the same settings as I do, you can try to update the firmware.
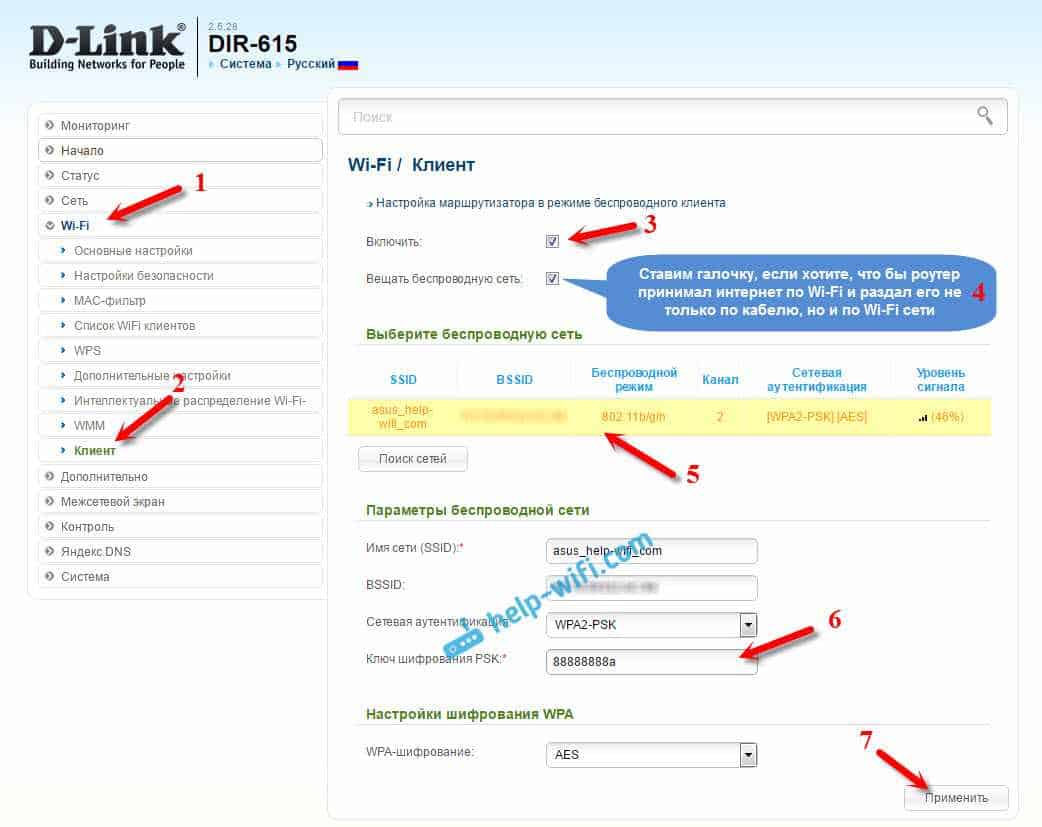
- Go to the tab 'Wi-Fi' – 'Client'. Check the 'Enable' checkbox.
- If you want the router to distribute Internet via Wi-Fi, then check the 'Broadcast Wireless Network' checkbox.
- Next, in the list below highlight your Wi-Fi network, to which the router should connect and receive the Internet.
- All that remains is to fill in the 'PSK encryption key' field, in which you need to specify the password from the main Wi-Fi network, and click 'Apply'.
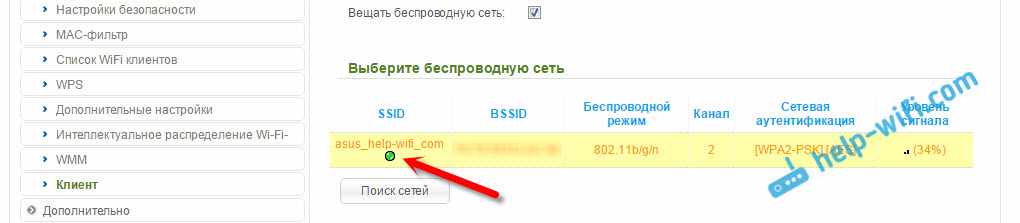
You should see a green icon next to the name of the Wi-Fi network you connected to.
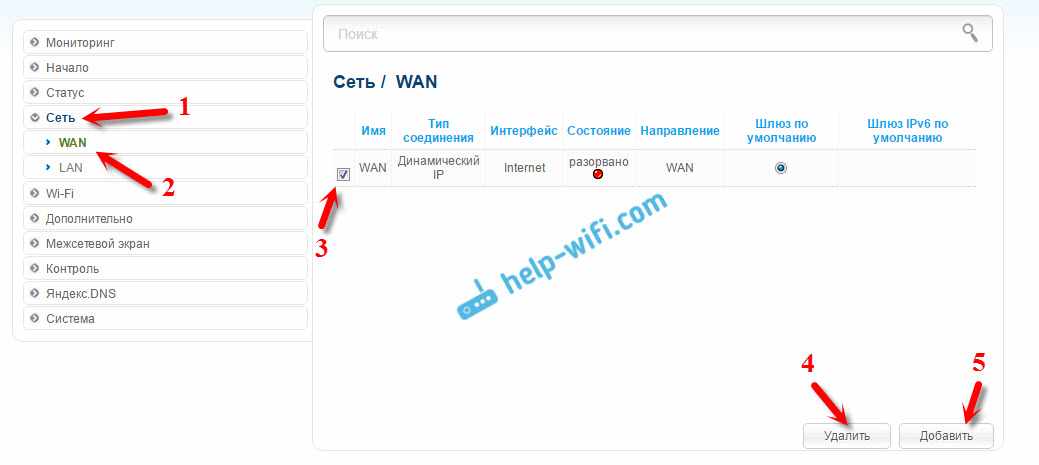
Next, go to the 'Network' – 'WAN' tab. Highlight the connections you have there and press the 'Delete' button.
Then press the 'Add' button. Select 'Dynamic IP' from the list.
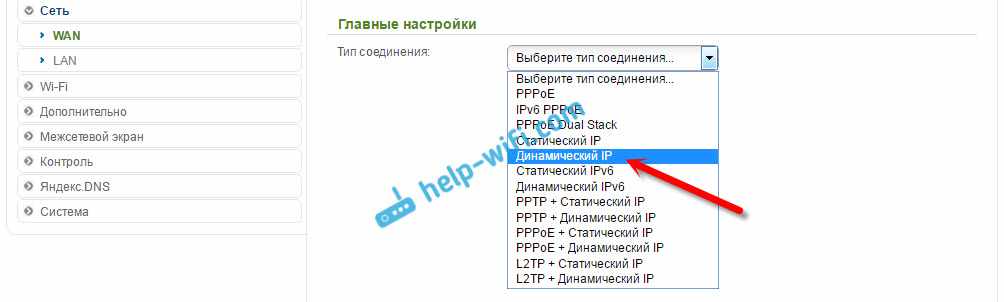
We only need to select 'WiFiClient' in the 'Interface' list. Click the 'Apply' button.
D-LINK router as a Wi-Fi network repeater (amplifier)
The method described above is also suitable for enhancing a Wi-Fi network. But, when configured in 'Client' mode, you will have two Wi-Fi networks. And when the repeater works, there is one Wi-Fi network, just amplified. And the devices automatically switch between the main router, and the repeater (second router).
As it turns out, everything can be set up. And use a D-LINK router to extend the range of the Wi-Fi network.
The first thing to do to set up the 'Client' mode.. Everything is exactly the same as I showed above. When everything is set up, and the Internet through the router will work, you need to set up exactly the same Wi-Fi network settings as on the main router.
To do that, open the 'Wi-Fi' tab. In the field 'Network Name (SSID)' you need to write the name of the network exactly as on the router whose Wi-Fi network you want to enhance, and to which you connected D-LINK.
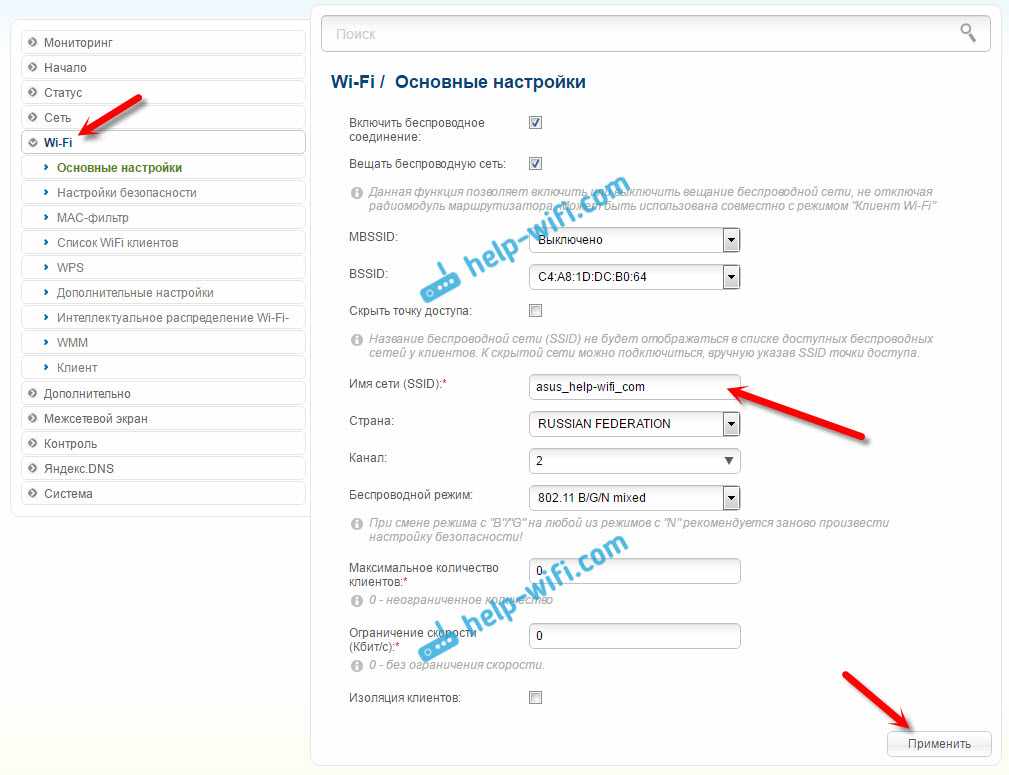
Open another tab 'Wi-Fi' – 'Security Settings'. There you need to write exactly the same password that is used to connect to the Wi-Fi network, which we strengthen. Click on the 'Apply' button, and then click on the message to save the settings.
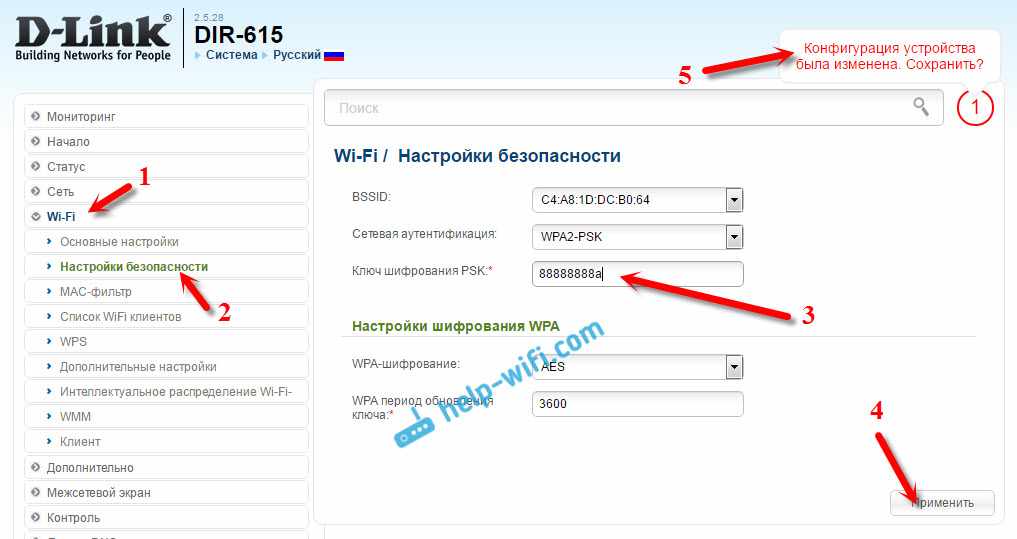
Reboot the router. After rebooting, there should be one Wi-Fi network that will be amplified by the D-LINK router.
Wi-Fi Receiver from a D-LINK router
In fact, the 'Client' mode is the adapter mode. After all, the router connects via Wi-Fi to another router and transmits Internet through the network cable. Set it up exactly as I showed you in the first section of this article. Only if you don't want to have Wi-Fi internet from the other router, but only cable, then during the setup uncheck the 'Broadcast wireless network' box.
Configuring by the example of ZyXEL
So, we have already found out that not every device with WISP mode can be connected to any Wi-Fi network. But when it comes to ISP networks, it makes sense to try enabling WISP. This is when the ISP will consider that the only device is connected to it, and you will be using the local network with the ability to access the Internet. Wi-Fi-client mode is used in other cases. But be aware that when using it, all your "subscribers" will be visible to both the ISP and other clients of the Wi-Fi-network.
Keenetic V1 router interface
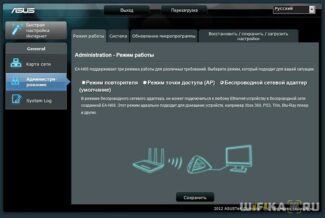
Let's look at the features provided in the Keenetic first generation router firmware. The web-interface in this firmware is available at 192.168.1.1. By default this value is used, and also the password "1234" and login "admin" are used. It is recommended to go directly to the next tab: "System" -> "Mode of operation".

On the tab we marked with numbers those two items that are relevant to this review:
- WISP – just set the selector, click "Apply", and you will activate the desired mode
- Wi-Fi client (called "bridge" here) – set the selector and also check the "Disable DHCP" checkbox and press "Apply".
The word "bridge" is synonymous with "switch" when it comes to networks. There, and once again we have seen that the "Wi-Fi client" device is a switch (not a router). To such a "switch" you will connect local devices: computers, network printers, etc. The figure shows exactly what will happen.
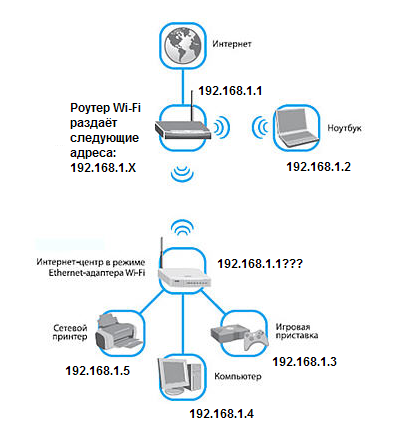
You can see an interesting thing in the figure: there are two devices on the network that have the same address. To fix it, before you go to the "System…" tab, you should change the local address of the device to, say, the following: 192.168.1.2. In ZyXEL interface we can do this in the tab "Local Area Network" -> "Network Organizing":
User complaints and questions
According to reviews posted on forums, it is possible to connect using the WISP method in rare, exceptional cases. The thing is that the very equipment that gives out Wi-Fi in cafes and other establishments is household or budget office equipment. You need the Internet – please, use it, but connect a regular subscriber device (preferably – one). If you use another method, you may also encounter certain difficulties. However, they are predictable.
Suppose there are 4 wired subscribers connected to the router, which is a "Wi-Fi client". Then, connecting to the existing access point, we immediately increase the number of its subscribers by 4 (not by 5, but also not by 1). Conclude what this implies. The owners of TDs also know how to configure equipment, and opening the web-interface will be able to understand everything. MAC-addresses of your "devices" will be remembered and banned as well. Moreover, you do not have to invite hackers to do this.
Look at how the DD-WRT interface looks at the access point statistics:
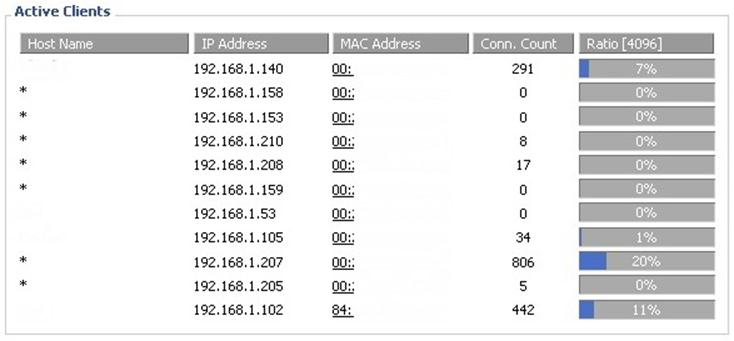
In other variants this page may contain even more information. Suppose that the same set of devices appears in the list periodically, and that these "subscribers" are connected at the same time. Then it makes sense to block them, just go to another tab where you can configure the MAC filter.
WISP mode on different routers
Most routers support connection via wireless network. Zyxel Keenetic and many MikroTik models have it. Other modern routers will also be suitable for connection, but it is better to clarify this point in the characteristics of your model. If it was purchased a long time ago, it may not be WISP support.
In general, the configuration for different models and manufacturers is different, although not much. If you have already configured your router for wired operation, you know where the necessary parameters are located. It remains to connect the wireless signal from the ISP, instead of the wire from the WAN port. In case of difficulty, find the instructions for your particular router model.
Setting up a TP-Link router as an example
Let's look at the TP-Link router as an example. On average, other routers will be set up in a similar way. If you have configured it yourself and remember the procedure, look for similar names in the menu items of your device.
First, go to your browser and enter tplinklogin.net in the address bar. In the window that appears, type your login and password, the standard admin/admin, if you have changed it, then type yours. In the left menu, select "Operation Mode" and then "Wireless Client Router". Save your settings.

Now go to Wireless, go to Wireless Settings. On the right side of the window, click on "Survey" and select the network you want to connect to. At the bottom of the same window, configure the name of your network as it will be displayed at home. Leave the rest of the settings the same.
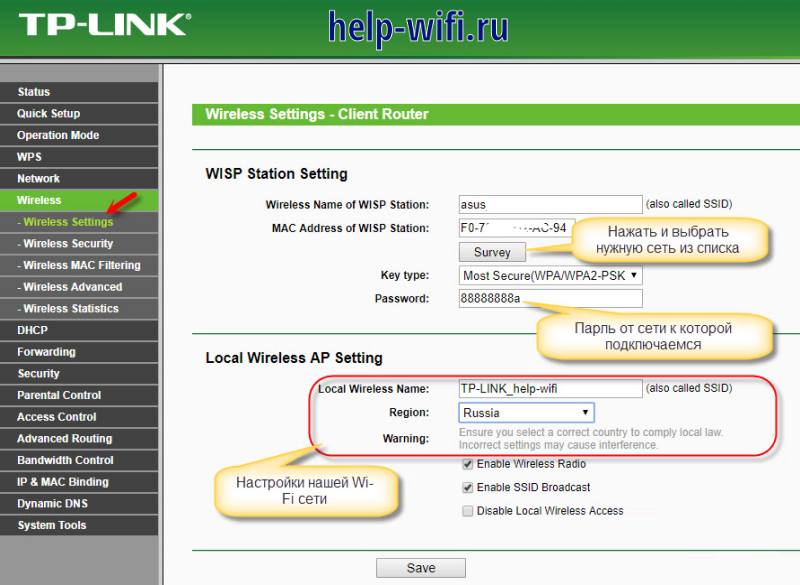
Older stations had a separate item for settings, as shown in our instructions. The new ones do not have that, it is enough that your router knows how to work in wireless bridge mode. You need to switch it to this mode, sometimes you can do it from the advanced settings, and sometimes you completely reset all settings to the factory settings in order to switch to the desired mode of operation.
Preparing to configure
First you need to enter the web interface of the router. Open your browser, type 192.168.0.1. You will see an authorization window. In the login field, enter admin, the password is admin, standard data. If an error occurs and you do not know the login and password, reset to factory default.
This will reset not only the login data, but also all existing settings.
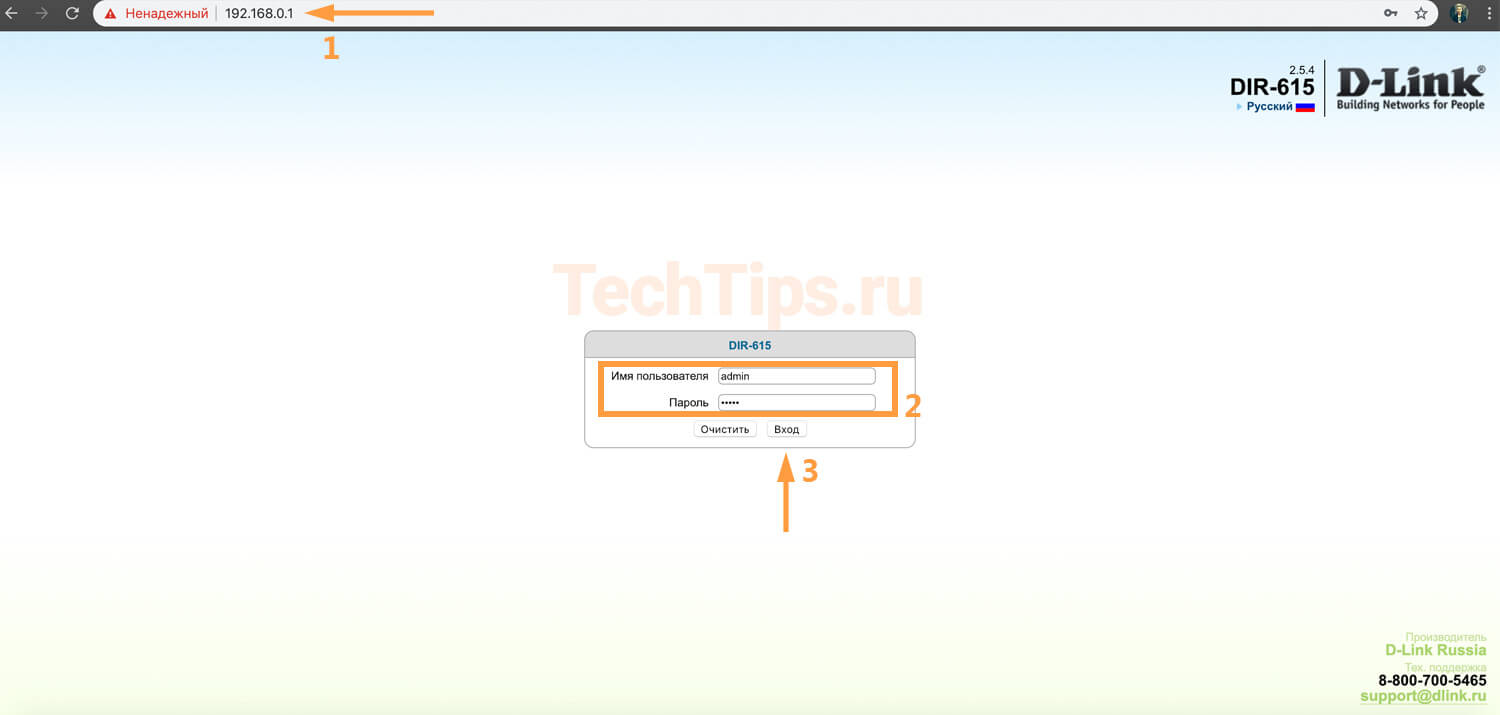
If you can't log in, there is a separate article on logging into D-Link that should help.
When using two routers together, check each router's gateway address, they should be different.
They are often the same. The DIR-300, like most D-Link routers, has the standard address 192.168.0.1. If the first one is the same, then in the settings of DIR-300 it needs to be changed, so that there is no conflict between them. Go to "Network" – "LAN". In the IP Address field replace 0 with 1 to get 192.168.1.1. In the DHCP Server do the same – "Start IP" to 192.168.1.2, "End IP" to 192.168.1.100. Click on "Apply."
Click on the red number at the top, then on "Save and Reboot." Wait 95 seconds.
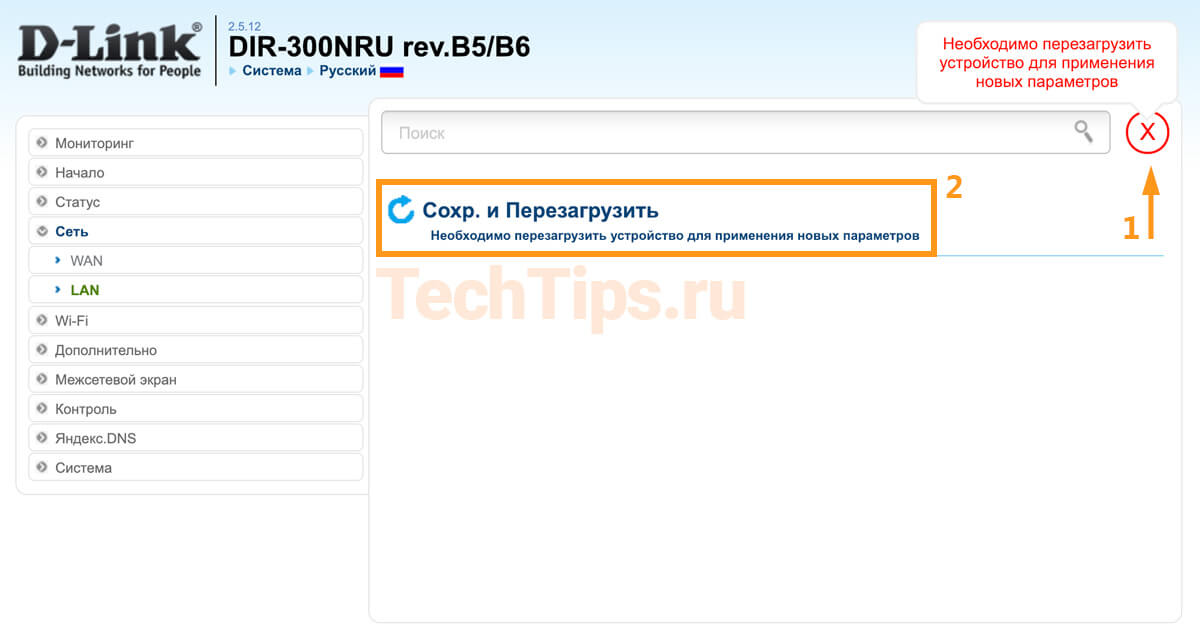
Note that after that you have to type 192.168.0.1 instead of 192.168.1.1 in your browser to log in to DIR-300.
"Repeater" via cable
The first router starts the Internet depending on the provider – PPPoE, 2LTP, Dynamic IP. After the second router – DIR-300, receives a signal through cable and distributes the Internet to other devices in two ways: by cable and by Wi-Fi. Let's look at both options.
By cable
Scheme #1: Internet cable into the first router's WAN port. Then from his LAN port network cable is connected to the WAN port of DIR-300. From his LAN port cable into any device: computer, laptop, monoblock.
Above I wrote, it is important that the gateways of the routers are different from each other. Connect the devices according to the scheme.
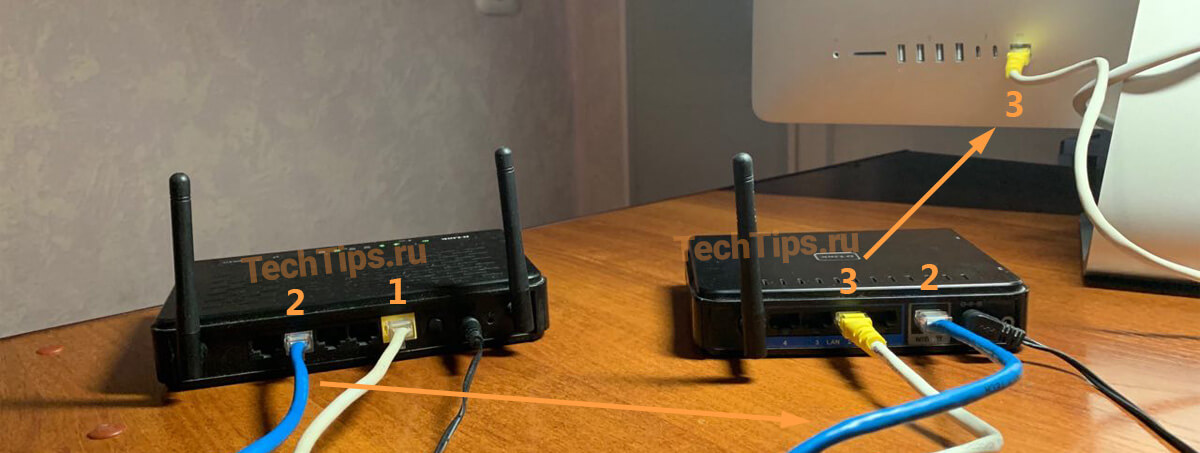

- ISP network cable;
- patch cord – connects both routers;
- Patch cord – connects the second router DIR-300 with your computer.
If the router is new or reset at the factory settings, he initially selected the type of connection "Dynamic IP" does not need to change anything. Immediately after connecting a computer or laptop, the Internet should work.

If the browser gives an error, check what type of connection is selected on the router. Go to "Network" – "WAN". There is probably nothing there, or you have the wrong connection or multiple connections. Check the boxes, then click "Remove".
Then "Add", select the connection type "Dynamic IP", click "Apply". Save your settings.
How to secure your connection
Even if you managed to disconnect unwanted users, the next time it is better to reinsure and protect the network:
- For starters, it's a strong password. Do not be lazy and create a good key that the average user is unlikely to figure out.
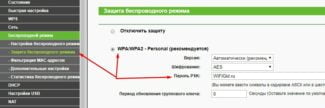
- Make sure you are using up-to-date security standards. WPA2-AES is a strong security protocol. We recommend that you use it instead of WEP, WPA.
- If you do not use the WPS function (to connect by pushing a button on the router), turn it off. It may also be marked as QSS on some router models.

Changing your password
It does not hurt to change the wireless password. To do this (using TP-Link as an example):
- Go to the router control panel page (192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1).
- In the main menu, select "Wireless Mode".
- Next, click on "Wireless Security".
- You will see the "WPA/WPA2-Personal (Recommended)" section.
- In the "Password" field, change our key.

Guest Mode Setting
Guest mode is a special feature that allows you to create a separate network, which will not be connected directly to your main network. And this ensures security and no hacker can harm your computer if he has access only to guest network. It is not available on all routers (medium and expensive segment).
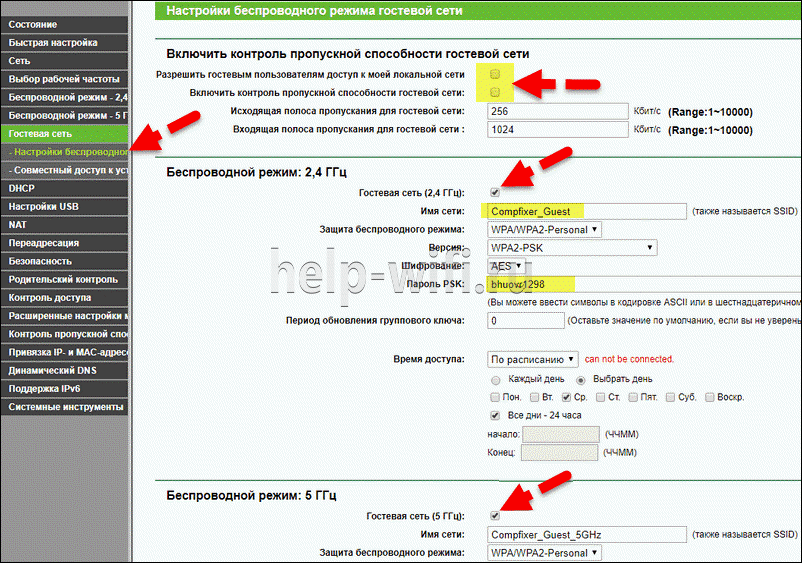
- In the main menu, find the item "Guest Network".
- Configure it for you, namely:
- Name/Password;
- Access time (when you can use the Internet);
- Change of key;
- Type of encryption.
How to teach a lesson to fans of free Internet
People are always looking for free cheese. Do not be surprised if a lot of freeloaders connect to the network with the password 12345678. The best way to teach unwanted users a lesson is to kick them off the network. Disconnect them by adding them to the router's blacklist. He will see that the laptop does not connect and he will have to pay a monthly rate from his ISP. And you will get stable and fast Internet on your computer again.
You already know how to see the list of connected devices to the wifi router, know how to disable some of them. The user must keep an eye on the security of his home network, because more advanced connoisseurs can use your Wi-Fi for illegal purposes or gain access to your computer. So check everything from time to time – virtual security is more relevant than ever.
Read More: