This answer is incorrect. The Wi-Fi coverage area forms a toroidal field, which is shaped like a donut. The omnidirectional antenna of the router acts as the axis of this doughnut, and its rotation determines the Wi-Fi propagation angle.
- Abstract
- Models for calculating Wi-Fi radio signal losses
- Access control: Wi-Fi network protection against theft
- How do I set up access control?
- TP-Link Tether app
- Network Diagram" section of the web interface
- The "Access Control" section of the web interface
- Determine the number of access points
- Selecting equipment
- How to correctly position the router antennas to achieve maximum Wi-Fi signal range
- Complain to comment
- Comments from NAG specialists
- Comments and additions
- Differences from a router
- Characteristics
- Подключение режимы работы
- Varieties of
- Switching to the 5 GHz band.
- Sequence of actions to improve coverage
Abstract
This article describes how to calculate the range of Wi-Fi signal inside a room without using any software at all. It explains in detail what a radio propagation model is, and how to use it to calculate the radio signal propagation range.
Sometimes it is necessary to at least approximately estimate the range of wireless equipment. This estimation may be required both at home, when you need to understand where the limit of your access point is, and in the case of designing a small office network, when the almighty system administrator has to tell the boss how many devices you may need to have "Wi-Fi everywhere" in the office.
It seems to be simple, you need to calculate how far the signal (electromagnetic wave) from the access point antenna will travel. But the peculiarity of calculating the attenuation of the electromagnetic wave in free space from the attenuation in the cable, is that the cable is usually well shielded, and in free space can appear outside objects, or it (space) itself can change its electro-physical properties from time to time. In addition, due to interference and diffraction of radio waves, the direction of propagation of electromagnetic wave and its energy reserve can change many times, both in a smaller or larger way on the path of the wave from the transmitter to the receiver.
If the signal attenuation within a cable assembly is to be determined, it is often sufficient to know the linear attenuation of the cable and the losses at its (the cable's) connectors. Thus, the formula for calculating the total attenuation in this case may look quite simple:
Where: Pк– is the attenuation at the connector(s);
Рn – is the linear attenuation in the cable;
L is the cable length.
Models for calculating Wi-Fi radio signal losses
Radio loss models allow you to estimate the attenuation of the electromagnetic wave emitted by the Wi-Fi adapter, taking into account the number and type of obstacles in the path of the signal. This article deals with signal propagation models used to calculate signal strength inside buildings. There are many models that will be discussed and their modifications. In the article the most simple ones are considered, which can be used even in the field without deep mathematical knowledge.
Before the beginning of consideration of various models of spreading of a radio signal we will notice, that in ideal conditions (there are no obstacles on a way of a signal passing and there are no multiple re-reflections of a signal) to estimate signal power in any point of free space (free space – FS) it is possible by the so-called Friis formula:
Figure 1 shows a graph of the dependence of the attenuation LFS with increasing distance for Wi-Fi signal on the first frequency channel (center frequency 2437 MHz) in the range of 2.4 GHz – blue curve, and in the range of 5 GHz – red curve. At the same time, the gain of the receiving and transmitting antennas were taken equal to one.
Access control: Wi-Fi network protection against theft
![]()
The router's Wi-Fi coverage area is not limited to the walls of the house – it can also be outside the house, including the neighbors, and anyone in the Wi-Fi network coverage area can easily hack it if they accidentally or deliberately got the password to it through your family members or through network hacking technologies. TP-Link router access control will help prevent this.
How do I set up access control?
TP-Link routers have many ways to control devices' access to the network.
TP-Link Tether app
The Tether app is the easiest way to control TP-Link routers and Wi-Fi signal boosters from your mobile device. The app allows you to view a list of clients and quickly allow or deny network access to devices. Devices that are denied access will be added to the blacklist. If you want to allow access to a previously blocked device, simply remove it from the blacklist.
Network Diagram" section of the web interface
In the web interface of the newer TP-Link routers there is a section Network Diagramwhere you can open a list of clients and allow or deny access, just like with Tether. Devices that are denied access will be added to the blacklist. If you want to allow access to a previously blocked device, simply remove it from the blacklist.
If your router's web interface does not have the Network Diagram, use another way.

The "Access Control" section of the web interface
If your router's Web interface does not have the Network Diagram sectionIf your router does not have a Network Diagram section in the web interface, or if you want to whitelist a device to block all but the specified devices, go to Advanced Settings > Security > Access Control. The appearance of the interface and the layout of the items on the page depend on the model and firmware version. If you need detailed instructions, refer to the user manual for your router model in the Downloads section.
If your router's web interface does not have the Access Controlthere is no Access Control section in your router's Web interface, there's another way to do it.

Determine the number of access points
Mytishchi Park is a rectangle of 400 by 600 meters with fountains, trees, a Ferris wheel, a rook, a concert hall, playgrounds and many paths. Since park visitors tend to walk around rather than sit in one place (except for the café and rest areas), the access points must cover the entire area and provide seamless roaming.
Some access points have no wired lines, so Omada Mesh technology is used to communicate with them. The controller automatically connects a new point and chooses the best route for it:
If communication with the point is lost, the controller builds it a new route:
Access points connect to each other at a distance of 200-300 meters, but on client devices Wi-Fi receiver power is lower, so in the projects between points is laid 50-60 meters. It took 37 access points in total for the park, but the network includes another 20 points of the WI-FI pilot project on bus stops, and the administration also plans to connect to this network free internet at other sites and all stops in the city.
Selecting equipment

Since we are dealing with the Russian climate, in addition to dust and moisture resistance, according to the IP65 standard, attention is paid to temperature conditions of operation. In this project we used access points EAP225 Outdoor. They are connected to 8-port PoE-switches T1500G-10MPS, which in turn are combined with T2600G-28SQ. All equipment is consolidated in a separate switch cabinet, which has two independent power inputs and two different communication channels.
EAP225 Outdoor support Omada Mesh function, work in the range from -30 ° C to +70 ° C, and rare temperatures below the range withstand without loss of performance. Severe temperature fluctuations can shorten the life of the devices, but for Moscow it is not so critical, and we give 3 years warranty on EAP225.
Of curiosity: as the access points are powered by PoE, the grounding is carried out on a special line which was previously wired with the power and the fiber optic line. This precaution eliminates problems with static. Another thing to consider when installing outdoors is lightning protection or placing the points in safe locations and not trying to put them too high.
The EAP225 uses the 802.11 k/v standard for roaming, which allows for soft switching without draining the end devices. In 802.11k the user is immediately sent a list of neighbor points, so the device does not waste time scanning all available channels, but in 802.11v the user is notified about the load on the requested point and if necessary is redirected to a freer one. Additionally, forced load balancing is configured in the park: the point monitors the signal from clients and disconnects them if it falls below a specified threshold.
Initially, for the centralized management of all access points planned to install a hardware controller OS200, but in the end we kept the software EAP controller – it has a larger capacity (up to 1500 access points), so the administration will be able to expand the network.
How to correctly position the router antennas to achieve maximum Wi-Fi signal range
Quite often, when I visit friends and relatives, I see that their wi-fi router antennas are arranged as desired, but not as needed. And the reason for this is that people simply don't know how the signal from wi-fi antennas spreads. And in fact, everything is very simple. And even the manufacturers themselves show exactly how the antennas should be located. Look at the box from your router (if you haven't already thrown it away), there will be a hint. Below I will tell you exactly how to position the antennas for better signal reception and transmission.
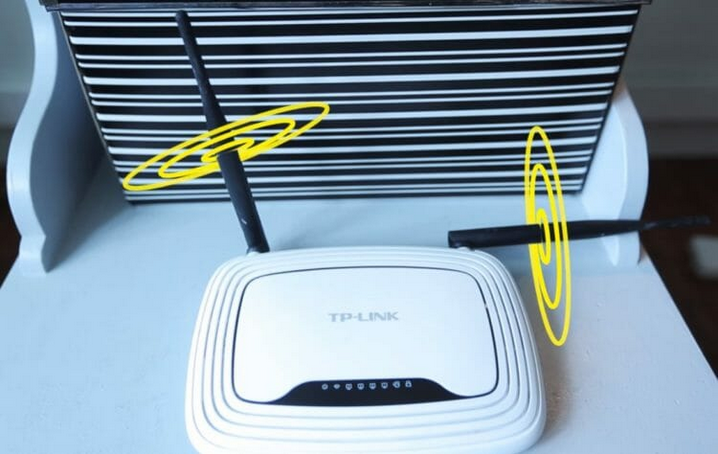

In order to understand how to place the antennas on the wi-fi router, it is necessary to understand how the signal from these very antennas is dispersed. And here, of course, not everything is so simple. And there are many different types of antennas. But we are interested specifically in the antennas in household routers, which are usually a spring, with the right number of coils, hidden in a plastic pin. The classic antenna on a router looks like this:
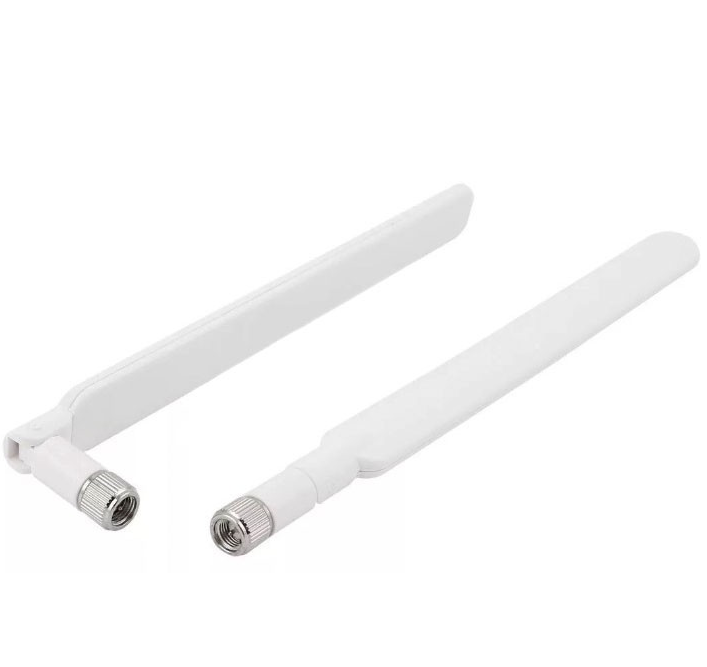


This is the type of antenna installed in most home routers. Although there are models with built-in antennas and omni-directional antennas. But we will not consider them, because in this case, the manufacturer himself has taken care that the antennas were installed in the right direction.
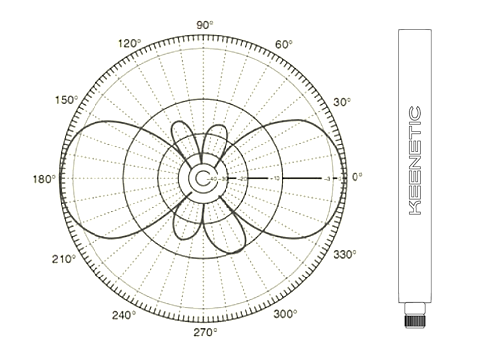
Now let's see how the Wi-Fi signal diverges from this type of antennas. Googling will help us for this, where you can find a bunch of different studies and measurements. If we take a simplified diagram, it looks like this:
Complain to comment
Then you have to wrap your head in tinfoil. Because apart from the router, the apartment is full of other radiations: microwave, cellular, neighbor's routers, 5G towers, reptiloid transmitters, radio waves from radios and repeaters, radio and TV signals.
Oh, my gosh, I'm so scared myself.
If you ever stood next to a spectroanalyzer, your confidence would be shaken to some degree.
What's the use? You need a grounded screen with ground resistance less than 0.01 Ohmm, which is a minimum of 2,000 15-meter metal pins driven into the ground at a distance of 20 meters from each other. Then your screen will help, otherwise hide in a bunker with walls of one meter of armor:)
Knock on the door and introduce yourself as an employee of an Internet company, say preventive maintenance, and then do with the antennas what you need!
For example, here at my apartment catches 3 router from the sasedej all with a password, of course. And what is free? Without knowing the password, I can not use the Internet, then.
It also happens that the router is lying somewhere on the floor behind the desk in a pile of wires and of course there are complaints about the poor connection. So it was with friends in an old building in St. Petersburg, where, thanks to the wooden ceilings, WiFi worked more for the communal neighbors downstairs and there was no full coverage of the not so big three-bedroom apartment. As soon as we got the router up on the closet, immediately the connection in the far room was stable.
And my router does not have any antennas outside.
What am I supposed to do, put it on its side or upright?
What are you smoking out there that's got you so worked up?
What difference does it make which side you put the oil on, it'll fall down anyway!
Well, lamers don't get it.
And who at least the user – they get.
//Ps
How strange, my router is 15 years old.
The incoming channel is 250 Mbps, by youfly 220-230 Mbps load holds steady…
And what are the numbers claimed?
For example claimed gigabit per second.
And here you have to understand that first, this gigabit is possible only in ideal conditions – the air is clear, the signal is good, and the subscriber's device supports it.
Secondly, gigabit is the speed of the link – the radio channel through which the data will be transmitted. Data can be service and user data. In wi-fi, the share of service data is about 55%.
Accordingly, the transfer rate of user data will be around 450 megabits.
Comments from NAG specialists
Dmitry Portnov, an engineer of wireless equipment department, comments.
If you do not have the need for a more in-depth study of the question, then this article is worth taking into account. The principles and criteria of indoor access point placement and Wi-Fi network configuration are quite thoroughly described in the article.
But the devil is in the details. It's worth noting that the 802.11 standard was not created to provide the highest possible bandwidth per megahertz of busy airwaves, but to ensure uncompromising compatibility and performance of the protocol even in the worst conditions. Therefore, to say "make fast Wi-Fi" is not quite right, it is better to say "make high-quality, stable Wi-Fi"!
Nevertheless, the article correctly described:
– recommendations for the location of access points,
– information about the directional diagrams,
– information about the state of the airwaves.
And, dear readers, what other parameters do you think are important for high quality and stable Wi-Fi?
Comments and additions
For some reason people, looking here, are interested in other things:
- Some are looking for a portable hotspot – here the emphasis should be on battery life, and often 4G support. Since full-fledged outdoor spots are still aimed at creating a bridge out of an off-the-shelf network, but they don't support basic 4G. There is another concept for this purpose – portable routers. That's what I recommend you look for in our country as well.
- Ceiling access point – for this purpose, the most common home router will do. Many of them have the usual attachable wall mount – with the right hands and ingenuity you can easily try it on the ceiling, don't forget what country we live in! But again, this article is not about you!
- I'll leave the option of running the bridge over the plates in the video below:
Were looked at and some models from MicroTik, Cisco and even ASUS – but on familiarity, budget, quality and our audience – models from Ubiquity will be better. So let's try on, think, go to the store and consult on all questions. I hope our review article on outdoor Wi-Fi access points has helped a little to make a choice and set the right direction. Go for it!
Differences from a router
We've discussed in enough detail what a Wi-Fi hotspot is and why it's needed. But not all users understand the existing equipment, can confuse the types of equipment with each other.
Wireless Wi-Fi hotspot and router have one important similarity – both types of equipment are used for signal distribution, allowing different devices (PC, phone, tablet) to connect to the Internet.
Despite the external similarities, there are a few important differences that users should be aware of.
| Router | TD |
| Multifunctional device that can work as a router and TD | Performs a single function |
| Can be used as a local network element in indoor areas only | Installed indoors and outdoors |
| Has one incoming and multiple outgoing LAN ports | Equipped with one LAN port for cable connection |
| Flexible IP address setting | IP address is displayed without additional adjustments |
| Equipped with built-in firewall and firewall for extra protection | No encryption, no built-in security features |
| Easy home networking setup – IP is handed out automatically | Organizing a home network is almost impossible |
| Connection is made directly from the device – no need to configure the hardware in the network | Connection is transferred by the device – each PC has to be configured separately |
Characteristics
So what is a WiFi hotspot, how is it different from a router? It's time to understand what technical characteristics the equipment may have – these are important parameters that you should pay attention to when choosing a AP.
- Wi-Fi access points for home: Most often made of plastic and other, not the most durable materials;
- Devices for outdoor placement: Technics for outdoor installation are made of durable materials that can withstand the effects of external factors.
Some modern models can operate on two frequencies simultaneously.
This parameter affects the strength and distance of the signal transmission:
The maximum transmitter power allowed is 20dBm.
Each device has a certain standard of supported communication – it is this standard that determines the maximum available WiFi Internet speed.
The more antennas installed on a device, the faster the wireless speed. There are two types of antennas:
This port is responsible for connecting the transmitter to the wired Internet. It is worth choosing one of the two options:
Let's take a brief look at what modes of operation a WiFi Internet access point has:
- TD. Creates a WiFi network to connect different devices;
- Bridge . Connects two wireless connections together;
- Repeater. The AP acts as a signal repeater to increase network coverage;
- WISP. Used for desktop computers and allows you to convert a wireless signal to a wired signal.
We've figured out what a WiFi hotspot means – it's time to explore helpful tips for choosing the right equipment.
<iframe src="https://www.youtube.com/embed
Подключение режимы работы
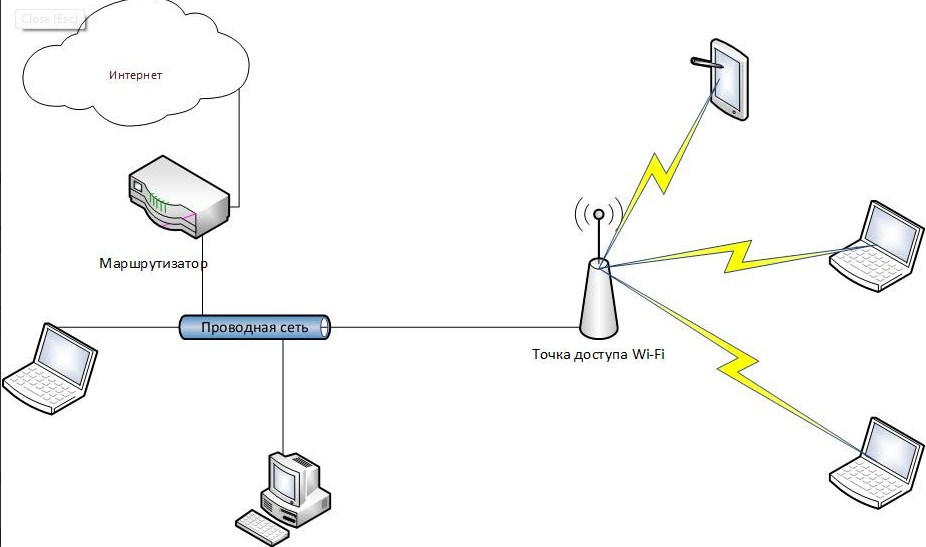
Let's take a look at the router first. It has a blue port for the ISP wire and local ports. And it has two antennas on the sides to amplify the Wi-Fi signal.

But this one is an access point and it has only one port. So the connection will be like this. Sometimes you can see the PoE port. It is designed for powering through the network wire in places where there are no sockets.
NOTE! As mentioned earlier, another router can act as an access point. To do this, simply configure it by going to the Web interface. But on some devices there is a special switch of modes.
But also the access point can work in "Bridge" mode. In this case, the second device connects to the network of the first via Wi-Fi. And in the wired port is the connection of several devices. For this purpose, a regular switch is suitable.
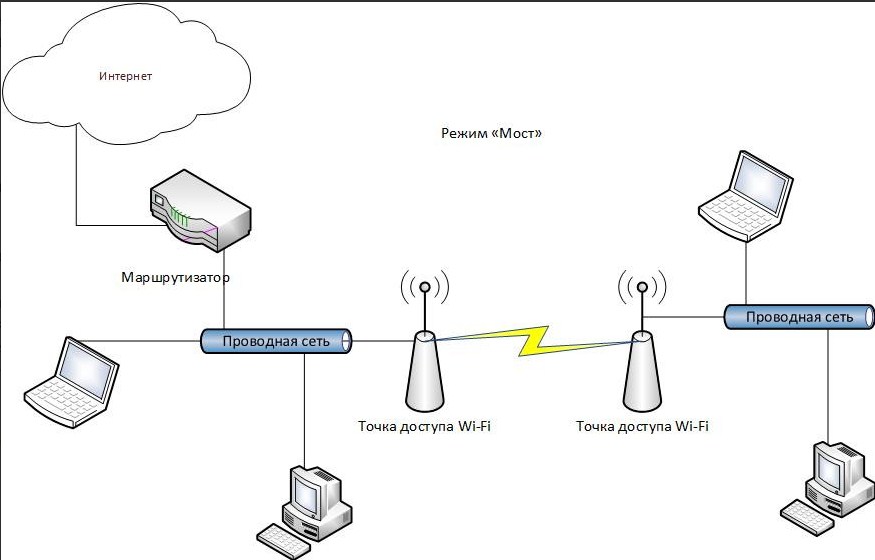
But you can not use a wired port at all, and receive and send a signal only over the air. In this case, the device turns into a wireless access point, working in "Repeater" mode.
There is another interesting mode of this device. It is called a WISP receiver. This technology is widely used in rural areas, where there are special WISP stations, which distribute Wi-Fi with the Internet for a few kilometers.
Varieties of
- External – Are installed outdoors. They have a more robust housing, as well as protection from moisture, dust and cold. Before buying, be sure to look at the allowed temperature mode, which will depend on the winter of your region.
- Indoor – Are installed at home and have no special protection.
You can also divide by shape and method of connection to the network:


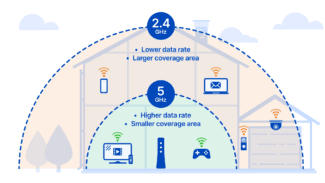
Switching to the 5 GHz band.
This transition requires upgrading the network equipment, both the router and the adapters of smartphones, laptops and other equipment. This method allows you to achieve high data rates on the new frequency, which is a kind of salvation for apartments and offices, where the airwaves are crowded with neighboring radio waves at 2.4 GHz.
Sequence of actions to improve coverage
The key factor in improving is determining what area should be covered:
- Rooms in one plane – proper router placement will help.
- Rooms on several floors – work with the slope of the antennas, but most likely for each floor will have to buy at least one repeater – a repeater to expand the Wi-Fi zone.
- Complex design – you can't do without repeaters.
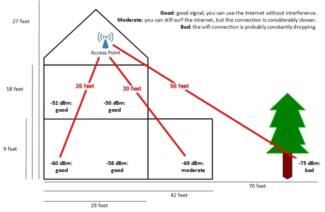
How to organize the best location? Use computer modeling. Now on the Internet or on the application site you can find many services for the modeling of the coverage. They are a kind of constructor, with the help of which you can:
- Build a room with walls, windows, doors, to which the characteristics of communication absorption are attached.
- Set the source of radio signals in any point and move until the blind spots completely disappear.
- If you can not achieve this, then try to practice changing some of the parameters, rearrange the furniture or use another network device to strengthen the wireless signal.