This solution is recommended only when the number of connected WiFi devices is very small.

- Wi-Fi network operation modes.
- Residential Wi-Fi
- Router operating modes
- Router in client mode
- Operation modes of the router
- The disadvantages of bridge mode
- In addition to the fact that the router does not know how to establish a connection itself, it also ceases to perform the following functions:
- Configuring routers
- Setting up bridge mode
- Setting in router mode
- Operation modes and router settings
- Bridge .
- Access point, client, repeater
- What are the wireless modes
- Legacy
- N-Only .
- Differences of Wi-Fi b/g/n
- Which Wi-Fi router mode to choose
- What is better, 11b/g/n or 11b/g
- What to set in the router settings to get the highest speed
- Setting the wifi standard on Keenetic
- Why change the wireless mode?
- See also:
- How do I change the b/g/n mode in my Wi-Fi router's settings?
Wi-Fi network operation modes.
Since the advent of consumer devices with Wi-Fi connection (smartphones, tablets, laptops), this wireless technology has become very popular. This has undoubtedly influenced the housing and home market, where Wi-Fi has found its niche of greatest growth. For many people, having a Wi-Fi network is associated with a router that provides an Internet connection. However, Wi-Fi technology offers a wide range of all sorts of configurations for both the professional and home markets, and in this article, we will look at just such a range.
Technically, Wi-Fi is a technology that allows you to create a wireless local area network, that is, a wireless connection between multiple devices, that is, without cables.
The device uses Wi-Fi to join a network known as a wireless access point, also called a WAP – an acronym in English or simply an AP. This is the device that sets the operating parameters of the Wi-Fi network and centralizes and manages all wireless communications.
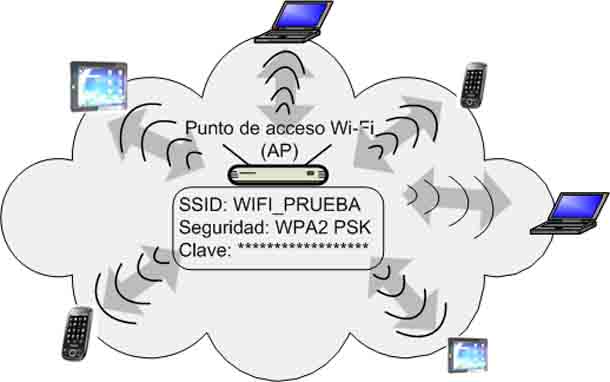
The AP is said to be a Wi-Fi network operating in infrastructure mode. Many manufacturers have called it AP mode. In this mode, the AP establishes the Wi-Fi network, basically allowing you to configure the network name (a parameter known as SSID), security type (WPA, WPA2), and if necessary, the network access code.
As shown in the previous figure, the access point is a Wi-Fi network, but it does not itself provide access to the Internet. The AP, in addition to creating a Wi-Fi network, allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network. All APs have an Ethernet port for this purpose. If the AP is connected to a wired network with an Internet connection (or directly to the router), Wi-Fi devices will have access to the Internet.
You can see the back of the access point where the Ethernet port is enabled, and on the right, the access point's connection directly to the router to provide Internet connectivity for wireless devices.
Residential Wi-Fi
In the previous section, we saw how the main way to set up a Wi-Fi network is through a Wi-Fi access point (also just called an AP). However, almost no one has an AP at home to be able to connect to a Wi-Fi network. Why?
For several years now, all Internet service providers, that is, companies that provide Internet access, have provided their users with routers with wireless access point functionality. Consequently, these users do not need an access point because the router itself already includes access point features.
Even the name of the Wi-Fi router was familiar for this type of device, as can be seen from information extracted from the web pages of several Internet service providers:
Usually (though not always) this type of Wi-Fi router only supports the mode of operation described above, known as infrastructure mode or access point mode. In this mode, Wi-Fi connectivity needs are fully covered in most cases, especially in residential networks.
But there are scenarios in which infrastructure mode with a single AP (or router that includes this feature) is insufficient to meet the connectivity needs of various devices. In the next section, we look at the most common configuration modes in Wi-Fi technology.
In fact, any device with a Wi-Fi interface and associated software can function as an access point. For example, a PC with a Wi-Fi card or a smartphone. In the case of Android smartphones, the operating system itself includes software to control the phone, as if it were an access point.
Router operating modes
The device of the router allows you to use it in different modes of operation (access point, bridge, repeater, client).
Router mode wi fi access point is the main mode for the operation of WiFi equipment and is called – AP (Access Point). The router, in Access Point mode, creates a zone of radio coverage around itself at a certain distance, determined by the signal output power. All devices located within this zone and capable of working as an AP-client (WiFi adapters and individual models of access points) can be connected to the WiFi network.
Thus, a wifi router access point is used to connect to a WiFi network and this mode is set by default in routers.

Router in client mode
In basic AP-client mode, only WiFi routers are available. Some access point models also have this functionality and can operate in this mode. In this mode, the router allows a computer or other devices to connect to the WiFi network. For example, if you get the Internet via radio, and then it is already distributed via cable to desktop computers.

Operation modes of the router
Almost all ADSL routers can work in two modes – bridge and router. If your model does not have both modes, you either need to update the firmware or it is a quite rare case and your model does not support both modes.
Let's look at what these modes are, their pros and cons. Let's start with the bridge mode.
This word is translated from English as bridge, that is, the router works in the so-called transparent bridge mode.

This mode "turns" the router into a silly intermediary between your computer and ISP, it does not perform any functions, only forwarding data flow from the telephone port to the computer connection interface and back. In bridge mode the router can only work with one computer, it is not possible to create a local network or access point. And that means that you can't connect a computer and, for example, a smartphone to the router at the same time. This is the first "minus" of this mode.
The disadvantages of bridge mode
As already mentioned, in bridge mode the router does not perform any functions other than uncontrolled traffic transfer. This means that the router will not be able to connect to the ISP itself when it is switched on. This is the second disadvantage.
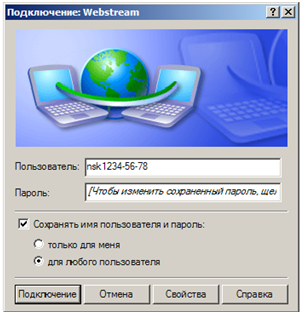
Now when you turn on your computer, the user must manually establish a connection to the ISP, and therefore to the Internet, through the operating system, by entering the username and password in the appropriate fields and clicking "Connect".
In addition to the fact that the router does not know how to establish a connection itself, it also ceases to perform the following functions:
- DHCP-server. As you know, this service automatically assigns IP addresses to the devices connected to the router. In bridge mode DHCP makes no sense (no more than one computer can be connected);
- Built-in firewall, also called firewall or firewall, does not work. Now firewall threats and attacks will have to fend off the computer;
- The router also does not provide additional services (depending on the model), such as time synchronization, DNS server, address translation (NAT), network printer and hard drive.
Configuring routers
In this chapter we turn to the practical part and look at specific settings in both modes. Let's take the different routers as an example.
Let's start with configuring the devices in bridge mode.
Setting up bridge mode
We will take the ZyXEL router as an example.
Any router adjustment starts with entering its web interface, which provides us a graphical menu of the settings. Open a web browser and go to the settings at 192.168.1.1.
If you have a different router, the address may be different, check the configuration manual. Next, enter the administrator password, and in the settings menu that opens, go to "Network", submenu "WAN", tab "Internet Connection".
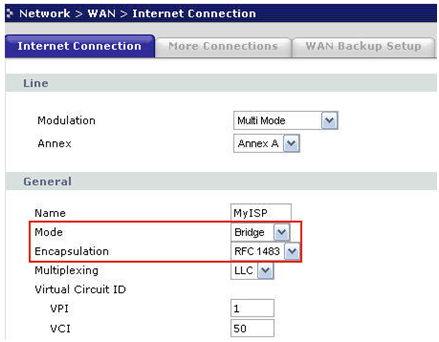
In the "General" area we see the "Mode" line – it is the point to choose the mode of the device. Choose "Bridge" and set the Encapsulation to RFC 1483. The rest of the values are set according to the contract with the provider. Click "Apply", the configuration is done.
We remind you that in this bridge mode the router only establishes an ADSL connection with the ISP, while the authorization of the client must be set by the operating system.
Setting in router mode
Repeat the previous entry steps to configure the router. We go to the same submenus and tab, but in the line "Mode" now select "Routing" mode.
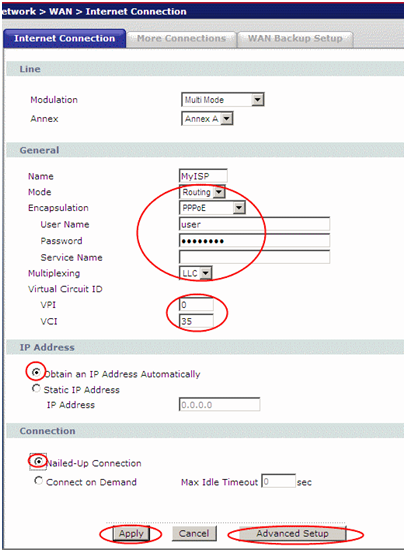
The settings window will immediately change its appearance, there will be much more settings. In the encapsulation we choose the PPPoE mode (or the one supported by your provider), in the fields "User Name" and "Password" we enter the login and password for Internet access issued by your provider. We also set the IP address to automatic. Click "Apply".
Operation modes and router settings
One of the main advantages of modern routers is their multitasking capability. These days, it's hard to find devices such as a connection point, a modem, or a repeater in isolation. Any Wi-Fi router supports bridge mode and router mode, can become a connection point or perform the function of a signal repeater.
According to the way they are used, it is customary to distinguish all wireless Wi-Fi devices into the following categories:
1. Bridge;
2. Router;
An access point;
4. Client;
5. Repeater.
Bridge .
This method is used to connect two networks into one. Two devices with this bridge mode are used in the connection. This method is suitable, for example, to connect two neighboring buildings. You therefore do not need to wire them together.
Router
Most routers work in this mode. It can convert the IP address of an Internet service provider into an internal address and distribute it to devices within the network range. The router can forward ports, share network printers and file storage.
It can automatically authenticate so that the user does not have to do it every time he tries to access the Internet. After all, the router in this mode can be used like a normal switch.
Access point, client, repeater
This method is confused with the previous one. Unlike Router mode, this method is simpler and only involves the device receiving a wired signal and converting it to wireless.
What are the wireless modes
Users often ask what Wi-Fi modes exist at the moment. There are two main ones, Legacy and N-Only. The first has compatibility with b/g/n protocols. In turn, N-Only can only work with the communications standard N.
Legacy
The question, N-Only or Legacy Wi-Fi – what is it, is relevant for owners of wireless routers. Legacy mode allows devices that support the 802 b/g/n communication standard to connect to the router. The maximum data transfer speed will not exceed 54 Mbit/s.
N-Only .
It makes sense to set this mode if the devices support 802n connection standard. In this case the users can get the maximum transmission speed of more than 100 Mbps. However, it is important to know that it will be impossible to connect the devices with 802 b/g protocol support to the router.
Differences of Wi-Fi b/g/n
When configuring a router, the following questions often arise: Wi-Fi b/g/n – what does it mean and how can they differ? To begin with, it is necessary to consider each of the modes in detail and understand what their difference is.
- "b": this type of connection has a low internet speed of up to 11 Mbps.
- "g": this type of mode has a speed of at least 54 Mbps.
- "n": provides data rates of more than 150 Mbps.
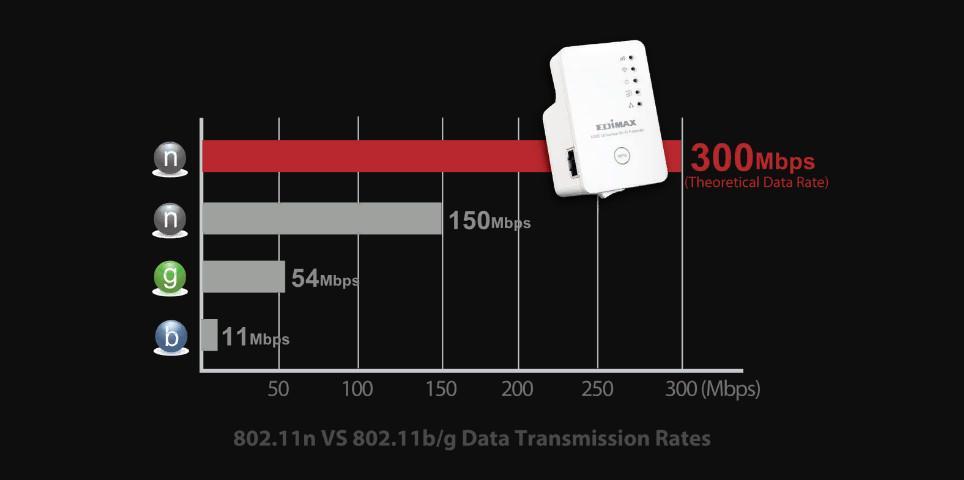
Example of using b/g/n Wi-Fi modes: The owner of a Lenovo A2010 smartphone in the router has set the settings for the 802n access point. According to the technical specification, the phone does not support the "n" standard protocol. When connecting to the network, a communication error appears. This is due to the fact that the device can only work with b/g modes.
Important! Errors when connecting to the access point on laptops are often also due to the fact that the device cannot support newer communication standards. It is necessary to carefully read the instruction manual.
Which Wi-Fi router mode to choose
As a rule, when setting up the router automatically, a combined mode of operation of the wireless network "Auto 802 b/g/n" is set. This setting ensures the compatibility of the device and, therefore, prevents errors or malfunctions when connecting to the access point. Many router owners want to understand which is better, Wi-Fi 11b/g/n mode or 11b/g.
Before you change the mode or channel, you should use the network card in the web interface of the router and see which channel has the most connected devices, then choose the least loaded one. If the network card is not provided by the router settings, you should use special software. The most preferred and functional option is the utility "Wi-Fi Home".
What is better, 11b/g/n or 11b/g
The 11b/g mode can only work on frequencies not exceeding 2.4GHz. On the other hand, 11b/g/n has maximum device compatibility and can go up to 5GHz. Thus, the main difference is the speed of operation: the higher the frequency, the faster the user can download content on the site and get the minimum signal delay.
How to change wireless mode (universal instructions for all types of routers):
- On the back of the router, find the sticker where the web interface username and password will be spelled out.
- Then open your web browser and enter the router's IP in the address bar. For most models it is as follows: 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1. For Huawei routers the address for web configuration: 192.168.8.1.
- In the main menu open the sequence of items: "Wireless network" (or Wi-Fi), "Mode" (standard or settings) and "Radio frequency range". Set the parameter "11b/g/n" (mixed) or "11b/g". It only remains to reboot the router.
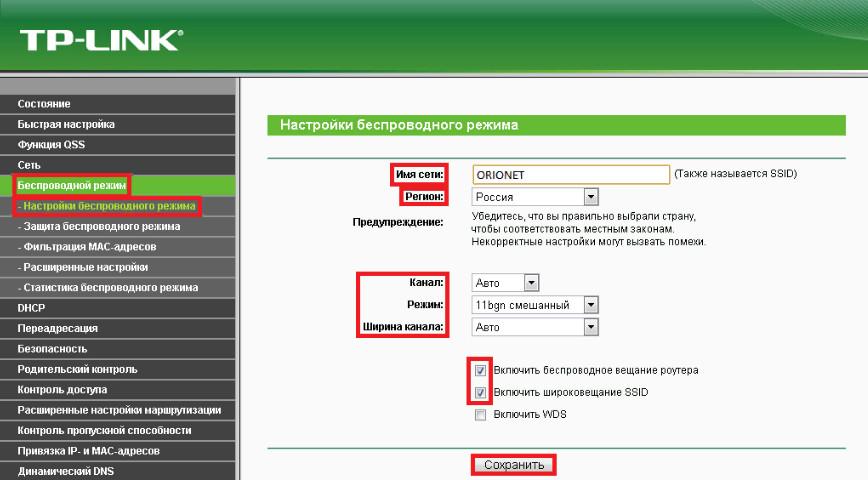
What to set in the router settings to get the highest speed
Wireless Auto Setup WlanSvc is not running – the solution
To get the maximum speed, you should specify the following parameters in the router settings:
- Use only one wireless mode, 802n.
- Set the encryption type to WPA2 AES.
- TP-LINK routers allow you to disable the speed limit option.
- Set the bandwidth to 20MHz.
- Install new driver updates for the Wi-Fi controller.
- Install the router away from televisions, microwave ovens, and radiotelephones.
When selecting the wireless mode, take into account the specifications of the router and the devices connected to it. To increase the data transfer rate, it is better to set mixed settings. To improve the quality of signal reception, you should choose the channels with the lowest load.
Setting the wifi standard on Keenetic
To specify the wifi mode on the Keenetic router, you need to go to the "Home network" section in the control panel and open the "Advanced settings" link

Here in the "Standard" item put on "802.11bgn" and mark the channel width as 40 MHz





Why change the wireless mode?
It's very simple, let's use an example. Here we have an iPhone 3GS, it can work in Wi-Fi only in b/g mode (if the specifications do not lie). That is, in the new, high-speed mode n it can not work, it simply does not support it.
And if you have the router, as the wireless mode will be nAnd if you have a router with n , without any mixed, you will not be able to connect the phone to Wi-Fi, but you will have to bang your head against the wall :).
But it does not have to be a phone and especially the iPhone. Such incompatibility with the new standard may be observed in laptops, tablets, Wi-Fi receivers, etc.
A few times already noticed that when there are a variety of problems with the connection of phones, or tablets to Wi-Fi – it helps to change the mode of Wi-Fi.
If you want to see what modes your device supports, look in its specifications. Usually supported modes are indicated next to the "Wi-Fi 802.11" marking.
You can also check on the packaging (or on the Internet) to see what modes your router can operate in.
See also:
Here are the supported standards listed on the TP-LINK TL-WN721N adapter box for example:

How do I change the b/g/n mode in my Wi-Fi router's settings?
I'll show you how to do it with two routers, from ASUS и TP-Link. But if you have a different router, then change the wireless mode settings (Mode) look in the Wi-Fi settings tab, where you set the name for the network, etc.
Go to the router settings. How do I get there? I got tired of writing about it in almost every article :). Why don't you check out this one: https://f1comp.ru/sovety/ne-zaxodit-v-nastrojki-routera/.
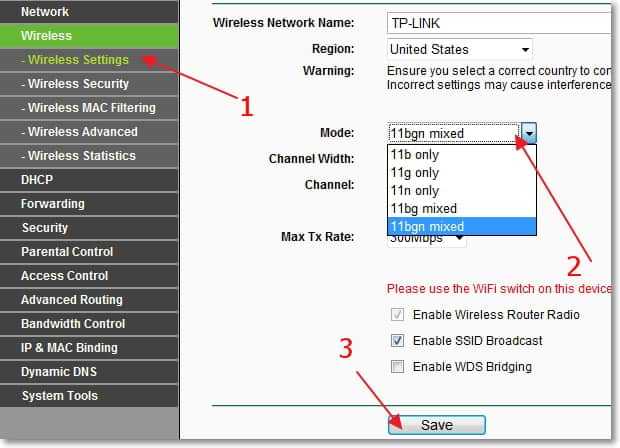
Once you're in the settings, on the left, go to the Wireless – Wireless Settings.
And next to Mode You can choose the standard for wireless networking. There are many options out there. My advice is to set 11bgn mixed. This option allows you to connect devices that work in at least one of the three modes.
But if you do have trouble connecting certain devices then try the 11bg mixed, or 11g only. And for a good data transfer rate you can set 11n only .. Just make sure that all devices support the n.
Remember to save your settings after making changes by clicking on the Save. And reboot the router.
Here everything is the same. Go to settings and click on the tab "Wireless Network" tab..
Next to "Wireless Network Mode" you can select one of the standards. Or you can set Mixed, or Auto (which I suggest you do). For more details on the standards, see above. By the way, the ASUS displays help on the right side, where you can read useful and interesting information about these settings.
To save the settings, click on the "Apply" button..
Read More: