Provides grounding as lightning protection.
Top 12 Wi-Fi hotspots ranking: review and characteristics of the best models of 2023
Review and rating of popular models of access points. The main features, advantages, disadvantages and conclusions.
Access points are needed everywhere – at home, in the office in various public places. They are used to wirelessly distribute the Internet using Wi-Fi.
They are not routers – they can't give out ip-addresses or internet from a provider, only connect to an existing network. But how to choose the right access point?
What is a Wi-Fi hotspot?
First of all, you need to understand that a router and an access point are different technical units.
The access point gets the Internet from the router and distributes it via Wi-Fi.
Some models can distribute IP, create a separate network and so on, but these functions are limited because they only work via Static IP, or DHCP.

Also keep in mind that the access point has a single connector, hence no internet is transmitted via cable.
Band steering
Band steering technology allows the wireless network infrastructure to move the client from one frequency band to another, usually this involves forcing the client to switch from the 2.4 GHz band to the 5 GHz band. Although band steering is not directly related to roaming, we decided to mention it here anyway because it is related to client device switching and is supported by all of our dual-band access points.
In what case might it be necessary to switch the client to a different frequency band? For example, such a need may be related to the transfer of a client from the congested 2.4 GHz band to the freer and higher speed 5 GHz band. But there are also other reasons.
It is worth noting that there is currently no standard that strictly regulates the work of the described technology, so each manufacturer implements it in its own way. However, the general idea is similar: access points will not announce to the client which carries out an active scan SSID in the 2.4 GHz band if the activity of the client on the 5 GHz frequency has been noticed for some time. That is, access points, in fact, can simply be silent about the presence of the range of 2.4 GHz, in case it was possible to establish the presence of the client's support for the frequency of 5 GHz.
- Forced connection. In this mode, the client is basically not informed about the presence of 2.4 GHz band support, of course, if the client has support for the frequency of 5 GHz.
- Preferred Connection. The client is forced to connect to the 5 GHz band only if the RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indicator) is above a certain threshold value, otherwise the client is allowed to connect to the 2.4 GHz band.
- Load balancing. Some clients supporting both frequency bands are connected to the 2.4 GHz network, and some are connected to the 5 GHz network. This mode will not overload the 5 GHz band if all wireless clients support both frequency bands.
Technology and standards
Now back to the process of switching between APs itself. In a typical situation, a client will maintain its existing association with an access point for as long as possible. Exactly as long as the signal strength allows it to do so. As soon as the situation arises that the client can no longer support the old association, the switching procedure described earlier is initiated. However, handover is not instantaneous; it typically takes over 100ms to complete, which is a noticeable amount. There are several IEEE 802.11 workgroup radio resource management standards aimed at improving wireless reconnect time: k, r, and v. Our Auranet product line has 802.11k support on the CAP1200 access point, and our Omada product line has 802.11k and 802.11v support on the EAP225 and EAP225-Outdoor access points.
802.11k
This standard allows a wireless network to report to client devices a list of neighboring access points and the channel numbers on which they operate. The generated list of neighboring points makes it easier to find candidates for switching. If the signal of the current access point weakens (e.g., the client is removed), the device will look for neighboring access points from this list.
802.11r
Version r of the standard defines the Fast Basic Service Set Transition (FT) feature to speed up the client authentication procedure. FT can be used when switching a wireless client from one access point to another within the same network. Both PSK (Preshared Key) and IEEE 802.1X authentication methods can be supported. It is accelerated by keeping the encryption keys on all APs, i.e. the client does not need to go through a full authentication procedure involving a remote server when roaming.
802.11v
This standard (Wireless Network Management) allows wireless clients to exchange service data to improve overall wireless network performance. One of the most used options is BTM (BSS Transition Management).
Typically, a wireless client measures its connection to an access point to make a roaming decision. This means that the client has no information about what is happening to the AP itself: the number of connected clients, device load, scheduled reboots, etc. With BTM, the access point can send a request to the client to switch to another point with better operating conditions, even if with a slightly worse signal. Thus, the 802.11v standard is not directly aimed at speeding up the client wireless device switching process, but when combined with 802.11k and 802.11r it provides faster software performance and a better experience with Wi-Fi networks.
Using
This networking principle is used where a good seamless and uniform coverage of the wireless network is needed. It can be a company that needs to constantly exchange information over the network, a large apartment with thick walls that won't get through wifi, a house or a site. There are many options when you need a constant connection to the Internet. The whole question here is how even coverage is required and how much you are willing to invest in it.

To create your Mesh network, you will need multiple devices that work with Mesh technology. There is no difference between the devices, each one is able to act as a Mesh router as well as a transmitter. Still, we must distinguish between the seamless Mesh router and those devices that transmit the signal further. The router is connected to the Internet, and the other devices are placed within range of the wireless network.
How it works
A Mesh-based Wi-Fi system is a mesh network, all the parts of which are equivalent. It is impossible to single out any element here. All of them are connected to each other and are within reach. The exception is the router, to which the ISP cable is connected, it is isolated as a separate element. As a result, all information flows to it, but the rest of the exchange is equivalent.

When attempting to transfer information, a short or unloaded path will be chosen. If at the moment the closest link is already busy transmitting information, the data will go through any other transmitter on the network that supports the technology. If the exchange is within the network, for example, between a computer and a TV, then the router can be turned off from the exchange of data, because its task is to exchange information with the Internet.
Such a network of independent cells has a rather flexible structure. It greatly simplifies the exchange of information in high-load systems. In home use it is not so noticeable, but when used in an enterprise with a large number of computers in the internal network, it will make itself felt.
How to make a seamless wifi at home on the equipment
If in the corporate and public environment Wi-Fi roaming requires separate equipment, then every user can build it in the home environment.

It takes time and following simple instructions. The algorithm is similar for setting up most routers of well-known brands. The only difference is in the nuances outlined below.
TP-Link
The company TP-Link is one of the manufacturers of network equipment. Wi-Fi roaming technology has been implemented in Auranet hardware and software. The controller can work autonomously after a one-time configuration "out of the box".
Access points for the internal infrastructure and the outer perimeter of the building of the ceiling type. A Gigabit router of AC1200 model of the described brand can be responsible for Internet distribution. It works in two wireless network bands. All devices are compact, easy to install and configure.
TP-Link's minimum seamless Wi-Fi kit consists of such equipment:
- Omada OC300 hardware controller;
- TD EAP660 HD for dorms and apartments;
- TD EAP245 for access to the wireless network in the corridor or private house.


The software part of the devices is implemented in such a way that access points are also able to work offline in case the network core hangs up, shuts down or temporarily fails. The controller and AP are controlled both from a PC and mobile devices from anywhere in the world.
Keenetic
Keenetic brand equipment is popular for implementing seamless Wi-Fi network access. The system can be set up in the web interface of the Keenetic configurator.
Creating a network based on two routers
You can set up a seamless home Internet connection using two routers. At the beginning of the work, you need to determine which method of connection between the two routers is most convenient.
There are two ways to connect devices: by cable or by Wi-Fi connection. Each of them has advantages and disadvantages.
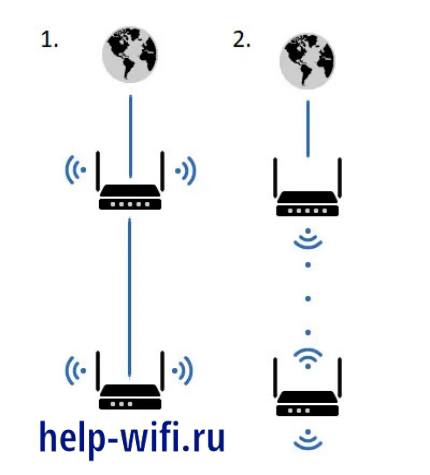
Cable connection of routers is not always convenient and quick to do, but it is the most reliable and durable type of connecting devices. If the need is primarily for reliability, high speed and continuity, this method is preferred.
Wi-Fi router connection is made by WDS bridge. In this case, the equipment is configured as a client (repeater). However, it should be noted that the interfaces of different brands of devices may have different settings of these modes.
For example, you can use the settings of TP-Link routers. As an alternative, you can use Zyxel equipment, but the described company is more common in the home segment. TP-Link devices are the most common and easy to understand for home users.
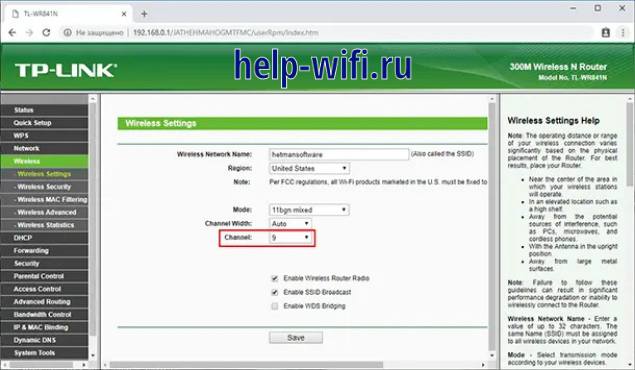
First, you need to configure the basic router so that it distributes the Wi-Fi network. A static connection channel must be set up. Then you have to connect to it by SSID name.
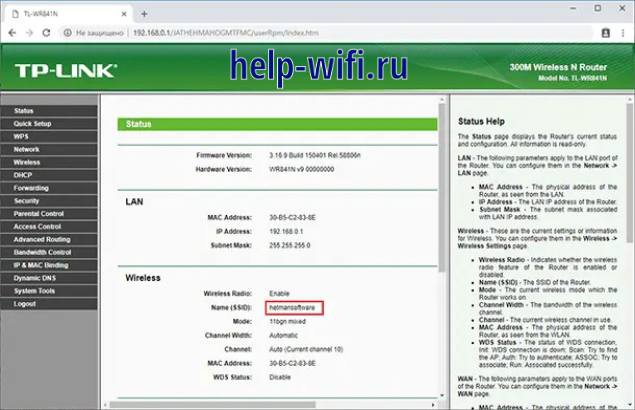
Channel is changed in the menu Wireless -Channel. In this item, you must specify a channel from 1 to 9. After completing the router settings must be saved.