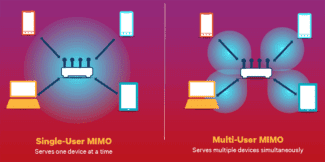
In the spring of 2015, the first 802.11ac Wave 2 devices hit the market. This standard has data rates up to 3.47 Gbps, a wider channel (160 MHz) and uses software-based Multi-User MIMO technology. MU-MIMO algorithms ensure that multiple streams of data are transmitted to different users, rather than sequentially from user to user, as in conventional SU-MIMO technology. Because access queues disappear and data is processed simultaneously, MU-MIMO dramatically increases frequency efficiency. Unlike legacy technologies, MU-MIMO does not divide the total channel rate by the number of client devices, but rather allows for maximum channel speed for all devices. MU-MIMO requires more complex processing algorithms and more computing resources, but maximizes the benefits of multi-antenna systems. Ultimately, Wi-Fi standards with MU-MIMO will allow wireless networks to scale up and increase their throughput. This is especially important for the Internet of Things.

- What kinds of Wi-Fi networks exist?
- Older Wi-Fi network standards
- Basic types
- Twisted pair
- Fiber optics
- Coaxial
- Comparison of fiber optic and twisted pair
- Connection types
- How to know the type of connection
- What types of Internet connections are available
- Dial-up access.
- Connection via asymmetric digital subscriber line
- Cable TV connection
- How to know your Internet connection type
- How to determine the type of Internet connection available in your home
- Technologies
- Settings in Windows
- Outlook on Wireless Networks
- What are the types of connections to the Internet?
- Types of connection technologies
- Connection via modem, using a telephone cable
- ADSL connection .
- What is wired internet
- Features and description of wired Internet
- Wi-Fi 802.11g
- 802.11ac Wi-Fi
What kinds of Wi-Fi networks exist?
Wi-Fi networks play an important role in today's technological world, with billions of devices connected to Wi-Fi networks. Already today, most of the world's Internet connections are through wireless networks. According to Juniper Research, by 2019 60% of mobile traffic will go through them. The global Wi-Fi market will grow from $14.8 billion in 2015 to $33.6 billion by 2020. With the spread of the Internet of Things and in-car hotspots, Wi-Fi networks will become the main link in the information space. For most users, the word Wi-Fi is synonymous with Internet connectivity. But in fact, Wi-Fi is a standard for wireless connection to a local area network. Simply put, Wi-Fi is a link capable of connecting many devices to a router that can be connected to the Internet. There is no need for wires and it is possible to connect on the fly, for example while walking or riding a bicycle.
Wi-Fi networks can be built according to different principles, depending on the tasks that a particular wireless network serves. There are three basic principles which most Wi-Fi networks of all sizes are built on.
Access Point (Access Point, or AP for short) is the most common type of connection. It is used in homes or offices as a combination of a wireless access point and a router. Usually such Wi-Fi networks are designed for Internet access, but they can also perform other tasks, such as organizing a local network without access to the World Wide Web. An access point is like a theater: many spectators (client devices) receive information from one actor (access point).
Photo 1: The principle of a Wi-Fi access point
- the router assigns IP addresses and provides a firewall between the network and the Internet;
- The wireless access point (AP) creates a wireless bridge between the router and the users' devices;
- Users' devices – tablets, smartphones, PCs.
Older Wi-Fi network standards
Wi-Fi wireless was given the green light in 1985, when the 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, and 5.8 GHz frequencies were opened for free use without a license.
Photo 8: Generations of Wi-Fi standards
The 1st generation IEEE 802.11 standard provided speeds of up to 2 Mbps over a range of up to 20 meters indoors. The main drawback was the use of 2.4 GHz frequencies, where there is interference from household and industrial equipment. The 802.11b standard: the same 2.4 GHz frequency, but the speed increased to 11 Mbps. This was the first mass standard to bring Wi-Fi to the global market. The 802.11a/g standard operates in the 2.4 GHz band like 802.11b, but uses the faster OFDM of 802.11a. The speed has increased to 54 Mbps. The current 802.11n standard has speeds up to 600 Mbps and an indoor range of up to 70 m. It uses MIMO antenna systems and operates at 2.4 GHz. Optionally, it can operate at 5 GHz, which saves battery life in mobile devices. It was the basis for the IEEE 802.11ac-2013 standard.
Basic types
There are three types of cable for the Internet: coaxial, fiber optic, and twisted pair.

Twisted pair
This network cable is a suitable solution when conducting local area networks. It consists of two or four twisted pairs of wires. Each two wires, connected in pairs, are only used to send or receive a signal.
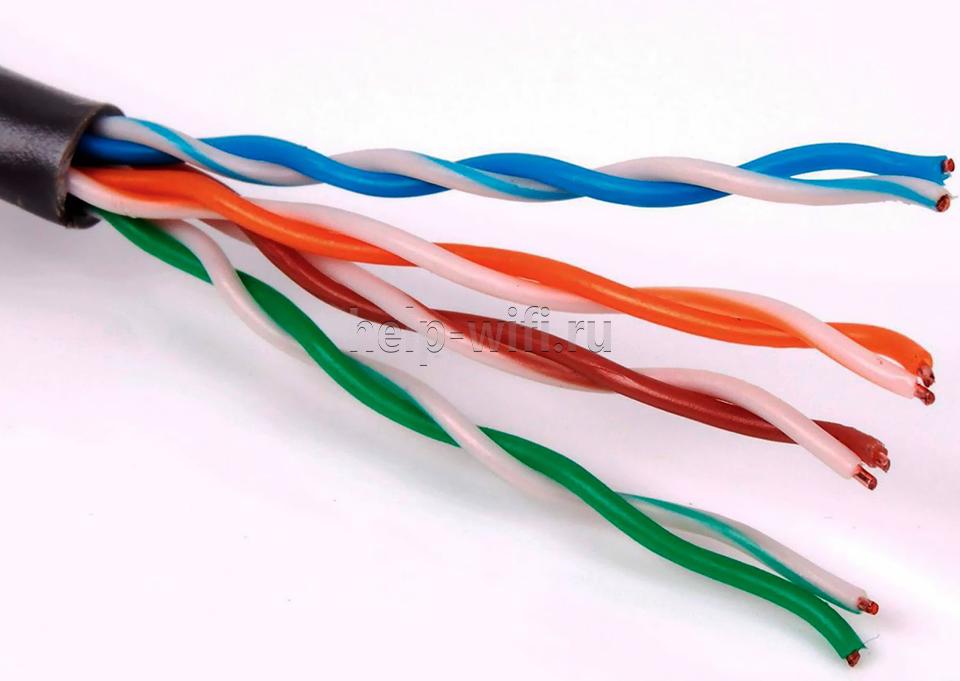

The principle of twisted pair is to connect two nodes and use separated media to transmit data in different directions.
Twisted pair connects equipment up to 100 meters away in a single network. Because of its low cost and ease of use it is increasingly being chosen to form local area networks (LAN) and the Internet in the room.
Fiber optics
Fiber optics is the fastest way to transmit information today.

- high bandwidth;
- long service life;
- quick detection of unauthorized connections, which makes the network more secure;
- high noise suppression, good protection against interference;
- fast data transfer.
Fiber-optic network wires use the method of transmitting light rays using total internal reflection. An important advantage of such a cable for connecting to the Internet is the absence of restrictions on the length of the trunk. That is why it can connect significantly distant objects.
Fiber optic itself is inexpensive, but the equipment for it has a very high price.
Coaxial
This type is used in security alarms, video surveillance and television. The principle of its work is the transmission of radio-frequency electrical signals, and the strength of the signal is closely related to the length of the backbone and the distance to which it will be sent.
Comparison of fiber optic and twisted pair
To determine which wire for the Internet is better to buy – fiber optic or twisted pair, you need to decide under what conditions it will be used.

For the usual connection of the computer to the network well suit a twisted pair. It is inexpensive, easy to lay, and the transmission speed is sufficient for home and office. This computer cable for the Internet bends well and can be stretched in the most awkward places. If it happens to be damaged, it is not difficult to replace it, because the price is very low.
Fiber optic for home and office is expensive due to the equipment, it is unreasonable to use it as a wire for a local network. The main advantage – a significant speed of information transfer – will not justify the costs, since a few computers are not able to create the kind of traffic for which it is designed. Fibre optics is used for Internet connection to populated areas or multi-storey houses. It is not afraid of line interference and long distances, so it is well suited for such tasks.
So, a fiber optic cable usually goes to a high-rise or private house. And inside the building there is already wiring with twisted pair.
Connection types
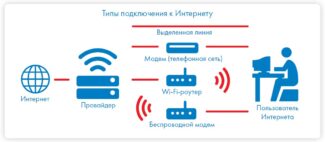
Providers use different types of connections. To properly configure your router, you need to know what type is used in your case.
What types of network connection are available can be seen in the router's settings.

- Dynamic IP is the most common and convenient type of connection. Its advantage is that you do not need to configure anything at all. Most manufacturers' routers are set by default to dynamic IP. That's why you just need to plug the router to the socket, plug the ISP cable into the WAN-port and the Internet will start automatically.
- PPPoE is also often used by Russian providers. To connect you need to know a username and password. They are given by the provider.
- PPTP and L2TP are rarely used. They are similar in their configuration. Besides a login and a password you have to specify the server address.
- Static IP is not frequent connection type. Mostly used by regional providers. Its essence is that the user is given a fixed IP-address, which must be prescribed in the router or in the settings of the network card.
If PPPoE, PPTP or L2TP are configured on your computer, a special connection is created and you need to run it to connect to the Internet. Read the detailed article on how to set up the Internet on your computer.
How to know the type of connection
To configure the router, you need to know the type of connection to the Internet. Look, it is probably specified in the connection contract. If it is not there, the easiest and most correct course of action is to call customer service. They will tell you what type of connection you have and answer other questions.
But you can figure this out on your own. It's easy to find out what type of Internet connection your ISP uses.
First, if you have the Internet set up on your computer, look up the type of Internet connection. In Windows 7 and 10, right-click the icon of the connection you are launching to access the Internet. Go to the Security tab. There you will see something like this:
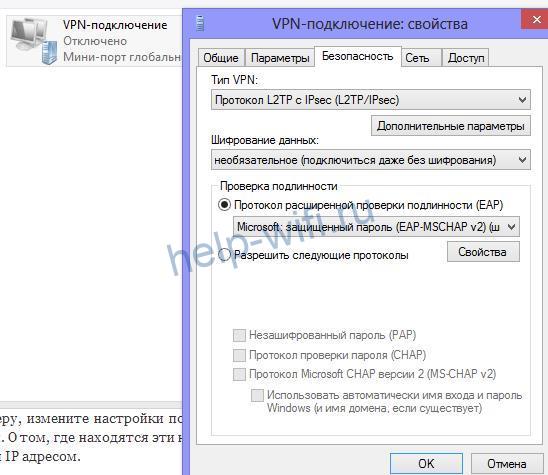
If you don't need to run the connection manually, that means you have a dynamic or static IP.
- Open "Network and Internet Settings" by right-clicking on the Internet icon in the lower right corner next to the clock (tray). Next, select "Configure Adapter Settings".
- Right-click on your network adapter icon and select "Properties".
- Find TCP/IP v4 in the window that opens, highlight it and click "Properties".
- This will open a window with the settings. Blank fields mean that you get an IP address automatically. If you see any numbers, then you have a static IP address.
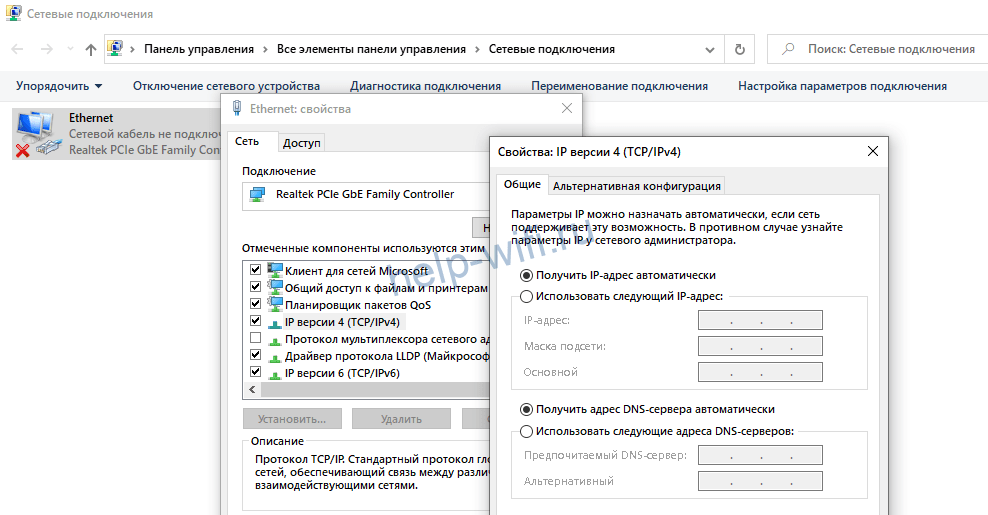
You can understand what kind of connection you have from the settings that are specified in the contract with your provider. If you do not need to enter any parameters, you have a dynamic IP. If there is a username and password, it is probably PPPoE. When they are accompanied by the server address, it's either L2TP or PPTP.
Read More:If you specify the wrong type of connection in the settings, nothing bad will happen. The Internet will simply not work. Check the settings and try another type.
What types of Internet connections are available
Dial-up access.
This is a modem connection over the telephone network. To set it up, you need to have a home phone and a service provider whose equipment is powerful enough to provide network access.
The disadvantage of dial-up connection is that the connection to the network is through the same line as the dial-up. Therefore, simultaneous use of the Internet and phone is impossible. In addition, on average, such a connection allows access to the network at a speed of up to 56 Kbps. Few online games work with this connection, and downloading files can take several weeks.
Nowadays dial-up connections are common in areas where population density or area characteristics do not allow for broadband Internet.
Connection via asymmetric digital subscriber line
It is also called ADSL. This is another type of modem connection. It also requires a telephone line, but a digital modem allows you to dial up and go online at the same time. The bandwidth of the line at this type of connection to the Internet is higher than in the method described above. It provides the subscriber with sufficiently high speed of access to the network – up to 24 Mbit/s on average. The load on the line is distributed asymmetrically – the incoming connection is faster than the outgoing one (up to 1.4 Mbit/s). Because of this, it takes longer to upload files to the server.
Cable TV connection
This is the type of access that is provided via DOCSIS – data transmission over a television cable. It is usually used when there are no internet providers in the house. With it you can get speeds of 27 to 50 Mbit/s. To set up access, you need to have cable TV and a special modem in your house.
How to know your Internet connection type
If your device is connected to the network, you can find out the access method through the settings. Just go to "Network and Sharing Center" on Windows computers or "Network" on a Mac. There will be information about the available connection options and the current connection method. If the Internet is not working at the moment, or if you need more information, contact the technical support team of your ISP.
Much depends on the service providers available in your home and your needs. Dial-up access offers low connection speeds and is inconvenient to use. It can only be selected if other types of network settings are not available to you.
If you want to connect the Internet through your phone, ADSL is more suitable. With this channel, you'll get speeds that are sufficient for normal surfing: running most online games, downloading movies, watching online videos. If you are planning to use the "smart home" technology and want to set up digital TV over the Internet, find out about the possibility of replacing the telephone cable with a GPON fiber optic, with simultaneous connection of phone, Internet and TV. It will cost more, but all three services will be provided through one cable. The bandwidth of such a line is much higher than that of analogues.
If you do not have the ability to wire your apartment, consider radio internet or cell phone service. The disadvantage of the first is the need to install an antenna at home, and the disadvantage of the second is the slow connection speed.
Satellite access should be considered only if you can not connect to the network another way.
How to determine the type of Internet connection available in your home
Use the form of selecting a provider by residential address on our website. Enter the name of the city, street and house number. The system will automatically select a list of available providers for you. You can see their rates, get advice about the service and make a connection.
Technologies
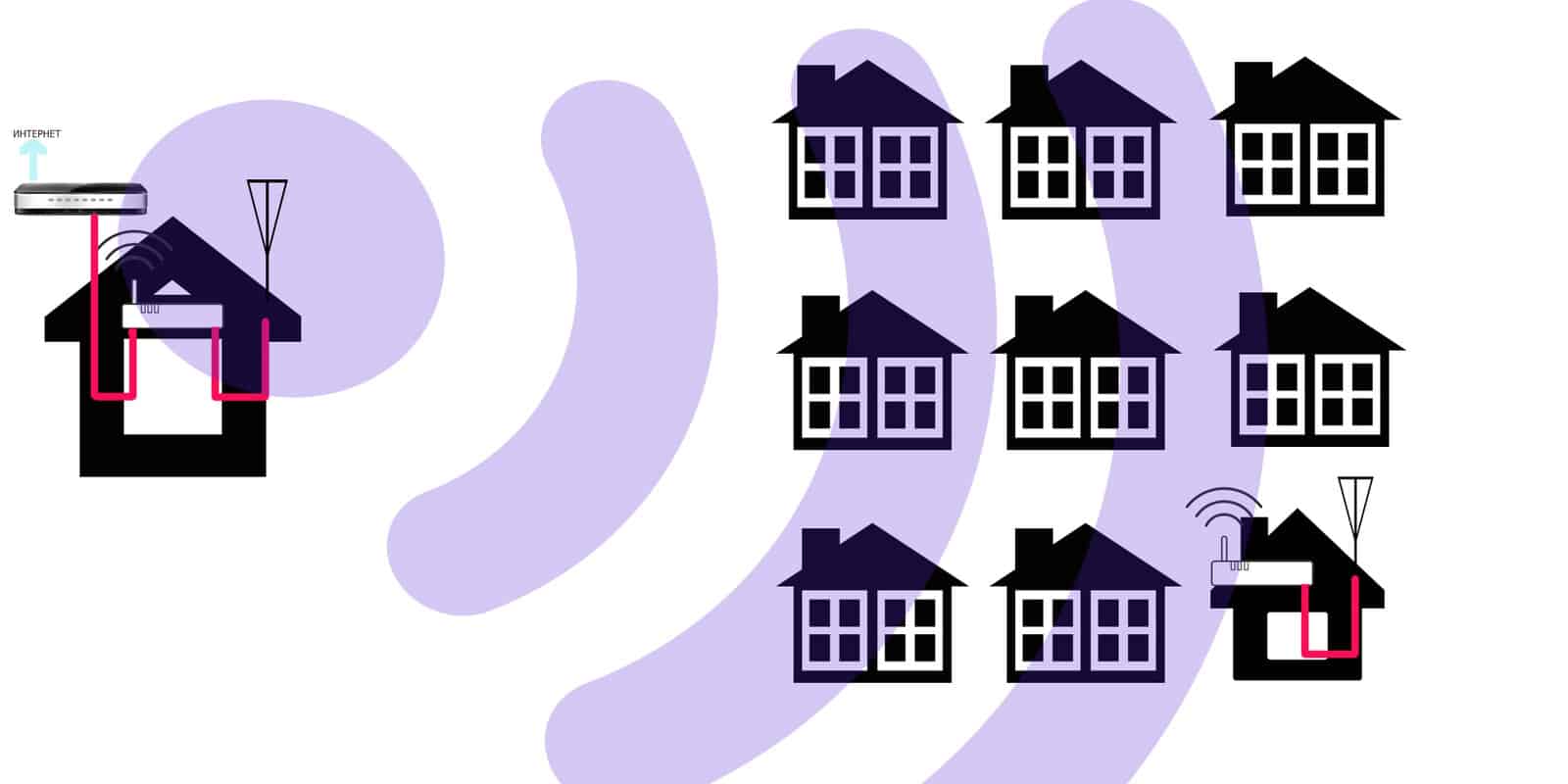
And everything, for the most part, depends on the technology of the provider. This chapter is not going to talk about each of them in detail, but it will briefly go over the main points. There is an interesting video on this topic:
- Local Area Network – over twisted pair or fiber. Connection types – Dynamic and Static IP.
- VPN – creating a virtual private network over the same twisted pair and fiber. These are voiced PPPoE, PPTP, L2TP.
- Combined classic types – like PPoE+Dynamic – at the provider's discretion.
- Telephone line – still existing ADSL and already extinct Dial-UP.
- Television cable – DOCSIS.
- Satellite.
- WiMAX – via Wi-Fi network provider.
- Mobile Internet – GPRS, 3G, 4G LTE.
Settings in Windows
In Windows, these types can also be created to connect directly without a router.
Using Windows 7 as an example, when using PPPoE. "Network and Sharing Center" – Internet Connection – High Speed with PPPoE:
That's it! Do not wait for miracles, in case of any problem call your ISP. In the case of a successful detection, specify your ISP and the right type. Maybe that will help future readers!
Outlook on Wireless Networks
The IEEE 802.11 wireless standard was created in 1997. Now a high speed connection to the line is possible in almost every region of the planet. Quantitative growth of wireless points was promoted by the appearance on the market of Centrino platform from Intel. Thanks to this utility, many laptops are now equipped with Wi-Fi controllers.
In the near future it is planned a mass transition to the technology and the IEEE 802.16a standard, which can provide WiMAX networks. It is assumed that the frequency band 2-11 GHz will be used, the data transfer rate will be supported in the range of 70 Mbit / s, and the coverage area will increase to 50 km.
WiMAX devices have already begun to produce some organizations, in particular Intel. Broadband networks are also in development at Telecom, BT, Millicom, the Russian operators Peterstar, MediaNet, Comstar.
- Improving the quality of communication, expanding functions.
- Internet access from anywhere in the world.
- Increased speed of connection to the network.
- Quantitative growth of users due to increased availability of equipment.
- Spreading of the possibility of remote control of electronic devices.
Local wireless technologies are spreading more and more. They are used both in offices, business centers and residential buildings. At the moment, Wi-Fi has a number of shortcomings. However, the means of communication are rapidly evolving, the quality is growing. In the coming years, you can expect to overcome the existing shortcomings, increasing opportunities and ensuring high security for customers.
What are the types of connections to the Internet?
The network comes in wired and wireless. In the case of the first option, there must be any two devices that are connected by wire to communicate with each other. Fiber optic or copper cable can be used as the connection. With this type of connection, the functionality of data transmission is limited by the physical properties of the cable. Wired networks are governed by IEEE 802.3, which clearly spells out all the basic requirements.
Wired Internet is a how? Initially a telephone line was used to access the network, as well as a special device – a modem. At the same time, the speed of data transfer was low. But with the development of progress, everything has become much simpler. Now the speed of wired Internet has increased, and there is no need to buy additional equipment. All motherboards have a built-in network card.
Attention! To connect to the network, simply insert a properly crimped cable in a special slot and then make simple settings.
The disadvantage of a wired network is that it requires cabling to each workplace. And since wiring is usually done immediately when renovating the premises, any changes in the organization of work will also directly affect the network infrastructure.
Wireless technology appeared relatively recently, but has already gained wide popularity among users. The Internet signal in their use is transmitted via radio channels of high-frequency bands, as well as by laser, optical and infrared radiation. Wi-Fi connection is regulated by the IEEE 802.11X protocol, which is constantly being improved.
To distribute a wireless signal to a computer, phone, tablet, laptop, a router (it may also be called an access point or router) is used. Once current is applied to the device, an electromagnetic field is created.
Types of connection technologies
Knowing what kind of Internet is, you should take a detailed look at all the possible connection options. This will allow you to understand the difference between them, and what advantages, as well as disadvantages each of them has.
Connection via modem, using a telephone cable
This type of home Internet assumes dial-up access to the World Wide Web, which is the oldest. To set up a wired connection, you need a landline phone and a telecom operator, whose equipment can provide such a service. To connect to the ISP network, the modem dials the pool number and connects to an identical device at the station.
The inconvenience lies in the fact that the connection to the outside world is on the same line that the telephone set uses. And this eliminates the possibility of simultaneous connection. Internet speed in this case does not exceed 56 Kbps. This means that small online games can work, but the duration of the downloaded files is likely to be several days. Charging in this case is depending on the amount of incoming traffic or by time.
Important! Nowadays the connection via telephone line is used only in places where there is no possibility to have broadband Internet due to low population density.
ADSL connection .
In this case the technology provides Internet connection thanks to asymmetric bandwidth allocation and priority for data transfer. Initially, the ADSL connection type was created for interactive television, and only later this standard began to be widely used by providers, who identified the potential of such a modem as an access point for Internet access.
For ADSL connection a telephone line is necessary, but in this case working in the network does not exclude the possibility of dial-up at the same time. This has been achieved by separating the frequencies used for voice and data. Such technology provides internet speeds of up to 24 Mbit/s.
What is wired internet
Internet today has become an integral part of the life of almost everyone around the world. The latest technology provides a variety of options for access to the World Wide Web, each of which has its own nuances. The most common connection today is wireless, but cables are not a thing of the past.
Wired Internet is a connection method in which you connect to the Internet using a cable.
What is the difference between wired and wireless Internet? They have serious differences.
- High data transfer speeds, security and reliability – that's what guarantees wired Internet, as cables are not affected by network interference.
- The disadvantage of such a connection is the change of provider when you move to a new place.
A modern wired Internet connection offers unlimited rates. It means that the user pays a fixed monthly fee, gets unlimited Internet access, and the amount of traffic is unlimited.
If the connection package also includes cable TV, you can watch your favorite channels for one month for the same monthly fee.
Features and description of wired Internet
Networks can be wired or wireless. Each of these types has its own strengths and weaknesses. When designing, "experts" who do not consider the details of each type of network often make mistakes.
A great example: installing a wireless network in an office without wired components inevitably leads to signal quality degradation, data loss and other problems.
Network performance is defined according to the IEEE 802.3 international standard:
- IEEE 802.3u. The maximum speed of the network is 100 Mbit/s. Used when high throughput is not required.
- IEEE802.3ab. Network speeds up to 1000 Mbps. Is the most common standard that guarantees high-speed transmission.
- IEEE 802.3an. Enables speeds up to 10 Gbps in some cases.
Wi-Fi 802.11g
As you have already figured out, this version of the protocol is backward compatible with previous protocols. This is because the operating frequency has not changed. At the same time, engineers managed to increase the speed of receiving and sending data up to 54 Mbit/s. The standard was released in 2003. For some time, this speed seemed even excessive, so many manufacturers of cell phones and smartphones were slow to implement it. Why do you need such a fast data transfer, when the built-in memory of portable devices is often limited to 50-100 MB, and the full-fledged Internet pages on a small screen is simply not displayed? And yet gradually the protocol gained popularity, mainly due to laptops.
The most massive update to the standard happened in 2009. Wi-Fi 802.11n was born. At that time smartphones already learned how to display high quality heavy web content, so the new standard came very handy. It differed from its predecessors in increased speed and theoretical support of 5 GHz frequency (although 2.4 GHz did not go anywhere either). For the first time, support for MIMO. It consists in the support of receiving and transmitting data simultaneously over multiple channels (in this case, two channels). In theory, this made it possible to achieve speeds of 600 Mbit/s. In practice it rarely exceeded 150 Mbps. It was because of the interference on the signal path from the router to the receiving device, and many routers were deprived of MIMO support to save money. Just as the budget devices did not get the opportunity to work in the 5 GHz. Their creators explained by the fact that the 2.4 GHz frequency at that time was not yet heavily loaded, so the buyers of the router did not really lose anything.
Wi-Fi standard 802.11n is still actively used. Although many users have already noted a number of its drawbacks. First, due to the frequency of 2.4 GHz it does not support combining more than two channels, so the theoretical speed limit is never reached. Secondly, in hotels, shopping malls and other crowded places, channels begin to overlap each other, which causes interference – Internet pages and content are loaded very slowly. All of these problems have been solved by the release of the next standard.
802.11ac Wi-Fi
As of this writing, it is the newest and fastest protocol. Whereas previous types of Wi-Fi worked mostly in the 2.4 GHz frequency, which has a number of limitations, here strictly 5 GHz is used. This has almost halved the width of coverage. However, router manufacturers solve this problem by installing directional antennas. Each of them sends the signal in its own direction. However, some people will still find it inconvenient for the following reasons:
- Routers turn out to be cumbersome, since there are four or even more antennas in their composition;
- It is desirable to install the router somewhere in the middle between all the rooms to be served;
- Routers with 802.11ac Wi-Fi support consume more electricity than older, lower-priced models.
The main advantage of the new standard is a tenfold increase in speed and extended support for MIMO technology. From now on, up to eight channels can be interconnected! The result is a theoretical data flow of 6.93 Gbps. In practice, the speeds are much lower, but even they are enough to watch some 4K-movie online on the device.
For some people, the capabilities of the new standard seem excessive. That is why many manufacturers do not implement its support in budget smartphones. The protocol is not always supported even by quite expensive devices. For example, the Samsung Galaxy A5 (2016), which even after reducing the price tag cannot be classified as a budget segment, lacks its support. To find out which Wi-Fi standards are supported by your smartphone or tablet is easy enough. To do this, look at its full specifications on the Internet, or run one of the benchmarks.