When entering router settings, it is important to know which country to select in the WiFi settings. When using the 2.4 GHz band, the bandwidth used is 2401 to 2483 MHz. For European countries and Russia, this band is divided into 13 channels. The United States of America has a different frequency division. Here there are only 11 frequency bands. If you set the country incorrectly, you may find that instead of 13 (in Europe) there are only 11 frequency channels available (in the U.S.).

- 5 GHz Wifi Channels – Increase Your Internet Speed with the Right Channel
- Comparison of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz wifi data transmission standards
- About Channels
- Looking for a free channel
- Experiment results
- Wi—Fi 2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz, differences, pros and cons
- Comparison of speeds in the 2.4 band GHz и 5 GHz
- Criteria for choosing a module
- Installation and configuration
5 GHz Wifi Channels – Increase Your Internet Speed with the Right Channel
Sometimes a WiFi connection can cause connectivity problems due to the fact that the wrong channel has been selected to work. In this case, restarting the router can help. However, in some cases this does not help. To establish a wireless connection, you need to figure out what happens, which channel to choose for WiFi, 5 GHz or 2.4 GHz, and what you need to do to specify it in the settings. How to do this correctly will be explained in more detail in this article.
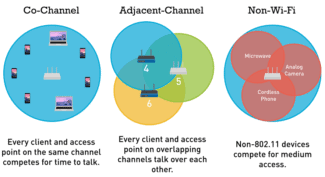
The router, when transmitting a wireless signal, works using certain frequencies. The entire frequency band is divided into several channels, each of which represents a portion of the original gap. The router uses one of the options available to it when operating. It is possible that one of them is used by several people. In this case, they will interfere with each other.

Important! Different channels can partially overlap each other. In this case, at any given time for each of them can transmit a signal only one source. In this case, the connection speed will be much lower.
Routers use two bands: 2.4 and 5 GHz. In the first case, according to European and Russian standards there are 13 channels, of which 3 have no common frequencies. Each of them has a width of 20 MHz. The second case uses 33 frequency gaps, of which 19 do not overlap.
Comparison of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz wifi data transmission standards
Wireless operation is defined by a group of 802.11 standards. The names use a numerical code with a letter index: a, b, g, n, ac. The first four of these are the most common. The 802.11ac standard is the newest of these. It only works with the 5 GHz band.
Standards with the codes b, g, n work only with the 2.4 GHz frequency band. They are more popular and affordable. Home appliances that can be connected to WiFi also work in this frequency range.
The 5 GHz frequency is rarely used. It improves the quality of communication, but is not yet widespread enough. Routers of this type are backward compatible and can operate in both bands. There are 19 non-intersecting channels in this band, while on 2.4 GHz there are only 3.
The range of this communication is smaller, and objects and walls create more interference than for 2.4 GHz. Not all gadgets are capable of operating in this range.
About Channels
The topic of channels is getting more and more relevant every year. I used to not pay much attention to it, but now we can really face situations, when theory becomes reality: loaded channels create interference to all users, speeds drop, connections are dropping. As a way out we have to look for a new channel.
This will be a universal instruction for all router manufacturers – TP-Link, ASUS, D-LInk, ZyXEL, etc. But if you want to configure your particular router exactly and step by step, I recommend you to search for the article on our website by entering your model there. There will already be an exact step-by-step instruction!
To get you started, here's a video on the subject. And about Wi-Fi channels, and about the choice and configuration:
Modern home routers operate on the following frequencies:
- 2.4 GHz is the very first Wi-Fi frequency. The range is 2.401-2.483 GHz. This is where most of the devices work. And the number of channels is limited – there are only 13, and even then from country to country is limited (so in the U.S. available only 11, which can cause some conflicts, and Windows sees only 12, etc.). As a result, channels are overloaded, interference increases, and there are problems with the network. Especially on this frequency. Standards to 802.11n.
- 5 GHz is a relatively new frequency. And there are more channels, too – 23. And there are fewer devices using it, too. Even personally, the author of this article only has a 2.4 GHz router on the premises at the moment. The standards are 802.11ac and newer.
| Channel | Frequency | Channel | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.412 | 34 | 5.170 |
| 2 | 2.417 | 36 | 5.180 |
| 3 | 2.422 | 38 | 5.190 |
| 4 | 2.427 | 40 | 5.200 |
| 5 | 2.432 | 42 | 5.210 |
| 6 | 2.437 | 44 | 5.220 |
| 7 | 2.442 | 46 | 5.230 |
| 8 | 2.447 | 48 | 5.240 |
| 9 | 2.452 | 52 | 5.260 |
| 10 | 2.457 | 56 | 5.280 |
| 11 | 2.462 | 60 | 5.300 |
| 12 | 2.467 | 64 | 5.320 |
| 13 | 2.472 | 100 | 5.500 |
| 104 | 5.520 | ||
| 108 | 5.540 | ||
| 112 | 5.560 | ||
| 116 | 5.580 | ||
| 120 | 5.600 | ||
| 124 | 5.620 | ||
| 128 | 5.640 | ||
| 132 | 5.660 | ||
| 136 | 5.680 | ||
| 140 | 5.700 | ||
| 147 | 5.735 | ||
| 149 | 5.745 | ||
| 151 | 5.755 | ||
| 153 | 5.765 | ||
| 155 | 5.775 | ||
| 157 | 5.785 | ||
| 159 | 5.795 | ||
| 161 | 5.805 | ||
| 163 | 5.815 | ||
| 165 | 5.825 |
Looking for a free channel
To begin with, we need to determine which Wi-Fi channel is the most congested at the moment, and therefore which one we should choose. It is the one that will be the best for us at the current moment in time. How do we do that?
Whatever you choose, the channel window will almost always be the same:
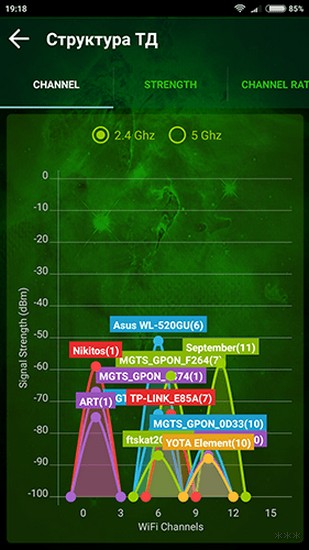
Looked at by eye, and determined that in this case, the freest Wi-Fi channel is 5. That's what we'll use. A universal quick technique to check your environment and determine the best channel. And here is the same for inSSIDer, you can compare:
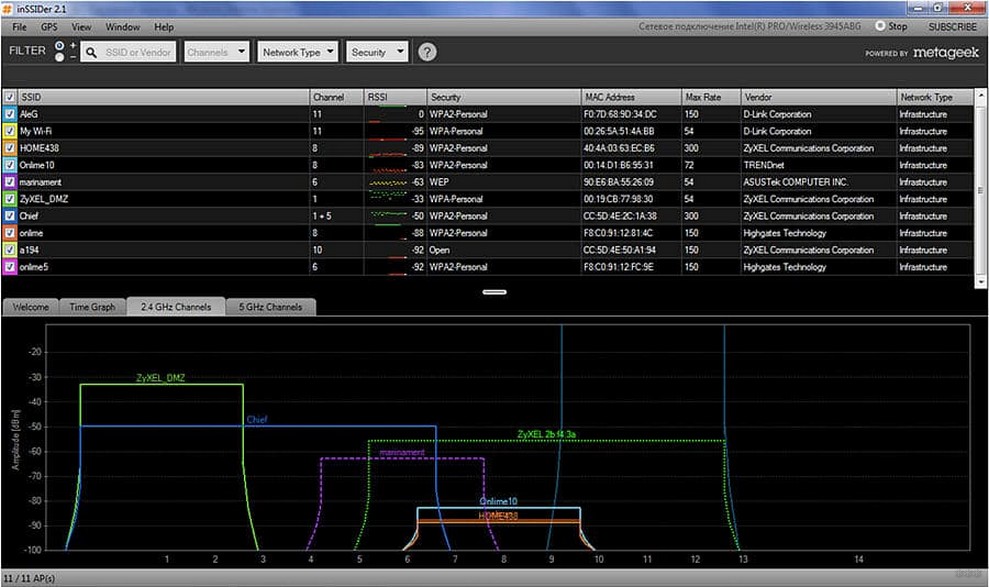
As you can see, it's not that hard to find out. The only thing that may discourage is that many channels overlap each other in the frequency range, creating additional interference. So you really have to choose the least busy ones. But you can always find one!
For theorists. List of non-intersecting channels:
Be careful about setting channels 12 and 13. Some devices may not see them!
Experiment results
I must say that the results on weekdays in the evening were very different from what I got during the holidays. This is especially noticeable with 2.4 GHz data transfer, as everyone goes home and starts actively surfing the Internet.
The best way to see the speed of the networks is by looking at the chart. Here I measured the speed of a single thread, as if it was just a single file being downloaded. At the same time I opened and closed the door and tried different frequencies.

From the diagram it is clear that the closed door is quite good at cutting down the transfer speed, and the Wi-Fi adapter is slower due to the fact that the antenna on the router has a better gain. By the way, the theory that the signal at a higher frequency has worse penetration through obstacles was confirmed: the speed of transmission at 2.4 GHz with the adapter is higher than at 5 GHz with the door closed. Anyway, if you want to watch Youtube at normal speeds, you have to connect the router at 5 GHz.

Let's move on to the second graph. Here I ran 20 transfer streams, as if a page with a bunch of photos was loading or a torrent download was running. Immediately it was obvious that the 5 GHz frequency was less busy and therefore provided higher data transfer speeds. And also the effect of the open door became noticeable.
And now I'll separately give a graph of operation at different frequencies, with the door open and transferring 20 streams.

A closed door more than 1.5 times cuts the data rate. Thus, indeed, the open door allows you to surf the Internet faster.
Wi—Fi 2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz, differences, pros and cons
Note! When buying a router, you can pay attention to the fact that it supports two frequencies: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. In them work all home wireless networks, depending on which router is chosen, the choice can fall on both the older band in 2.4 GHz, and the newer type in 5 GHz.
The difference is fundamental. The 5 GHz frequency is newer, the channels within it are better isolated and overlap less. Achieving good wireless speed and full use of the high speed Internet in this case is much easier and more convenient. Most importantly, there is definitely less conflict between the different networks, which stabilizes the speed of the network.
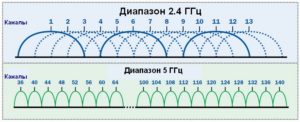
Life in block houses is a big obstacle to work in the 2.4 GHz band, as it is known that the broadcast of wireless networks is limited by their channel, and the living conditions in panel houses assume a forced neighborhood with many people at once, who are forced to share the Internet space. Because of the cheapness of the 2.4 GHz equipment is commonly available, and therefore most often used, so it is not surprising that the network traffic load at some points can be enormous.
Note! As a result, the 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi network is more congested with neighboring networks, which can lead to performance degradation and even disconnection. It is also associated with lower transmissions and increased ping (latency), which interferes with voice and video conversations and comfortable playing online games.
Comparison of speeds in the 2.4 band GHz и 5 GHz
The main, though not the only difference between the two is speed. The speed threshold of v. 2.4GHz reaches 450 or 600 Mbps, while the 5 ghz version of the wifi connection can easily go up to 1300 Mbps.
Important! This maximum speed is quite far from the actual speed. It clearly depends on the wi-fi standard your router uses, such as 802.11 b, 802.11 h, 802.11 n, or 802.11 ac.
Criteria for choosing a module
There are several criteria for choosing an adapter:
- The most efficient choice is to buy a receiver with speeds up to 300 Mbit/s, or, even better, with support for the modern 802.11ac standard;
- if the user will have (or already has) a modern router supporting the new 802.11ac standard, and a module supporting 802.11n, the ability to connect to a Wi-Fi network is present, the devices are compatible. However, the speed will be limited to the slower 802.11n standard. And the user will not see the full potential of the router with 802.11ac support, because the receiver will limit the speed;
- the adapter and the router can be from different manufacturers, however, it is better to choose devices from one manufacturer.

Installation and configuration
For any laptop, you can buy an internal or external wireless adapter that will be able to support the selected frequency. It needs to be properly connected and preconfigured. The router can be from any manufacturer (Asus, Lenovo, Hp), as well as the purchased module. The procedure of installation and configuration is described for the TP-Link Archer T4U model.
To connect the laptop to the network you need to insert the module into the USB 3.0 port. It is also compatible with the older 2.0 standard; however, the connection speed will be slower. From the media that comes with the device, you must run the driver installer and the official program. After that, the following sequence is followed:
- After launching the application, a special window will open with the possibility of selecting a Wi-Fi network for connection;
- It is necessary to find your own network and connect;
- The system will prompt for a password, which should be entered;
- After that, the configuration is complete and you can use the connection.
In case the module was purchased second-hand and has no installation media, you can download the software and the latest driver version from the official site. To do this, you need to enter the address tp-link.com. To avoid searching for a long time, you can simply enter the name of the adapter model in the search bar and click on the support link. In the list that opens, you should find the latest hardware version of the device, which is indicated on the sticker. Then go to the "Utility" section and download the driver version for your notebook.
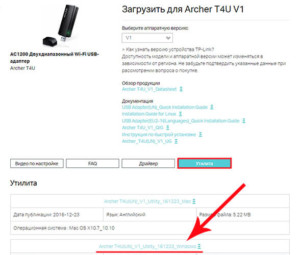
The wireless network adapter is a built-in device for your notebook that allows you to connect to these types of networks. You can purchase a separate external device if the standard one is not capable of supporting the 5 GHz frequency. In addition, you need to know how to turn on and configure the adapter, and to know if the frequencies are compatible with your router. Select a new model with specific criteria in mind.
Read More: