One of the places where Wifi 6 is already working is the Adygei State University in Maikop. All campus buildings are covered by a single communication network. For distance learning and various content that can be used in training and conferences, high-speed data transfer is key: more people can connect to the network, and more information can be received and transmitted. Regional universities need such technological capacity so that motivated applicants do not go to study in metropolitan regions.

- Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) – what is it? All you need to know about the new Wi-Fi standard
- What's new in Wi-Fi 6 and how is this standard better than the previous one?
- Speed in Wi-Fi networks 6
- Improved performance when more devices are connected
- What is Wi-Fi 6?
- What's different about Wi-Fi 6 technology?
- Conclusion – what to expect from Wi-Fi 6E
- What are WiFi 6E devices compatible with?
- What is the purpose of the advanced standard?
- What are the advantages of Wi-Fi 6
- Speed boost
- Improved handling of multiple clients
- Do I get a router that supports Wi-Fi 6 now?
- Which routers support Wi-Fi 6
- How fast is Wi-Fi 6
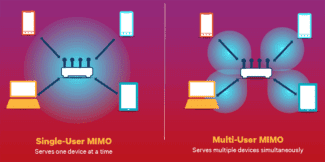
- Multiuser MIMO for receiving and transmitting
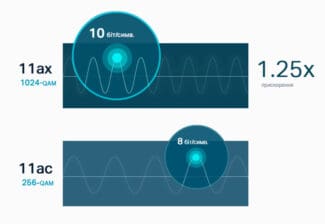
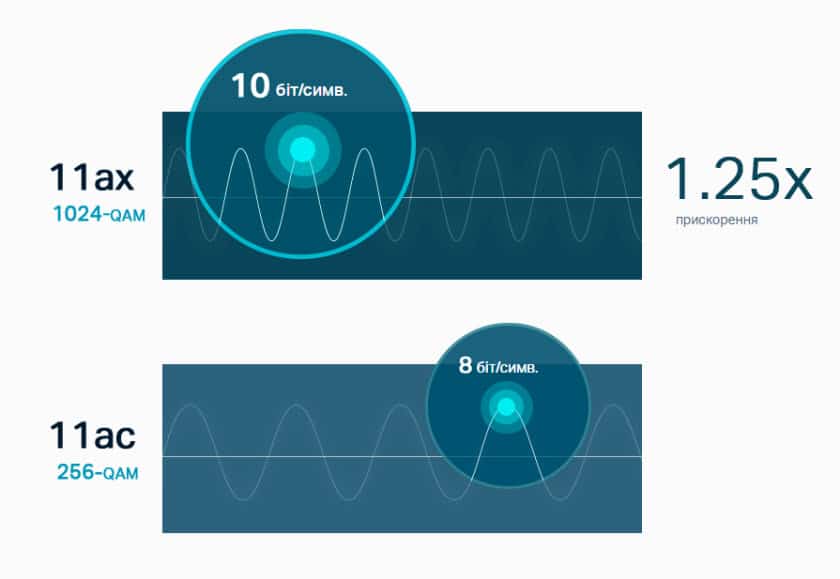
- 1024-QAM modulation and extended OFDM symbol length
- Features and differences Wi Fi 6
- How to get Wi Fi 6 at home
- Crowds and neighbors are no hindrance to Wi Fi 6
- What happens to Wi-Fi next?
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) – what is it? All you need to know about the new Wi-Fi standard
In September 2019, the Wi-Fi Alliance organization officially introduced the 802.11ax standard. It's also Wi-Fi 6 (the new name) . And as expected, in 2020, manufacturers of various network equipment, mobile devices and computer equipment began to actively market devices that support the new Wi-Fi standard. The 802.11ax standard replaces the previous 802.11ac standard. It was designed to improve wireless connectivity and to solve some problems related to stability and congestion of Wi-Fi networks. The new Wi-Fi standard is an improved and updated version of 802.11ac.
Wi-Fi 6 and 802.11ax are the same. It is just that the Wi-Fi Alliance decided to give a simpler and clearer name for the Wi-Fi standards. So 802.11n became Wi-Fi 4, 802.11ac became Wi-Fi 5, and the new 802.11ax was named Wi-Fi 6. It's simple and straightforward.
Wireless networks are evolving very rapidly. And we see the need for higher data rates and for connecting a greater number of devices. More and more access points are appearing, interfering with one another and causing interference. These are the problems that the Wi-Fi Alliance specialists were focused on when developing Wi-Fi 6. What improvements have been implemented in the new standard, how it affected the connection, stability and speed – we will consider in this article. I will try to explain in simple language. I'll also answer the most popular questions related to Wi-Fi 6.
What's new in Wi-Fi 6 and how is this standard better than the previous one?
- The speed of the connection.
- The stability of the connection when a large number of devices are connected.
- Working in places with a lot of neighboring networks (where there is a lot of noise).
- Power efficiency.
Speed in Wi-Fi networks 6
Of course, everyone is primarily interested in connection speed. Wi-Fi 6 offers wireless connectivity at speeds of up to 11 Gbps. But you have to understand that the actual connection speed will be much lower. Of course, compared to 802.11ac the speed increase is significant (almost 2 times faster). But there is another important point here – the connection speed according to the tariff of your Internet provider. If your wireless rate is up to 100 Mbps, then 802.11ac is more than enough there. If up to 1 Gbit/s, then switching to Wi-Fi 6 can, of course, increase the actual connection speed, because using equipment that works on 802.11ac is unlikely to squeeze that gigabit over the wireless network.
The speed has been increased by changing the information encoding algorithm. Whereas the previous standard used 8-bit information coding the new standard uses 10-bit information coding.
The important point is that 802.11ax can operate in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
Improved performance when more devices are connected
The more devices connected to your router and the more they use the connection, the slower the speed and stability of the connection. Wi-Fi 6 has greatly improved this situation. Routers that support older Wi-Fi standards can communicate with up to a few devices at a time. Thanks to OFDMA technology, which appeared in Wi-Fi 6, it became possible to conduct parallel data exchange with a large number of devices. Shorter packets are transmitted, but to a larger number of devices. Graphics from the TP-Link website:
What is Wi-Fi 6?
Wi-Fi is a group of wireless network protocols based on the IEEE 802.11 network standard. They differ in bandwidth, signal range, and more. The term was coined by the non-profit Wi-Fi Alliance in the late 1990s. Serial naming of Wi-Fi was introduced for convenience. In terms of throughput per subscriber, Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) is four times the previous generation of Wi-Fi 5, which runs on 802.11ac.

The Wi-Fi Alliance officially launched the Wi-Fi 6 certification program in 2019. The Wi-Fi Certified 6 program focuses on verifying the compatibility of user devices, ensuring that they work well together and support all necessary features, proper performance and security.
Wi-Fi 6 provides potentially faster connection speeds. On these networks, more users can connect at the same time without delay or loss of speed.
In addition to Wi-Fi 6, a new Wi-Fi 6E technology has been approved that can use a different 6 GHz frequency band. This makes the network ideal for transmitting large amounts of data over short distances.
What's different about Wi-Fi 6 technology?
What's new about Wi-Fi 6 technology is that it supports multiple channel frequency division multiple access (OFDMA), which allows you to serve more devices on your network. The router's communication channels are divided into multiple carriers, and it can communicate with multiple devices simultaneously.
Wi-Fi 6 also adds mandatory support for MU-MIMO, which first appeared in Wi-Fi 5, and transmit beamforming technology for better coverage of each individual user.
MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) is a method of spatial signal encoding that allows data to be transmitted between multiple devices simultaneously without loss of speed or connection quality. Directional signal technology means that the router is able to detect the location of the device itself and direct the data flow in that direction.
Conclusion – what to expect from Wi-Fi 6E
In short, Wi-Fi 6E means Consistently fast Wi-Fi 6 near-field speeds over the all-new 6 GHz frequency band.
Wi-Fi 6E is not exactly better (or worse) than Wi-Fi 6. It is simply an additional option, applicable in certain situations.
At the moment, the new wireless standard is available in limited variants. Realistically, 2022 is the earliest time when Wi-Fi 6E will really start to play a meaningful role in everyday life.
When it comes to Wi-Fi, it always connects at the right time And it doesn't have to have the latest and greatest. The first existing 2.4 and 5 GHz bands will be enough for a long time.
Think about it, 5 GHz has been around for over a decade, and 2.4 GHz is not even close to extinction – probably never will be. It will be the same with 6 GHz. It's an additional band that doesn't replace anything. There's no need to rush to upgrade.
Here's something interesting: As more and more devices support the new 6 GHz bands, the other two (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) will become less busy. So both new and old equipment will benefit from the addition of Wi-Fi 6E.
Don't hold your breath and wait for Wi-Fi 6E. Go ahead and purchase equipment that meets your needs today.
It's always a good idea to give a new standard time to fully mature before moving to it.
What are WiFi 6E devices compatible with?
Almost all of the previous standards – otherwise there would be no point in producing them. But, understandably, since older devices "could not" in 6 GHz, the speed of such a connection will not be the maximum. But if the device with the 6E communication module connects to the same router – this is a different situation, in which case the speed will be exactly that maximum.
At the moment, you don't have to worry too much about the small number of devices with WiFi 6 – there will only be more of them by the end of this year or even at the beginning of next year. Since the new standard is actually a superstructure over WiFi 6, there will be two modules in devices supporting WiFi 6 (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz range are possible here) and WiFI 6E itself.
The extended standard offers excellent transfer speeds and quality, while supporting multiple devices without reducing bandwidth.
What is the purpose of the advanced standard?
First and foremost, to improve the communication quality of mission-critical applications. WiFi 6E can significantly improve the quality of wireless gaming and video streaming, even in environments where multiple devices are connected to the same network.
WiFi 6E can be useful for enterprises that require video transmission and telecommunication platforms with video conferencing capabilities.
Specifications for the new standard are already in place, so developers can begin creating network devices, access points and mobile devices. According to experts, the first WIFi 6E systems will be available in the next two years. Broadcom has already released the first chips supporting 6E, despite the fact that not even a standard has been developed for it yet.
What are the advantages of Wi-Fi 6
Speed boost
The new standard supports 10-bit information encoding – 2 bits more than the previous standard. This means that the data density per wavelength has increased by 25%. The improvements will be noticeable on both the 5 GHz band and the 2.4 GHz band.
| Standard | Number of subcarriers | Bits/symbols | 1SS | 4SS | 8SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 802.11ac | 234 (80 MHz) | × log2(256) | 433.3 Mbps | 1.74 Gbps | — |
| Wi-Fi 6 | 1,960 (160 MHz) | × log2(1024) | 1.2 Gbit/s | 4.8 Gbit/s | 9.6 Gbit/s |
Wi-Fi 6 is capable of transferring data at up to 9.6 Gbps, but in practice it will be more modest: there are simply no networks with this kind of bandwidth today. But even such an increase compared to 802.11ac Wi-Fi will be significant.
CNET has seen speeds increase from 938 Mbps to 1,523 Mbps, an increase of more than 60 percent. With the new routers, even gigabit networks will become bottlenecks, and ISPs will have to upgrade their infrastructure.
Improved handling of multiple clients
Right now, routers can't exchange data packets with multiple devices at the same time, causing them to compete for bandwidth. To avoid confusion, the router queues up the transmissions and the receivers wait for their data packet.
Do I get a router that supports Wi-Fi 6 now?
Products that support the new standard are available now. This includes almost all flagship smartphones, tablets and some laptops.
If you have Wi-Fi 6 compatible gadgets, buying such a router makes sense. The Honor Router 3, Huawei AX3, Redmi AX5 and Xiaomi Mi Router AX1800 are already available. However, they are not yet sold outside of China, and the firmware without localization is unlikely to comfortably use them.
In Russia, solutions with Wi-Fi 6 are offered by Asus and TP-Link, but the prices are biting. For example, ASUS RT-AX56U will cost 12,000 rubles, and TP-LINK Archer AX6000 will cost 19,000 rubles. New technologies are always expensive at the start, so it is better to wait with the purchase of the router until the end of the year. By then there will be more options on the market for the mass consumer.
*The activities of Meta Platforms Inc. and its social networks Facebook and Instagram are banned in Russia.
Which routers support Wi-Fi 6
- Asus RT-AX86U AX5700 Router
- TP-Link Archer AX50 (AX3000) Dual Band Gigabit Wi-Fi 6 Router
- TP-Link Archer AX11000 Next-Gen Tri-Band Gaming Router
- Netgear Nighthawk Tri-Band Wi-Fi 6E Router (RAXE500)
- eero 6 Mesh Router
- eero Pro 6 Mesh Router
This is by no means a complete list of models with Wi-Fi 6, but if you have one of these, keep in mind that you also have a new type of network.
How fast is Wi-Fi 6
In theory, Wi-Fi 6 has a maximum speed of 9.6 Gbps. That's not to say you'll get those speeds, since Wi-Fi 5 offers 3.5 Gbps. But the speeds will still be pretty darn high for a normal network.
You won't get the maximum because of the fact that the measurements are taken in an ideal environment. It's kind of like riding a bike down a hill in a tailwind. In reality, there are many variables, and the main one is interference.. If there are a lot of wireless networks around, the speed will be slower. It will also drop as you move further away from the router. So you can't really talk about real speed. It will be different for everyone, but on average it will be about twice as fast under the same conditions as with Wi-Fi 5.

Not all devices support Wi-Fi 6, but if they do, you can forget about speed problems.
Just remember that your provider is unlikely to be able to deliver anything like that anyway. Therefore, such speeds will be more relevant for local networks and transferring files from one device to another.
And also don't forget that even if you have a 1 Gbit/s plan and 10 devices (smartphones, game consoles, computers, smart TV, etc.) are connected to the router, the speed will be shared between them. And if one computer "takes" 500 Mbit/s, the rest will be left with 500 Mbit/s for everyone. Of course, this is a rough calculation, but you get the gist.
Multiuser MIMO for receiving and transmitting
Expanded 802.11ac in the DL channel, where the access point determines that multipath conditions allow frames to be transmitted over the same channel to different receivers simultaneously by using multiple spatial streams.
802.11ax increases the size of MU-MIMO groups in the incoming stream, enabling more efficient Wi-Fi network operation. Multi-MIMO outbound channel MIMO is a new addition to 802.11ax but is delayed until the second wave (Wave 2).
This is a must know! MIMO 8TXx8RX:8SS provides up to 8 simultaneous spatial streams in both directions.
1024-QAM modulation and extended OFDM symbol length
Symbol OFDM is the basic building block of transmission in Wi-Fi networks. The main characteristics: the size of the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT – Fast Fourier Transform), subcarrier spacing and OFDM symbol length are related, given a fixed channel width. In Wi-FI 6 subcarrier spacing is reduced by a factor of 4, and the duration of the OFDM symbol is increased by a factor of 4.
Provided to increase the Guard Interval (GI) between OFDM-symbols, which reduces the inter-character interference and provides a more stable connection in the premises and in mixed environments – room / street.
Going from 256-QAM to 1024-QAM increases the number of bits carried per OFDM symbol from 8 to 10, which improves data rates and spectrum efficiency by 25%. But, as before, the improvement works in environments where signal strength is high and noise is low. This is because the receiver must decide the modulation level by choosing one of 32 states along each axis (amplitude and phase or quadrature) rather than one of 16 for 256-QAM or one of 8 for 64-QAM.
For example! The level of signal receiving power required to decode a frame in the 80 MHz band, 1024-QAM 5/6, MCS-11, must be at a level of -45 dBm, and this can only be achieved when the receiver and transmitter are close to each other!
Features and differences Wi Fi 6
With Wi Fi 6 router can handle many connections at the same time, send data quickly and provide a reliable connection.
If it is a large enterprise, for example, where the number of devices connected to one network is constantly increasing – Wi Fi 6 will show itself in all its glory.
You get not only fast access to the Internet (downloading and transmitting), but also seamless communication between devices that compete with each other for bandwidth. Adequate operation in a crowded network is something that previous versions of Wi Fi cannot boast.
The Wi Fi 6 standard has become popular not only in manufacturing, but also in the home, especially in homes where there is a smart home system and many devices depend on the Internet.
Thanks to WiFi Alliance technology, the network can work with all devices at frequencies from 1 to 5 GHz.
All versions of Wi Fi are compatible with the IEEE 802.11ax standard. The 2.4 GHz (frequency range) networks are also back, which is less susceptible to interference, but is often crowded because of its greater popularity. Another advantage of Wi Fi 6 is security, thanks to support for the Wi Fi Protected Access-3 encryption standard, making it more difficult to hack into the network.
This certified hardware security protocol anticipates attempts to infiltrate the network and, if it fails to prevent them, alters and encrypts the data so that the information obtained by the intruders becomes useless.
. The new Target Wake Time feature, the ability of devices to schedule communications with a router, is responsible for this. In this way, the activation time of the communication antennas is shortened and therefore less energy is used, which directly increases battery life. This feature is not needed everywhere, but is useful for low-powered, battery-powered devices.
How to get Wi Fi 6 at home
You need to buy a new router that supports Wi Fi 6 and use the latest devices with next-generation connectivity. Alas, updating the software will not help here.
Almost all modern smartphones, laptops, tablets, etc. will already be available with a new version of Wi Fi, the sixth standard will be in them by default. This does not mean that you have to drop everything and run to the store for new devices. As you replace your old gadgets, you will automatically become the owner of the new Wi Fi standard.
But there is an important nuance, if you buy a device with Wi Fi 6, but do not buy a new router, the technology will not work.
It must necessarily support this standard, otherwise you will not get any benefits.
Devices with the new communication standard have just started to appear on the market, and so far are quite expensive, as they are not widespread. However, as time goes by, Wi Fi 6 will take up more and more space. Buying a new device or equipment (whether smartphone or laptop) is already worth paying attention to the markings. The company Alliance puts its logo (label), indicating the specific version of the supported Wi Fi standard.
Now routers that support Wi Fi 4 and Wi Fi 5 are more affordable, so they are common. But without Wi Fi 6, you'll have a hard time maintaining a properly loaded wireless network and creating a smart home. For now, Wi Fi 6 is optional, but already desirable.
Crowds and neighbors are no hindrance to Wi Fi 6
Wireless access points have one unpleasant feature: if you connect a lot of equipment to them, the speed sometimes drops a lot. This is especially critical for crowded places like airports, shopping malls, hotels, and even offices. Wi-Fi of the previous generations in such conditions works very slowly. In the case of the "six", the developers have provided a number of technologies that speed up data transfer and reception in such scenarios. For example, Intel claims at least a fourfold increase in speed in congested networks.
Wi-Fi 6 will improve connectivity in public places, apartment buildings, and networks with a large number of gadgets.
Wi-Fi 6 improves speed and signal stability by dividing the wireless channel into multiple subchannels. Any of them transmits information that is specific to a particular device. This feature is called Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA).
Improved multi-user MU-MIMO technology allows not only to simultaneously broadcast a signal over the air, as it was implemented in Wi-Fi 5, but also to receive it. Even two sixth standard routers placed next to each other can operate on the same channel without interfering with each other. The secret is that each access point ignores the "alien" signal, preferring only its own.
What happens to Wi-Fi next?
Qualcomm said it's starting work on the next generation of Wi-Fi. They've already introduced an official technical name for it – 802.11be. The upcoming technology will please with such innovations:
- the maximum data transfer rate will increase to 30 Gbps;
- there will be a 6 GHz band in addition to 2.4 and 5 GHz;
- The number of simultaneously connected devices with CMU-MIMO technology will increase;
- amplitude modulation will increase from 1024 to 4096 bits to improve the information content of the radio signal.
The mass introduction of Wi-Fi 7 is supposedly planned for 2024. In the next four-plus years, we will experience all the benefits of Wi-Fi 6, the adaptation of which has just begun.
Read More: