Important! The standard band is subdivided into 3 independent channels, providing operation of three grids. Products released in this class are certified by WECA (international organization).
- Basic and additional Wi-Fi standards – differences and features
- Wi-Fi standards – what are they and who sets them
- What is a Wi-Fi signal frequency
- What the frequency affects, which are allowed in Russia
- What frequencies are allowed in Russia?
- How do I change the frequency of my WiFi router?
- 2.4 GHz
- How do I check if my device works on 5 GHz?
- Conclusions
Basic and additional Wi-Fi standards – differences and features
For more than twenty years, there is a technology of wireless data transmission, in which the standards of wi-fi are used. They differ significantly in speed of operation, constantly used for cell phones, laptops, personal computers and tablets.

Wi-Fi standards – what are they and who sets them
The original Wi-Fi standards were not labeled in any way. They emerged in 1996 and were in use for three years. Packets of information were being downloaded and uploaded at a speed of about 1 Mbit/s, but at that time portable devices were out of the question, and Internet pages "weighed" no more than 20 Kb.
Initially, the new technology was not appreciated and was used for certain purposes:
At the time, only a few had cell phones, and the notion of data transmission without cables only became common a few years later.
The lack of popularity did not affect the development of the protocol. Manufacturers created devices that increased the power of the module when transferring information. The first Wi-Fi standards began to operate at double the speed of 2 Mbps. The association of several companies began to develop a new technology that would be able to provide higher throughputs.
Important! The development of standards are officially engaged in the Institute of Electronics and Electrical Engineering (IEEE). Specialists from this nonprofit organization help companies produce compatible devices.

What is a Wi-Fi signal frequency
Each modem transmits digital data streams from one point to another point or points. A signal is an electrical pulse with 2 basic characteristics – Wi-Fi wavelength and frequency. Since wireless technology belongs to the category of radio waves, it works according to similar laws as light.
Wi-Fi frequencies are the number of periods of alternating current per second, in other words, the number of waves going in a particular place in space. The voltage frequency determines the total length of the radio wave.
Other bands are found – 0.9, 3.6, 10, 24 GHz. They are rarely used when the normal frequencies are busy, and only if the user has a license for them. Each frequency has individual properties. And even a weak signal can travel great distances, but in such a situation a special antenna or Wi-Fi gun will be needed to amplify the pulse.
To communicate using wireless technology, it is necessary to have an access point (equipment) and at least 1-2 Wi-Fi clients. Sometimes the connection is point-to-point, i.e. users communicate directly. In this case, the standard provides a significant degree of freedom in the choice of adapter settings and radio channel.
What the frequency affects, which are allowed in Russia
The frequency of the network signal directly affects the wavelength and other characteristics:
- Absorption or Penetration: the best properties are shown by a higher frequency. In buildings with many partitions, thick walls, coatings, this is a significant indicator.
- Reflective properties – the ability of the signal to pass through soft structures and reflect off surfaces. In this case, the quality of communication will be lower.
- Information density: a high range can process and transmit more information.
- Overcoming obstacles: high frequency but short wavelength wi-fi is more difficult to circumvent physical obstacles. Therefore, in residential buildings prefer to use the lowest possible modem operating parameters – 2.4 GHz.
- Attenuation is a natural reduction in the level of the electrical pulse of Wi-Fi. Its strength actively decreases at high frequency.
Thus, the main thing that determines the channel width is the quality and speed of the Internet.
What frequencies are allowed in Russia?
Each Wi-Fi frequency has individual characteristics and uses. For example, low-frequency signals cope better with obstacles in the way, but have a high level of interference and noise. That's why it's important to be guided by your specific tasks and current situation when choosing.
There are many choices in total – 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, 5.0 GHz, 10 GHz, etc. At the same time permitted WiFi frequencies in Russia only two – 2.4 and 5.0 GHz. These are the frequencies that can be used without a license. Most routers support 2.4 GHz, but recently there have been routers that allow you to select this setting yourself.
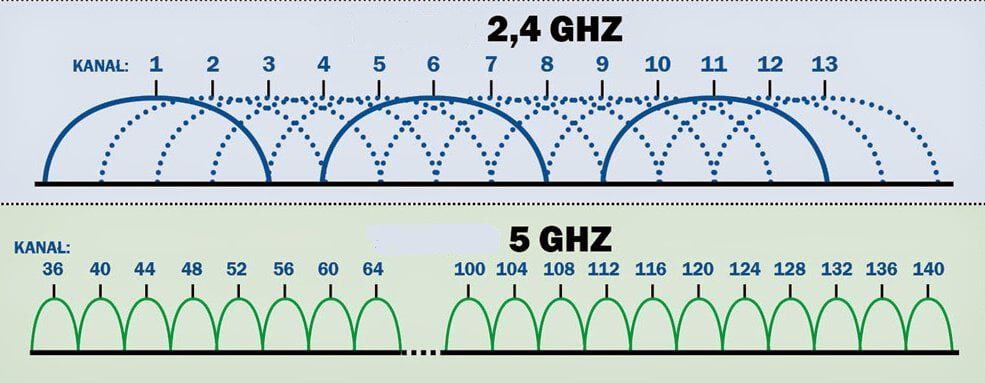
There is one more thing to be aware of – the range of frequencies that are available in RF. So, the frequency spectrum of 2.4 GHz implies a conditional division into 13 channels. Each of them is characterized by a certain range of operation. For example, the 1st channel transmits between 2.401 and 2.423 GHz. As for the 13th channel, the range from 2.461 to 2.483 works here. The situation is similar for the other channels.
A slightly different approach to the Wi-Fi frequency range is used for the 5 GHz. Unlike the last variant, here the "higher" channels are used – from 34 to 180 (some of the channels drop out of the list). Each variant is characterized by its own range – from 5.17 to 5.905. In Russia, the indoor band used is from 5150 to 5350 MHz.
How do I change the frequency of my WiFi router?
When buying, you need to pay attention to the frequency at which the Wi-Fi router works. Most of the devices that are installed in homes and lying on store shelves function on 2.4 GHz. Recently, a new type of router that supports two modes of operation – 2.4 and 5 GHz – has been gaining popularity. This solution allows the customer to choose the mode of operation taking into account the current situation and requirements for wireless network quality.
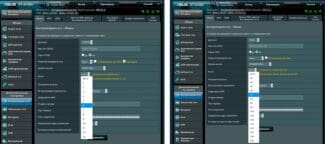
Knowing how to change the frequency of the WiFi router, you can adjust this parameter and achieve better communication quality. Approaches to changing the parameter are individual for each router, so let's take TP-Link Archer C5 as an example. The device supports two frequencies, which allows you to create as many WiFi networks. One will work on 2.4, and the second on 5 GHz. All settings are made through a PC or another device connected wirelessly.
To change the frequency of the router, open any browser and type 192.168.01 into the address bar.
You can type the router address tplinkwifi.net. After that, enter into the configuration panel with the standard data (if they have not changed) – twice admin. You can get the necessary information by looking at the bottom of the WiFi router.
Once you have made the changes, check the signal strength. Since changing some settings may cause other settings to drop or increase.
2.4 GHz
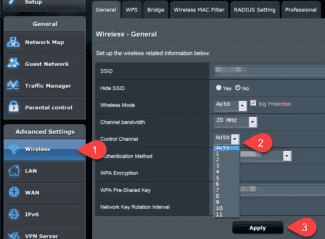
Setting up the first WiFi frequency (2.4 GHz) begins by going to Wireless 2.4 GHz. Next, do the following:
How do I check if my device works on 5 GHz?
It's not hard to do. On a laptop (e.g. Windows 7), go to "Start/Control Panel/System and Security/System/Device Manager" and evaluate the network adapters. If the name or properties of the adapter indicates supported specifications, such as "802.11 a/b/g/n", then your laptop supports 5 GHz WiFi. But that doesn't mean it supports 802.11ac, either. It's a new standard, and not all equipment works with it. But in any case it's not bad – you can solve the problem with the home network at a relatively low cost, especially if you live in an apartment building.
But if it says "802.11 b/g/n" in the adapter properties, it means that your laptop, unfortunately, can only work with WiFi 2.4 GHz.
To check if your Android smartphone supports 5GHz WiFi, you need to go to Settings and then select: Wi-Fi/Extended Settings/Wi-Fi Frequency Range. If the system supports 5 GHz, you will see the corresponding item in the menu.
Conclusions
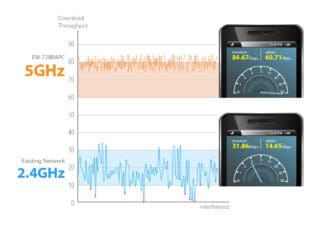
To summarize the above, 5 GHz WiFi has clear advantages over 2.4 GHz devices. If your WiFi network terminators support 5GHz 802.11n WiFi, then it makes sense to consider replacing your 2.4GHz router with a 5GHz one. By doing so, you can rid your WiFi network of the factors that interfere with it (interference from other wireless devices and appliances). The absence of interference and the greater number of channels will increase the data transfer rate of your WiFi network. Replacing the router to switch to a different frequency range in the 802.11n standard will cost relatively little money.
Those who would like to ensure the highest possible speed of data transfer over WiFi-network,
can be recommended to opt for the new standard 802.11ac. For connoisseurs of the latest technology, the higher cost of equipment (5 GHz WiFi router, 5 GHz WiFi antenna) compared to the 802.11n specification will not be an obstacle. Especially since the cost of devices tends to go down with the development of technology and cheaper production. At the same time it is necessary to remember that all terminal devices must be compatible with the access point, i.e. have a common standard.
Read More: