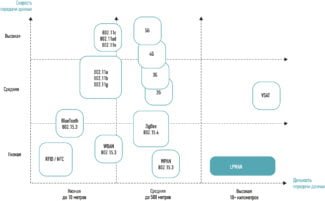
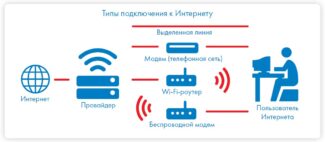
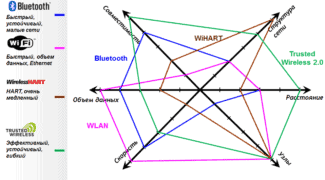
Li-1st was created as a base for pilot projects of Li-Fi developers.

Li-Fi technology (ultra-fast Internet on LEDs): overview, description, device and prospects
Li-Fi is a new data transmission technology that will revolutionize business in the future, creating opportunities ripe for use today and preparing to become a multi-billion dollar industry by 2022. Developments are underway to achieve 1Gbps speeds that will surpass ultra-fast broadband.
The term Li-Fi was coined by Professor Harald Haas and refers to a method of transmitting information using light that provides high-speed bi-directional mobile communications similar to Wi-Fi. It can be used both to offload existing networks operating on radio frequencies and to increase their bandwidth.
Ultrafast communication uses the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. This distinguishes this technology from such an established form of wireless communication as Wi-Fi, which uses traditional frequencies.
In Li-Fi, data is transmitted by modulating the intensity of light, picked up by a photodetector, and the signal is converted to electrical. The modulation is done in such a way that the human eye cannot perceive it.
Li-Fi high-speed optical communication technology belongs to the category of wireless communications, which, in addition to visible light, includes infrared and ultraviolet. Its uniqueness lies in the use of existing lighting networks.

Li Fi – ultra-fast internet on LEDs
When a constant current is supplied to the LED lamp, it emits a steady stream of photons of visible light. When the current is reduced or increased, the brightness also changes. Since LED lamps are semiconductor devices, the current and therefore the optical output can be modulated at a very high rate. It can be picked up by the photocell and converted back into electrical current. Luminance modulation is invisible to the human eye and is as convenient as radio. With this technique, the LED lamp is capable of transmitting information at high speed.
Radio-frequency communication requires electrical circuitry, antennas and complex receivers, while Li-Fi-technology is much simpler. It uses direct modulation techniques similar to those used in inexpensive infrared communication devices such as remote controls. The use of infrared communication is limited due to health and safety regulations for the eyes, while LED lights have a high luminous intensity and exhibit significant speed.

What is LiFi?
Li-Fi (light fidelity) is probably the lesser known term of the two (or maybe you haven't heard of it at all before). It is a form of wireless communication in which the information we send and receive is not sent through waves, but through light, and is based on LED lighting.

This technology has some advantages over WiFi. For example, it avoids electromagnetic interference between devices, which is one of the most frequent phenomena in WiFi. Another benefit it can develop is maximum speed.
Taking advantage of visible light, in some studies, developers have been able to achieve speeds of 10 Gbps. This allows very fast transmission of information through optical signals, which is much faster than what WiFi technology currently offers. Remember that no matter how fast your connection is, WiFi has a limit, according to which under favorable conditions you can get a maximum of about 300 Mbps.
With LiFi technology, we will be able to connect to the Internet using the lights of lamps, streetlights or LED TVs. In addition to being cheaper, safer and faster than WiFi, this technology does not require a router. Just point your cell phone or tablet at the light bulb to get online.
Differences from WiFi
The most obvious difference you already noticed when we explained what LiFi is. The technology completely changes the way data is transmitted, using light signals through LED lights, while WiFi uses 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz radio frequencies.

Another difference has to do with the distance the wireless signal can cover. WiFi can cover tens of meters, while LiFi has a much more limited range. For example, it is higher than Bluetooth, but we will talk about 10 meters in diameter as a reserve. Obviously, since the technology is based on transmitting light signals, it also does not accept obstacles, so the assumed theoretical maximum range can be further reduced.
As we said before, one of the major advantages of LiFi is the lack of interference. WiFi is very susceptible to problems when there are many devices nearby or when many neighbors are using the same channel. With LiFi, there is no direct interference with other devices, although there are problems with light. For example, the technology will not work in direct sunlight, which would severely limit its use.
LiFi technology is currently very limited, which is another significant difference from widespread WiFi. LiFi is mostly used in airlines, underwater operations and nothing more. This technology is not intended for mass domestic use, as in the case of WiFi.
From a security point of view, LiFi deserves attention. WiFi networks can be penetrated over a greater distance, while LiFi requires direct visual contact because it emits light. While a wall or obstacle is an obstacle to coverage, it also prevents information from passing through, making it a complete firewall.
Is Li-Fi much faster than Wi-Fi
In the promising future, Li-Fi technology will offer network speeds a hundred times faster than the Wi-Fi most users are accustomed to. Scientists in physics have achieved that the connection speed in the laboratory of the new development has reached 224 gigabytes per second, which is comparable to downloading 18 1080p movies.
In real life, however, the records are much smaller: during the test in Tallinn, the testers achieved a speed of 1 Gigabyte per second. But it is also more powerful and faster than Wi-Fi. In terms of radio wave frequency, Wi-Fi is about 5 GHz. The visible light used in Li-Fi, on the other hand, travels at about 500 THz, which means 10,000 times that of Wi-Fi.
Applications
Li-Fi is planned for military applications, Internet stuff, underwater communication and as a tool in information security. Maybe the technology will find applications in everyday human life in the near future.

Military Industry
The coverage of Ly-Fi is limited to a small illuminated area. For example, such as a tent. Similarly, it restricts unauthorized access to sensitive information under designated conditions and in an area where cell phones and smartphones are not used. Such a location is an ammunition depot.
Underwater communication
Li-Fi is also used in an underwater Internet connection. The light propagates through the water. The radio signals from Wi-Fi, on the other hand, do not penetrate the water. This instantly changes the way underwater vehicles communicate.
Internet of Things
Li-Fi has a shorter range than Wi-Fi. Therefore, the former technology is more responsible for information preservation. This specification becomes useful in areas where a lot of sensitive data is handled. For example, in the field of health care.

Information security
In the future, it is likely that every device will inevitably be connected to the Internet. Most likely, the Vi–Wi-Fi is likely to struggle with this task. Given the periodic growth in demand for communication devices, Li–Fi technology stands a good chance of being adopted sooner rather than later. After all, Li–Wi-Fi combines lighting and information transfer.
Today, Li-Fi is only improving and spreading to the domestic structures of the state. Most likely, the technology will be offered to consumers in the future as an alternative to the Wi-Fi connection.
Read More: