As a result, the bar serves many more customers per unit time. Four hands is not just for you. Indeed, WiFi 6 is able to perform 4 times faster than WiFi 5 in high traffic environments where there are a large number of devices connected to the WiFi network in a limited area.

- Is WiFi 6 or 5G? And if 5G, which one?
- Wi-Fi 6
- 5 GHz is one of two bands for Wi-Fi
- Why some Wi-Fi networks say they are "5G"
- Part 3: Is 5G Wi-Fi faster than 2G Wi-Fi?
- Part 4: Can I use both frequency settings on the same router?
- Part 3: Should I buy a 5G router now?
- Part 4: What 5G routers are on the market?
- HUAWEI 5G CPE Pro:
- Mi AIoT Router AX3600:
- TP-Link Archer C6 Gigabit MU-MIMO Wireless Router:
- STEP 2: Setup
- TP-Link
- Again about 5G.
- So what is WiFi 6?
- Interaction between Wi-Fi 6 and 5G:
- Do 5G-enabled routers exist
- 5G vs. home Wi-Fi
- How do I know if my laptop supports 5 GHz Wi-Fi?
- What to do if there is no 5 GHz support?
- Is your Wi-Fi router ready for 5 GHz
- Update your Wi-Fi driver software
Is WiFi 6 or 5G? And if 5G, which one?
Modern wireless networks are gradually approaching wired networks in data transfer rates and other important parameters and can be used as the main technology for building the telecommunications infrastructure of companies and corporations. But what wireless technology to choose to create a corporate network – Wi-Fi 6 or 5G?
Until recently, there was no alternative to Wi-Fi technology for providing an office or manufacturing facility with wireless Internet access. And the new Wi-Fi 6 standard (802.11 ax), compared to Wi-Fi 5, is a big step forward. It beats its predecessor in terms of bandwidth and the ability to communicate with multiple devices at once. And, in general, it is more reliable.
However, as an alternative to this technology, as Zeus Kerravala (Zeus Kerravala), founder and chief analyst at ZK Research, one might consider a 5th generation cellular connection. It all depends on the needs of the specific company and the network scenarios in each individual organization.
An important milestone in the life of 5G came on January 27, 2020, when the U.S. Federal Communications Commission authorized the use of 150 MHz bandwidth from the 3.5 GHz band (3550 MHz to 3700 MHz) for the commercialization of wireless service provider without any restrictions. Under the new rules, wireless carriers with these frequencies can deploy 5G mobile networks without having to purchase spectrum licenses. The regulator's decision made 5G networks an "enterprise reality," making it possible to create private 5G networks, for example, to work inside a single building or an industrial site.
The U.S. is the largest IT market in the world and the commission's decision has undoubtedly spurred the development of 5G technologies.
In Russia, where the most popular frequency band for the construction of 5G networks (from 3400 MHz to 3800 MHz) is occupied by military systems, cellular operators can only dream of such a decision of the regulator…
Wi-Fi 6
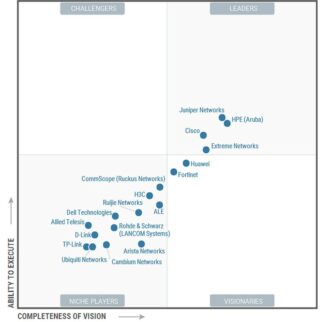
Wi-Fi 6 is a mature technology, supported by products from a number of well-established network equipment vendors. Among the leaders in the relevant Gartner Magic Quadrant are familiar faces, Cisco, Juniper, Aruba and Extreme Networks. Putting Huawei in the "visionaries" category may come as a bit of a surprise. But judging by the void in the upper left quadrant, new leaders will emerge from among the visionaries.
As mentioned above, the Wi-Fi 6 standard was a huge step forward from its predecessor, as it was augmented with technologies from the cellular world, such as OFDMA and MU-MIMO, to improve spectrum quality. However, this hasn't solved a fundamental problem: Wi-Fi networks operate in an unlicensed frequency band, making them susceptible to interference. That's why no matter how well the facility where this standard is to be deployed was surveyed and how well the architecture of the future network was thought out, problems with reliability of its functioning are inevitable in difficult conditions. In other words, Wi-Fi 6 technology does not allow to completely avoid the typical situation for a wireless LAN, when suddenly something stops working well. Although, thanks to improvements in technology, such outages will occur less frequently in Wi-Fi 6 networks than in previous generations.
The main advantage of Wi-Fi technology is its very low cost, especially "on the client side", laptops and IoT devices will cost not much more than Wi-Fi 5 devices.
All of this, along with the ubiquity of the technology, makes networks based on it preferable for non-critical applications. However, says Zeus Kerravala, caution should still be exercised when using Wi-Fi networks in mission-critical areas.
5 GHz is one of two bands for Wi-Fi
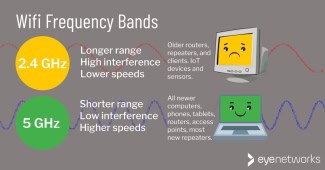
Wi-Fi can use two frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. 5 GHz is a newer standard. It gained widespread adoption through the 802.11n Wi-Fi standard, which was first published back in 2009. It is still part of today's Wi-Fi standards, such as 802.11ac and Wi-Fi 6.
The 5 GHz Wi-Fi is great. It offers more non-overlapping channels, making it less congested. This is excellent in places with many Wi-Fi networks, such as apartment buildings where each apartment has its own router and Wi-Fi network. 5 GHz Wi-Fi is also faster than 2.4GHz Wi-Fi.
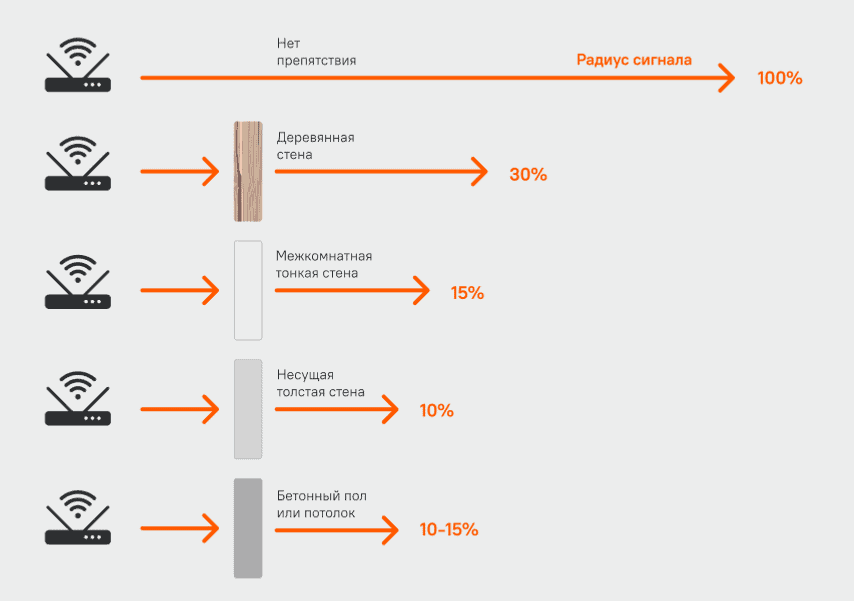
But despite slower speeds and increased congestion, 2.4GHz Wi-Fi still has its advantages. 2.4 GHz covers a larger area than 5 GHz, and it passes through walls better because of the length of the radio waves. The shorter 5 GHz radio waves provide a faster connection, but they can't cover the same area.
If you have even a fairly advanced router, it's probably a dual-band routerthat supports 5 GHz Wi-Fi and 2.4 GHz at the same time.
On the Internet, you might see users use the term "5G Wi-Fi" to refer to 5GHz Wi-Fi, but that is incorrect. It stands for "5GHz Wi-Fi."
Why some Wi-Fi networks say they are "5G"
To make things a little more confusing, people sometimes refer to their networks by names such as "My Network" and "My Network – 5G." It's misleading, but it wasn't too confusing until the advent of the 5G standard in mobile networks. Here, "5G" is simply short for "5 Ghz."
This is because Wi-Fi routers that support 5 GHz Wi-Fi can be configured in several different ways. These routers can operate on 2.4GHz and 5GHz networks simultaneously, which is useful for older devices that only support 2.4GHz, or larger areas where devices can go outside of the 5GHz band but still remain in the 2.4GHz band.
If both Wi-Fi networks are named the same – for example, if both your 2.4GHz and 5GHz networks are named "My Network" – every connected smartphone, laptop, or other device will automatically switch between networks, choosing the 5GHz or 2.4GHz network if necessary. Either way, that's the goal. In fact, many devices don't do it properly and just connect to the 2.4 GHz network, or they may try to connect to the 5 GHz network and fail.
This is why users often configure their routers to have two separate Wi-Fi network names. One might be called "My Network – 2.4G" and the other might be called "My Network – 5G." Both are placed on the same router, but one operates at 2.4 GHz and the other at 5 GHz. You can then choose which network you want to connect your devices to.
Part 3: Is 5G Wi-Fi faster than 2G Wi-Fi?
5G is faster than Wi-Fi That's the only thing that works on 2.4 GHz radio frequencies? Although 5GHz radio frequencies theoretically provide faster Internet speeds, this is not always the case. 5G Wi-Fi routers can only provide fast Internet speeds in a small area. For example, if you only want to work in one room and all your devices are also in the same room, 5GHz radio frequencies would be the best choice for you.
However, if we are talking about an entire building or a relatively large space, the 5 GHz radio frequency cannot provide the desired Internet speed, mainly because it can only generate shorter waves. Then 2.4 GHz radio frequencies will prove to be a better option. When your Wi-Fi router has 2.4 GHz radio frequencies, it will automatically generate larger waves and provide optimal Internet speeds for the entire building.
So, as far as speed is concerned, choosing the right radio frequency will largely depend on your network requirements.
Part 4: Can I use both frequency settings on the same router?

Since both radio frequencies meet different network requirements, many people also want to know if the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies can be set simultaneously. Fortunately, the answer is yes! Today, you can buy a dual-band router that allows you to transmit both frequencies at the same time.
After setting up such routers, you will see two different SSIDs (with the same name) on your devices. The only difference between the two networks will be that they transmit the Internet on different frequencies. This means that you will be able to choose the right frequency according to your current network requirements.
For example, if you are sitting in the same room with a Wi-Fi router, you can choose the 5 GHz frequency and enjoy fast & uninterrupted internet speeds. However, if you are in another room of the building, you can easily switch to the 2.4 GHz radio frequency and surf the Internet at optimal speed.
Note: Some of today's Wi-Fi routers even have an auto-switching feature between 2.4GHz and 5GHz, making it easier for the user to get the best speed for their current environment.
Part 3: Should I buy a 5G router now?
Buying products that support upcoming technological advances is always the best option. But it also depends on the circumstances. Because 5G routers are new to the market, the price is moderately higher than a regular 2.4 GHz router. However, because of its high speed and low likelihood of interference, fewer devices now use it. It may be worth its price for certain conditions. If you live in a place where the network is often disrupted by high utilization of too many devices, a 5G router may be the solution. A 5G router will also suit those who frequently participate in high-bandwidth online activities such as gaming, video conferencing, and video streaming.
That's why it would certainly be a good investment. Considering that in places far away from 5G cell towers, this would not be the right choice because long distances are not suitable for 5G.
Part 4: What 5G routers are on the market?
HUAWEI 5G CPE Pro:
The Balong 5000-based HUAWEI 5G CPE Pro supports both 4G/5G and fixed-line networks. It provides a more stable and faster Wi-Fi connection, allowing 4K video streaming without latency. The Balong 5000 is the world's first 7nm multi-mode 5G chipset, offering download speeds of up to 2.3 Gbps. Designed to be lightweight and portable. This router can be easily carried anywhere and gives you more free access to networks. It has 8GB of RAM and 2 Ethernet ports.

Mi AIoT Router AX3600:
The Mi AIoT AX3600 router offers two 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands, each with 802.11ax technology and no mutual interference. It features a 6-band high-performance external signal amplifier that provides reliable coverage without the fear of wall-crossing. The two bands provide combined dual-band wireless speeds up to 2976 Mbps. The 2.4 GHz band is associated with longer transmissions for better coverage and better wall penetration. The 5 GHz band offers low interference and high speeds for smooth HD video playback and smoother playback of large online games. It has 512MB of RAM and 4 Ethernet ports.

TP-Link Archer C6 Gigabit MU-MIMO Wireless Router:
Based on 802.11ac Wi-Fi technology, the Archer C6 supports 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands. The 2.4 GHz band delivers speeds up to 300 Mbps, which is ideal for everyday tasks such as email and web browsing, while the 5 GHz band delivers speeds up to 867 Mbps, which is ideal for streaming HD video and online gaming without latency. The bands provide a combined speed of 1,200 Mbps. This router contains 5 high-performance antennas – 4 external antennas and 1 internal antenna for Wi-Fi coverage throughout the home. It has 128 MB of RAM and 5 Ethernet ports.
STEP 2: Setup
Now we come to the question of how to switch and configure a 5GHz router. Again, routers have different firmware because they are released by different manufacturers. Also, the operating systems of the same manufacturer may be different due to different hardware versions of the routers. I have tried to list all possible options. But before we begin, let me briefly talk about certain 5 GHz network parameters that you might encounter:
- Mode or standards – Three popular standards can be found:
- N– Also works at 2.4 GHz. Has the lowest speed in the 5GHz range.
- AC . – 5th generation Wi-Fi. Has a fairly high speed. In the average of 400 to 500 Mbit per second.
- AX – 6th generation Wi-Fi. The highest speed and high reliability. Read more…
- WPA – The most unreliable and old method. It is used only on old devices.
- WPA2 – is the most popular and sufficiently reliable.
- WPA3 – is only supported by Wi-Fi The most secure.
TP-Link
In newer routers, you need to go to Advanced Settings – Wireless Mode – Configuration…. Here you can see two or even three networks (some models have support for two 5 GHz Wi-Fi). To turn off Wi-Fi broadcasting, uncheck the "Enable Wireless Broadcasting" box.
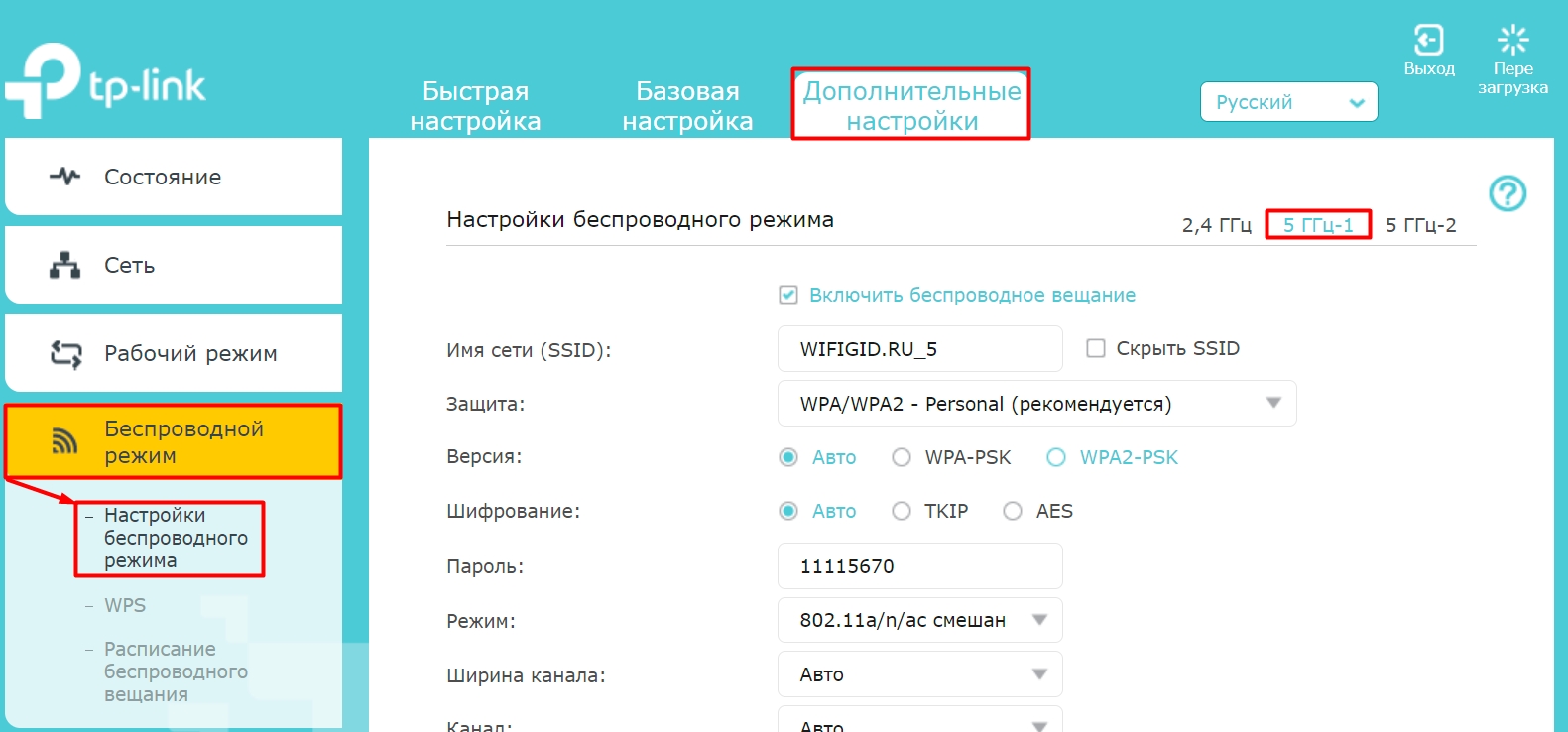
On some new models, "Smart Connection" mode is enabled by default – when there is only one network on the air, and the router itself chooses which wave to connect devices to. That is, both frequencies are kind of paired. You can leave this configuration or turn it off to put the router in dual-band 2.4 and 5 GHz mode. The two wi-fi will then begin to display below, one of which you can turn off if necessary.
Again about 5G.
So, 5G is not so much for ordinary users as it is for business and industry. Fifth-generation networks enable the active development of the Internet of Things. And this technology will make it possible to build smart cities, to put robot cars on public roads. The Internet of Things will give industry digitalization, robotics, big data analytics, and predictive forecasting of emergency situations.
5G makes it possible to connect hundreds of thousands and millions of devices to a single network, to work with IoT in real time.
The peculiarity of 5G is the need to create a large number of access points. If there are not enough of them, the connection will not be of very high quality – the signal loss in the case of the fifth generation networks is quite high even at a relatively small distance from the access point.
In addition, telecom operators can launch different 5G networks designed to perform specific functions. The same operator, using the capabilities of fifth-generation networks, can offer a network for subscribers and a network for IoT devices in a particular area that will not overlap. And there could be many more such networks than two.
The 5G infrastructure is being actively deployed in a number of countries, including South Korea, China, and the United States. The technology is gradually being introduced in Russia as well.
So what is WiFi 6?
This wireless standard is written about less often than 5G, although it is also important for industry and business (WiFi 6 is also not a particularly significant technology for ordinary users).
In general, this is the latest version of the 802.11 wireless standard, referred to as 802.11ax. It is backwards compatible with 802.11ac and allows you to transmit data more efficiently and with less power.

If you are wondering where the WIFi 5 standard went, don't worry, the Wi-Fi Alliance decided to update the wireless network types to make it clearer who is who. The previous standard, 802.11ac, has thus been dubbed WiFi 5.

The standard is scheduled to be approved in the third quarter of 2019. Although some network device manufacturers already offer equipment that supports the new type of network.
How is WiFi 6 better than previous standards? The main advantage of this technology is the ability to work simultaneously with a very large number of devices.
The capabilities of WiFi 6 can be clearly illustrated. Imagine a popular bar and the only bartender at the counter. He works well but he can't take all the orders because he only has two hands, so the number of simultaneous tasks is very limited. When there are few customers, everything is fine. But at peak hours, customers have to wait a long time for their beer or cocktail.
Now let's imagine that our bartender replaced Goro from Mortal Combat. Only instead of decades of pumping killer skills, he devoted time to the art of serving customers in bars. Plus, instead of two pairs of hands he has four.

Interaction between Wi-Fi 6 and 5G:
5G networks have some limitations, such as the high cost of indoor coverage and the inability to upgrade older devices.
Wi-Fi 6 technology addresses the challenges of high bandwidth, high capacity and low latency in indoor coverage scenarios.
These advantages make Wi-Fi 6 suitable for key applications requiring high bandwidth and low latency, such as VR/AR, 4K/8K content and automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
Thus, for enterprises, Wi-Fi 6 and 5G networks can interact with each other in most scenarios in synergy mode to achieve an optimal access and coverage ecosystem.
For some industrial scenarios – such as oil fields, coal mines and AGVs – 5G has unique advantages, including low latency and wide area coverage.
In scenarios with very high street density (such as plazas and stadiums), 5G network capacity will not always be able to meet user access requirements without adding a significant number of base stations.
In this case, high-density Wi-Fi 6 access is a cost-effective solution for large numbers of users and high-density terminals.
Do 5G-enabled routers exist
In the context of 5G WiFI, the very name of the technology is an acronym, not an Internet speed or connection type. Routers work from the cable connected to them, while repeaters work from the reception of the Wi-Fi signal. A variation on how a router with 5G (mobile technology) can work is to connect through another device.
The confusion with the names arose when configuring routers for the two streaming technologies. On the settings page, the user will see network types such as: "My Network" and "My Network – 5G". But in the latter case we are talking about 5Ghz connectivity.
For example, Huawei has introduced a 5G router, sixth generation and data rates of up to 11 Gbps.
5G vs. home Wi-Fi
Despite the high speed of mobile Internet, 5Ghz for routers – will provide a more stable and faster type of connection. The downside of new routers that will support this bandwidth is having eight antennas. As of 2019, several models have been released that are designed for online video games.
- Thirty channels for connectivity. Provide simultaneous operation of 15 devices;
- Compatible with all new devices, including computers and TVs;
- MU MIMO. Supports eight spatial streams that are designed for stable network operation;
- Beamforming – "directional beam" function. If the signal, overcoming an obstacle, was lost – the feed will be redefined and a failure will be detected.
One of the reasons why the phone does not see 5g wifi is that the device is outdated and does not support the new types of signal. Such a problem can only be solved by buying a new device or changing the router settings.
How do I know if my laptop supports 5 GHz Wi-Fi?
First of all, look at the specifications of your laptop, preferably on the official website. If it says 802.11ac, dual-band Wi-Fi, or just says 5GHz, then you're good.
You can also go to Device Manager, and open the Network Adapters tab, right-click on the Wireless Adapter, and select Properties. Next, go to the Advanced tab, and there should be information on 5 GHz support.

The very inscription "Dual Band" in the name of the Wi-Fi adapter indicates that there is support for dual band networks.
On my laptop, there is no such support, and in the Device Manager there is no information about it.

And if you have turned on a dual-band router and your laptop only sees one network, it is clear that there is no support for 5 GHz networks.
What to do if there is no 5 GHz support?
Just connect to 2.4 GHz networks. And if you just need to switch to a new frequency and your laptop does not support it, then you can buy an external USB Wi-Fi adapter that supports the 5 GHz frequency. I wrote more about these adapters here. It is true that this solution is only possible for laptops, and desktop computers. If you have a mobile device, you will have to put up with it.
The new frequency does not have any special and serious advantages. And the transition to the new standard will eventually happen automatically, even unnoticed by us. As I wrote above, the exceptions are places where it is simply impossible to use wireless Internet on 2.4 GHz, due to the large amount of interference.
Is your Wi-Fi router ready for 5 GHz
Be sure to check if your Wi-Fi router supports 5G. You may have a router that only supports 2.4 GHz bandwidth.
Take a look at the Wi-Fi router's box where you can find this information. If your router supports 5GHz but isn't transmitting a 5G WiFi signal, you may need to turn on 5GHz services. To enable 5GHz Wi-Fi on your router, you'll need to contact your Internet service provider. You can also enable 5GHz Wi-Fi on your router yourself. All you have to do is read the manual.
Update your Wi-Fi driver software
The drivers at – is the software that is responsible for the proper functioning of your Windows PC hardware. In order to use your PC hardware, you must update the appropriate drivers.
To manually update the driver, you can launch the Device Manager window on your PC. In the Device Manager window, go to the "Network adapter" section, right-click on the wireless driver and select "Update driver" from the context menu. You can now follow the instructions on the screen to update the Wi-Fi driver.
After successfully updating the driver, don't forget to restart your PC. Now check if the updated driver software supports the 5 GHz Wi-Fi bandwidth.
We hope this article helped you to enable 5GHz Wi-Fi on Windows 10/11.