Alexey :
HackWare.ru
Router Scan scans networks and collects information about routers, including Wi-Fi network passwords.
In order to find out your neighbor's Wi-Fi password you need to scan the whole IP range of your neighbor's ISP. If you don't know what your neighbor's ISP is, you need to scan the IP range of your locality. It will take a long time and the result is not guaranteed – the neighbor's router may be well protected and even if you scan it, you won't be able to get the password; also he may be behind NAT (the technology that allows several users to share the same IP), in this case we will not even be able to scan his router.
Router Scan community members share their scan results with the 3WiFi service, which puts them on a handy map. That is, right online you can find information about:
Using 3WiFi is free. To not only see the access points in the database, but also their passwords, you must log in to the site. You do not even need to register for this.
Guest account with limited rights (only for Router Scan community members):
Searching the Wi-Fi password database
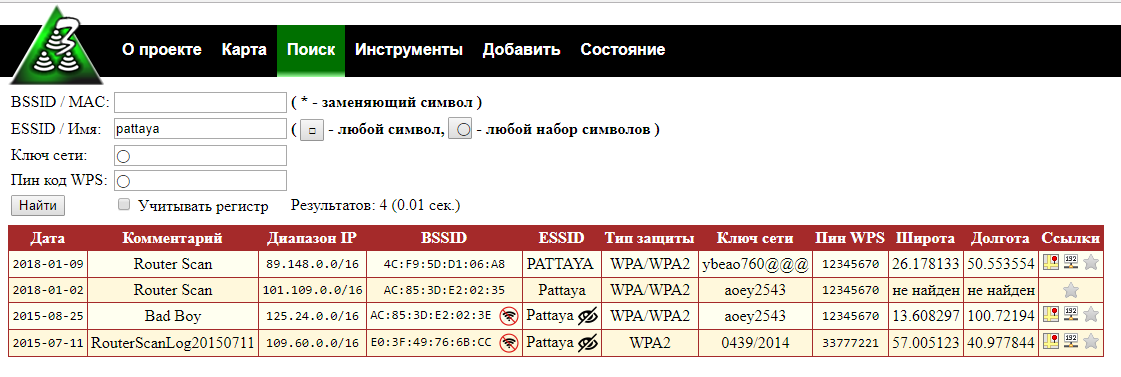
On the search page, you can search for access points by:
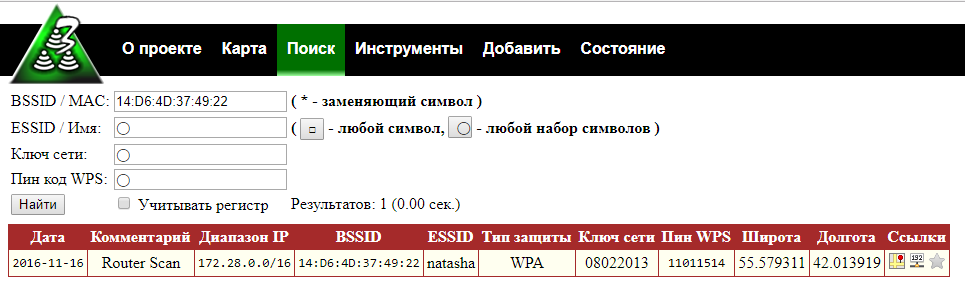
Search by BSSID using the wildcard 14:D6:4D:37:49:*
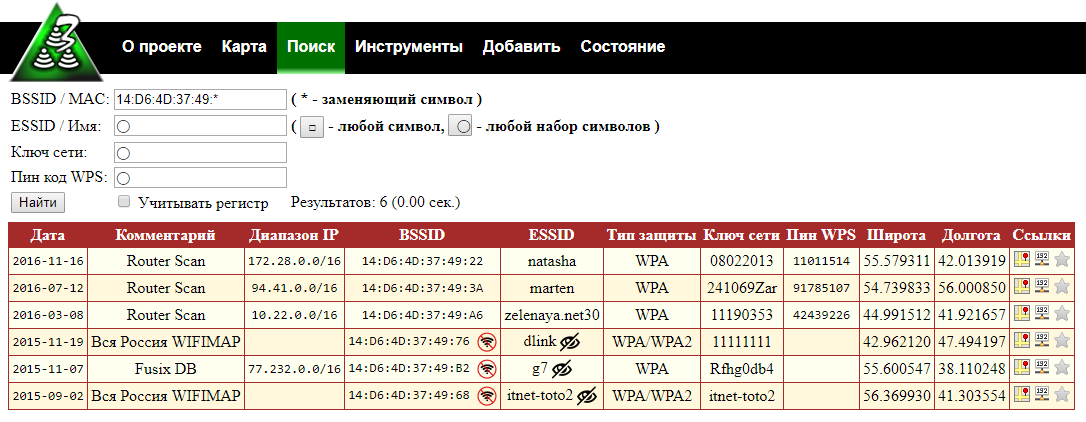
The asterisk (*) replaces any character and can appear anywhere in the search string.
The advantage of searching by BSSID (MAC address) is that devices usually have a unique BSSID, so you will find the exact AP you are interested in.
Not everyone knows how to find out the BSSID from the neighbor Wi-Fi (although you can do it directly in Windows with WirelessNetView and in Linux with numerous programs, such as Airodump-ng), so you can also search by network name (ESSID).
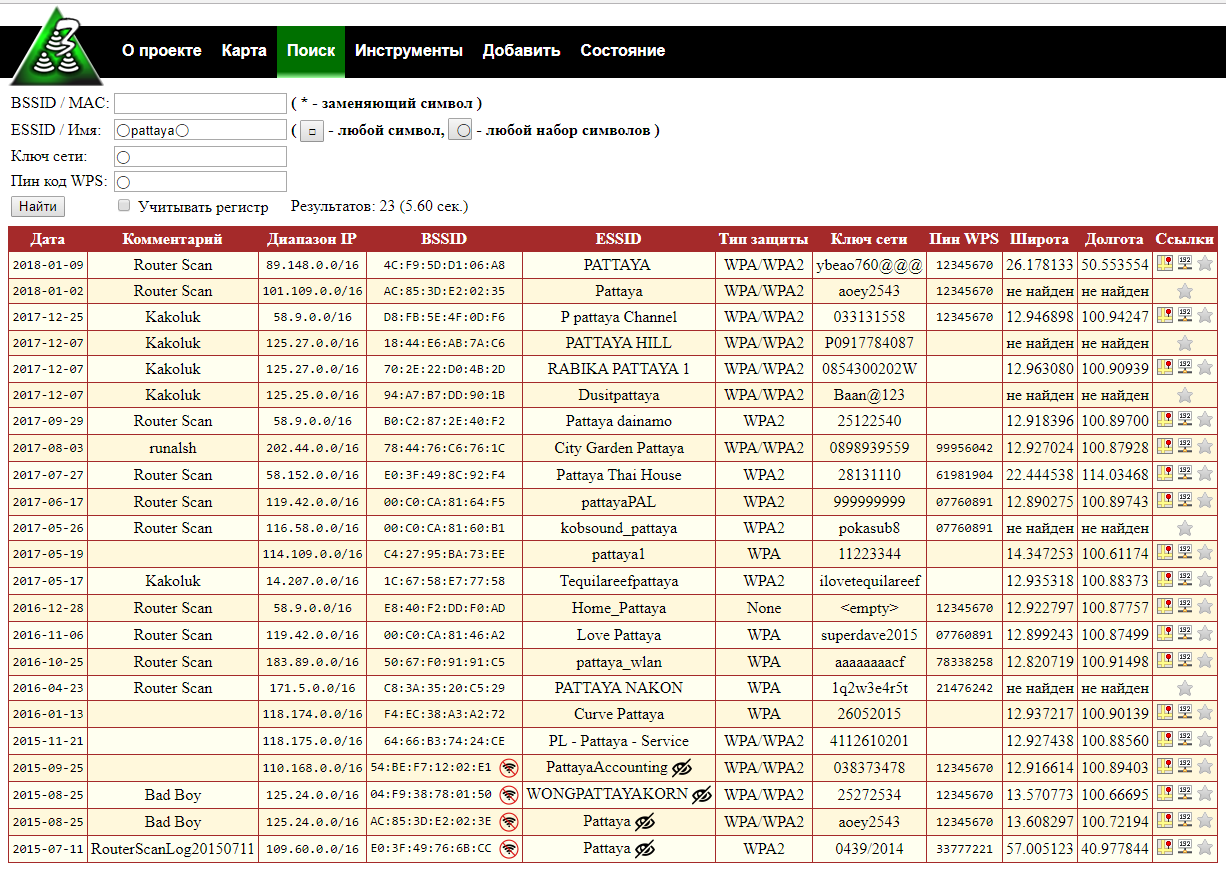
Wildcards are supported: □ – any character, ◯ – any set of characters. Example:
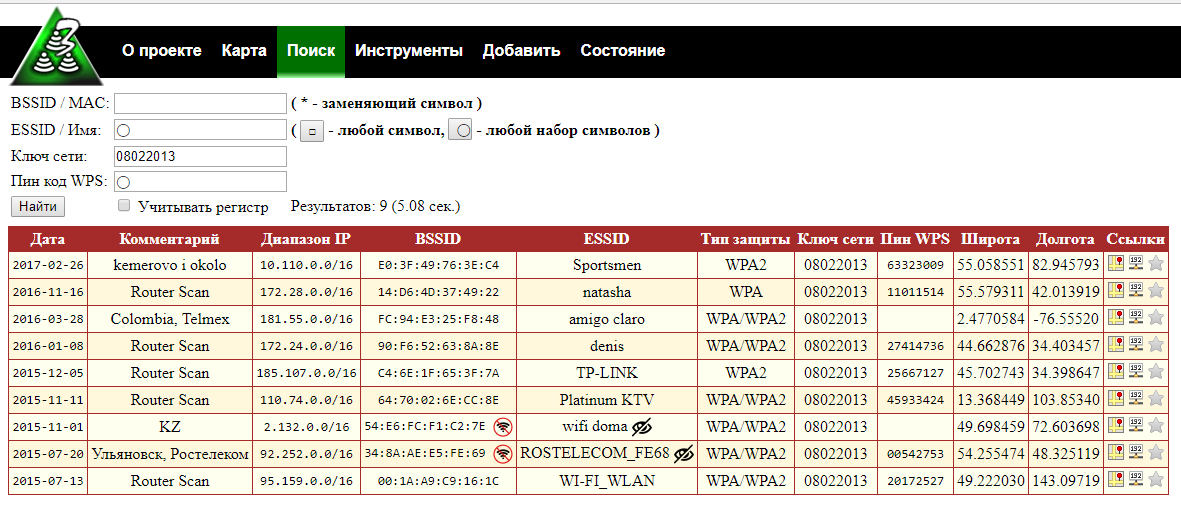
You can also search for access points by Wi-Fi password (network key) and by WPS PIN code – this can be useful for research purposes.
Check online speed
Check your internet and wi-fi speed with the Npnerf service. It's free.
- You have to select a server or leave it "automatic selection";
- Clicking on the wrench under the speedometer, select Mbps (top right corner);
- "Start testing." Scanning will take some time;
- Get the result.
Perform the measurement twice. For the first test, connect your computer or other device to the Internet via cable. Do the second test with a wi-fi connection. If the difference is noticeable, look for a problem with the wireless connection.
Internet speed and wi-fi – what's the difference
It is worth understanding the difference between the speed claimed by the ISP and the actual speed of the device and the access point from which the user will be surfing the Internet. The provider will never guarantee that they will be equal. If you measure the speed of the Internet under normal conditions, it will be, for example, 50 Mbit/sec. But if you hover over the characteristic icon in the system tray, there will be completely different data.

The explanation is very simple: the connection to the ISP's server is limited only by the equipment, and the speed at which the sites are opened is stated in the tariff, and there is no correspondence between them.
The situation is the same in the case of the router. The speed of the wi-fi connection is one thing, the speed of your connection to the ISP is another, and the speed at which the Internet sites are opened is a third. It's easy to check. What opens faster – the server provider or the main Yandex?
People often do not understand also that the connection speed DEFINITELY depends on the port through which the router communicates with the service provider. The latter promises 1 or more Gbit/sec. But if you have a mid-range router and use a port of 100 Mbit for the Internet connection, you cannot get higher than this mark, no matter what speed of the wireless network is mentioned in the instructions.
Often the wi-fi connection will also depend on the signal strength of the transmitter. Routers have a function to adjust the power, and if your laptop thinks the signal is weak, it will automatically run slower.
This also includes the range of reception. The farther the laptop is away from the access point, the slower the connection.
3. Go to a public place
- Most public libraries in the U.S.
- Various subway stations in the United States
- Amtrak
- Boltbus
- Megabus
- The Art Institute of Chicago
- National Mall
- Museum of Modern Art
- Louvre (specific access points)
- Byzantine Museum
- British Museum
- National Museum of China
4. WiFi router rental for travel
Depending on where you are going, it may be worth renting WiFi for travel. Free public WiFi can have fairly low connection speeds, not much security, and plenty of other travelers who will also use that connection. Mobile hotspots can offer reliable and fast Internet that won't force you to change the rate on your cell phone or buy a router when you travel.
This is the best option for those who need stable and reliable WiFi that keeps their data safe. It charges in less than 3 hours and allows you to use your device for up to 6 hours. Renting this "travel" WiFi starts at $10 per day, but the longer the rental period, the cheaper it becomes per day. You can order most WiFi devices for travel online.
Osmino WiFi
Osmino WiFi is a free application for mobile devices that helps you find Wi-Fi in an unknown location. More than 110 million wireless network points and their passwords are available in the program's database. The program works in 50 countries.
After installing the application, the system will automatically determine the location and start scanning the area. The found Wi-Fi points will be shown on a map of the locality. In large cities Osmino WiFi users leave comments on some wireless connection points: feedback on the quality of connection and Internet speed, as well as the presence of a password.
The app has a "Share" function. If you find an available Wi-Fi point that is not marked on the map, you can share the point with other Osmino WiFi users. All information about Wi-Fi points without a password is put on the map automatically. Data is collected by analyzing the devices of other users. If a person who uses the program connects to Wi-Fi without a password in a certain place, this point will be marked on the map and added to the database.
Instabridge by Degoo
Instabridge is a free application for mobile devices. The utility is used to quickly find Wi-Fi in an unfamiliar city. In the database of the program there are more than 4 million wireless Internet connection points and passwords.
Information about available Wi-Fi spots is displayed on the map. The database is replenished by Instabridge users: if you find a new Wi-Fi point in the city, you can share it with other community members. New zone with Internet access will be marked on the map.
The utility supports the offline mode. Download a map of the area and a database to your phone to use the basic functions of the program – search for a Wi-Fi point – without connecting to the Internet. The application has statistics on Wi-Fi: connection quality, connection speed, traffic consumption, the popularity of the point among users. There is support for WPA3, WPA2, WEP, WPA.
Read More: