You can check your IP address and find the IP address of the router by using the ipconfig command.
Ok, so you've used inSSIDer to select the best channel for your Wi-Fi network– awesome! The next step is to actually make the change in your Wi-Fi router settings. All routers and access points are slightly different, but this guide will give you a general idea of the process of accessing your router configuration to change the channel, security type, and other settings.
Note: An ethernet cable works a bit better, because your router will disconnect your from the wireless network for a moment while it switches channels.
Access the router configuration page by typing the router's IP address in to the address bar, and pressing enter.
| IP Address | Typical For |
|---|---|
| 192.168.0.1 | D-Link, Netgear, and others. Try this IP first. |
| 192.168.1.1 | Linksys, Belkin, TP-Link, and others |
| 192.168.15.1 | Clear/ClearWire |
| 192.168.100.1 | Virgin Media Superhub |
| 192.168.1.254 | TP-Link |
| 10.0.1.1 | This is pretty rare. |
Note: Even though there are a few more possible addresses, it doesn’t take long to see the pattern. Try changing the second to last number if none of those work.
Glad you asked! Each router hosts a tiny webpage that you access to configure it. Just like a website has an address (such as www.metageek.com), your router has an address. Since it's a home Wi-Fi router, it doesn't need a name reserved for it, so it's just a numerical address. Typing in the address in the address bar on your browser will take you to the configuration page for your router.
- Log in with the username and password.
- Zyxel Keenetic II and Keenetic III
- Setting up WiFi on TP-Link routers
- Setting up the Internet on the router
- About privacy and security warnings on your device
- Security
- Device features that can affect Wi-Fi connections
- Private Wi-Fi Address
- Location Services
- About privacy and security warnings on your device
- Security
- Device features that can affect Wi-Fi connections
- Private Wi-Fi Address
- Location Services
- DHCP Setup
- Port Forwarding Setup
- Expert Q&A
- You Might Also Like
Log in with the username and password.
inSSIDer shows you exactly how your network is configured, how neighboring Wi-Fi networks are impacting yours, and gives suggestions for fast, secure Wi-Fi.
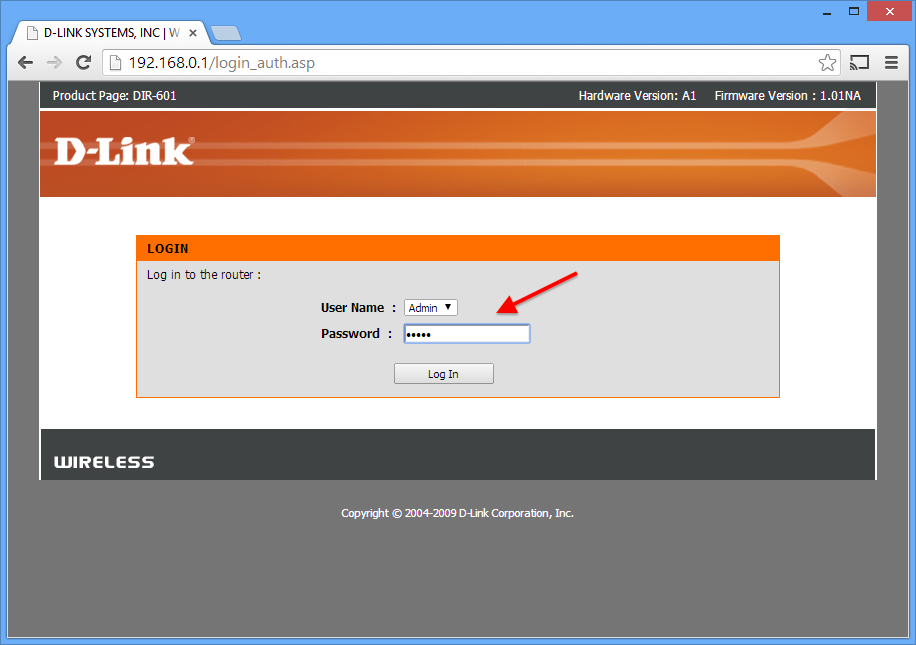
Most routers require a username and password. The default username is usually admin. The default password is usually on a sticker on the router, or printed on the paper manual or packaging. If you can't figure it out, Google the model number of your router and "password" together.
Zyxel Keenetic II and Keenetic III
To set up Wi-Fi on Zyxel Keenetic 2 and newer routers, you have to go to the same-named section and open the "Access Point" tab:

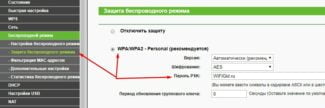
In the field SSID type in the name of the created Wifi, check the box for the standard WPA2 and enter the password in the The key. It remains to press the "Apply" button and check the connection.
Setting up WiFi on TP-Link routers
Basic WiFi settings on TP-Link routers can be found at Wireless -> Wireless Settings:

In the "Wireless Network Name" field enter the name of the network to be created. Check that the region of use (Region) should be set to "Russia". Do not touch anything else and click on the button "Save".
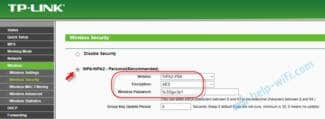
Go to the section Wireless Security to configure the security settings:

Select the checkbox at WPA/WPA2-Personal. Now the only thing left to do is to check the PSK Password enter the network access key and press the "Save" button to save the network settings.
Setting up the Internet on the router
We have configured the wi-fi network on the router and connected to it from the computer. We just need to help the router to see the Internet, so that the router can distribute the Internet to any device that connects to it via wi-fi or cable.
Step 1. . To make the Internet appear on the computers, you need to set up a connection to your ISP on the router. Let's take the same D-Link as an example.
Step 1.1. Let's type in the address line the ip-address of the router
![]()
Step 1.2. . We enter the login and password and press "Log in":

Step 2. . Go to the Internet settings section. Different router manufacturers may have different names for this section: WAN Setup, Internet settings, etc. In our D-Link, this section is called "Internet Setup":

Step 3. You will find yourself in the WAN port settings section.
Step 3.1. . Uncheck the "Enable Access Point Mode" checkbox.
Warning. For other manufacturers this option may be called "Disable NAT". The point is that the "Access Point" mode disables NAT and turns the router into an access point. This option comes in handy if this router is not connected to your ISP, but to another one of your routers.

Step 3.2 . Select the type of connection to your ISP.
To find out what settings you need to select to connect specifically to your ISP, you can:
Step 3.3. . If your ISP only allows connection from a registered MAC address, you have 2 ways to solve the issue.
About privacy and security warnings on your device
- If you administer the Wi-Fi network, we recommend that you update the settings of your Wi-Fi router to meet or exceed the security standards in this article.
- If you don't administer the Wi-Fi network, you can bring the recommended settings in this article to the attention of the network administrator.
To ensure your devices can connect securely and reliably to your network, apply these settings consistently to each Wi-Fi router and access point, and to each band of a dual-band, tri-band or other multi-band router. Before changing the settings, you should take these steps:
- Back up your existing settings, in case you need to restore them.
- Install the latest firmware updates for your router. This is generally done from the app or web page that you use to administer the router.
- Update the software on your other devices, such as on your Mac and on your iPhone or iPad, to ensure they have the latest security updates and work best with each other.
After changing the settings, you may need to forget the network on each device that previously joined the network. This ensures the device uses the router's new settings when rejoining the network.
Security
![]()
Set to WPA3 Personal for better security
Set to WPA2/WPA3 Transitional for compatibility with older devices
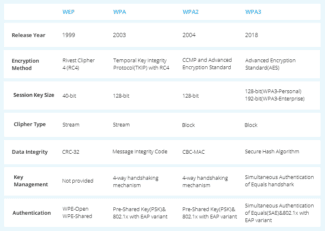
The security setting defines the type of authentication and encryption used by your router, and the level of privacy protection for data transmitted over its network. Whichever setting you choose, always set a strong password for joining the network.
- WPA3 Personal is the newest, most secure protocol currently available for Wi-Fi devices. It works with all devices that support Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), and some older devices too.
- WPA2/WPA3 Transitional is a mixed mode that uses WPA3 Personal with devices that support that protocol, while allowing older devices to use WPA2 Personal (AES) instead.
- WPA2 Personal (AES) is appropriate when you can't use one of the more secure modes. In that case, also choose AES as the encryption or cipher type, if available.
Device features that can affect Wi-Fi connections
These features may affect how you set up your router or the devices that connect to it.
Private Wi-Fi Address
If you're connecting to a Wi-Fi network from an iPhone, iPad or Apple Watch, find out about using private Wi-Fi addresses on those devices.
Location Services
Make sure your device has Location Services turned on for Wi-Fi networking, because regulations in each country or region define the Wi-Fi channels and wireless signal strength allowed there. Location Services helps to ensure your device can reliably see and connect to nearby devices, and that it performs well when using Wi-Fi or features that rely on Wi-Fi, such as AirPlay or AirDrop.
On your Mac with macOS Ventura or later
- Choose Apple menu > System Settings, then click Privacy & Security in the sidebar.
- Click Location Services on the right.
- Scroll to the bottom of the list of apps and services, then click the Details button next to System Services.
- Turn on "Networking and wireless", then click Done.
On your Mac with macOS Monterey or earlier

- Choose Apple menu > System Preferences, then click Security & Privacy.
- Click the lock in the corner of the window, then enter your administrator password.
- In the Privacy tab, select Location Services, then select Enable Location Services.
- Scroll to the bottom of the list of apps and services, then click the Details button next to System Services.
- Select Networking & Wireless (or Wi-Fi Networking), then click Done.
- Go to Settings > Privacy & Security (or Privacy) > Location Services.
- Turn on Location Services.
- Scroll to the bottom of the list, then tap System Services.
- Turn on Networking & Wireless (or Wi-Fi Networking).
About privacy and security warnings on your device
- If you administer the Wi-Fi network, we recommend that that you update the settings of your Wi-Fi router to meet or exceed the security standards in this article.
- If you don't administer the Wi-Fi network, you can bring the recommended settings in this article to the attention of the network administrator.
To ensure that your devices can connect securely and reliably to your network, apply these settings consistently to each Wi-Fi router and access point, and to each band of a dual-band, tri-band, or other multiband router. Before changing the settings, you should take these steps:
- Back up your existing settings, in case you need to restore them.
- Install the latest firmware updates for your router. This is generally done from the app or webpage that you use to administer the router.
- Update the software on your other devices, such as on your Mac and on your iPhone or iPad, to ensure that they have the latest security updates and work best with each other.
After changing the settings, you might need to forget the network on each device that previously joined the network. This ensures that the device uses the router's new settings when rejoining the network.
Security
![]()
Set to WPA3 Personal for better security
Set to WPA2/WPA3 Transitional for compatibility with older devices
The security setting defines the type of authentication and encryption used by your router, and the level of privacy protection for data transmitted over its network. Whichever setting you choose, always set a strong password for joining the network.
- WPA3 Personal is the newest, most secure protocol currently available for Wi-Fi devices. It works with all devices that support Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax), and some older devices.
- WPA2/WPA3 Transitional is a mixed mode that uses WPA3 Personal with devices that support that protocol, while allowing older devices to use WPA2 Personal (AES) instead.
- WPA2 Personal (AES) is appropriate when you can't use one of the more secure modes. In that case, also choose AES as the encryption or cipher type, if available.
Device features that can affect Wi-Fi connections
These features might affect how you set up your router or the devices that connect to it.
Private Wi-Fi Address
If you're connecting to a Wi-Fi network from an iPhone, iPad, or Apple Watch, learn about using private Wi-Fi addresses on those devices.
Location Services
Make sure that your device has Location Services turned on for Wi-Fi networking, because regulations in each country or region define the Wi-Fi channels and wireless signal strength allowed there. Location Services helps to ensure that your device can reliably see and connect to nearby devices, and that it performs well when using Wi-Fi or features that rely on Wi-Fi, such as AirPlay or AirDrop.
On your Mac with macOS Ventura or later
- Choose Apple menu > System Settings, then click Privacy & Security in the sidebar.
- Click Location Services on the right.
- Scroll to the bottom of the list of apps and services, then click the Details button next to System Services.
- Turn on “Networking and wireless”, then click Done.
On your Mac with macOS Monterey or earlier

- Choose Apple menu > System Preferences, then click Security & Privacy.
- Click the lock in the corner of the window, then enter your administrator password.
- In the Privacy tab, select Location Services, then select Enable Location Services.
- Scroll to the bottom of the list of apps and services, then click the Details button next to System Services.
- Select Networking & Wireless (or Wi-Fi Networking), then click Done.
- Go to Settings > Privacy & Security (or Privacy) > Location Services.
- Turn on Location Services.
- Scroll to the bottom of the list, then tap System Services.
- Turn on Networking & Wireless (or Wi-Fi Networking).
DHCP Setup
This is usually enabled by default, and if it isn’t enabled then you should enable it unless you are providing a DHCP service from another router.
Generally you should stay with the default configuration. The settings on mine are shown below and they are the default ones:
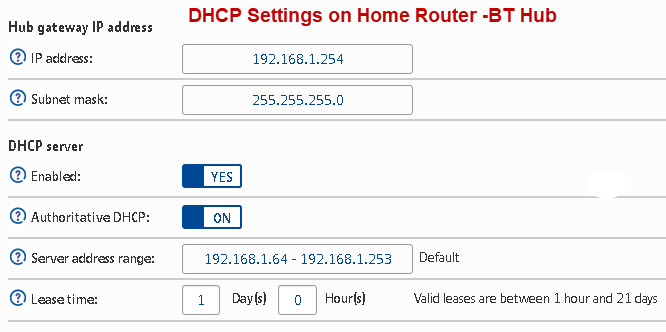
Note: You should only have one DHCP server on a home network.See Understanding DHCP on Home Networks
Port Forwarding Setup
This is a very common setting if you have someone playing computer Games of if you need to provide external access to your home network.
This setting can be potentially dangerous as it opens your home network to the Internet and it is covered in more detail in the understanding port forwarding tutorial.
However you should have an appreciation of IP addresses and the different types, and so I recommend you read the Internal and External IP addresses tutorial first.
Expert Q&A
Did you know you can get expert answers for this article? Unlock expert answers by supporting wikiHow
Luigi Oppido is the Owner and Operator of Pleasure Point Computers in Santa Cruz, California. Luigi has over 25 years of experience in general computer repair, data recovery, virus removal, and upgrades. He is also the host of the Computer Man Show! broadcasted on KSQD covering central California for over two years.
Firmware is essential for the operating system's security. It patches holes in the network. Updating the firmware ensures that your network is protected against the newest bugs and viruses out there.
Thanks! We're glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even 500 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHow
Luigi Oppido is the Owner and Operator of Pleasure Point Computers in Santa Cruz, California. Luigi has over 25 years of experience in general computer repair, data recovery, virus removal, and upgrades. He is also the host of the Computer Man Show! broadcasted on KSQD covering central California for over two years.
So the first thing you do is log in to your router. You do that by accessing your router's homepage, which is going to be an IP address or routerlogin.net, or whatever. Sign in with your username and password. Then, select "connected devices" to see a list of everyone who has been or is currently connected to your network.
Thanks! We're glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even 500 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHow
You Might Also Like


Mirror Your Screen to a TV: Miracast, Chromecast & Wireless HDMI



10 Easy Steps to Set Up a Wireless Router


How to Connect a Canon Printer to Wi-Fi on Windows or Mac
Read More: