One of the most common myths about wireless is that it gives your body a lot of radiation while using it. Yes, Wi-Fi has its own radio band at 2.4 GHz, but the same frequency is used by other equipment available in every living space.

VoWiFi technology from a Wi-Fi perspective
We're used to cellular and Wi-Fi existing separately from each other. But sometimes it happens so – we get inside a room where there is definitely no cellular service, but there is Wi-Fi. At the same time, it's still possible to make phone calls. How does it work?
VoWiFi (Voice over Wi-Fi) is a technology that allows cellular users to make voice calls in areas where there is no cellular coverage, but there is Wi-Fi coverage. In order for it to work, you need the following:
Most Russian cellular operators support VoWiFi. At the end of this article there are links to instructions on how to enable this technology, as well as lists of supported devices. Manufacturers specify support for this technology in the specifications of the device.
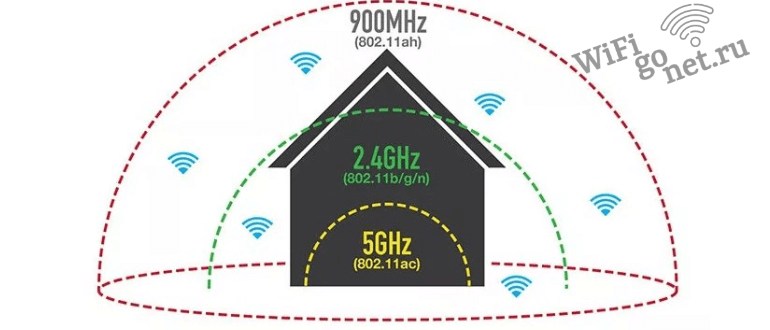
If you are planning to change your smartphone, it is better to choose a device with both VoWiFi support and 802.11ax/ac support for the 5GHz band. First, they will be able to reach you even if you are "off the grid". And second, the 2.4 GHz band is extremely noisy, and it almost always has interference problems, causing Wi-Fi to often "perform poorly," unlike the more "free" 5 GHz band.
When your smartphone registers on the network via VoWiFi, a corresponding indication appears in the status bar. Depending on the model of your smartphone, the display and icons may look different. In our case (Huawei smartphone), the icons in the status bar look like this:

In the picture above, both SIM cards are registered in the operator's network in two ways: both through the cellular network (signal strength indicators, one with an "R" icon – roaming) and through VoWiFi ("VoWiFi" icons). As a rule, when there is a VoWiFi connection, the name of the operator's network changes from "Operator" to "Operator-WiFi". In our case, the names are not displayed because there is not enough space in the status bar. Additional indication also appears on the call button, when calling and in the call list:
And now let's move on to the technical component
Let's take a closer look at VoWiFi traffic from a Wi-Fi network perspective. For the tests, we created an open Wi-Fi network without encryption and did a radio capture using Wireshark when a mobile device was connected to it.
WARNING: Just in case, let me remind you that in terms of information security, it is highly undesirable to use open networks in real life! Use key (PSK) or other security methods.
ePDG (Evolved Packet Data Gateway) gateway is an element of the cellular operator's infrastructure that allows a mobile device (smartphone) to establish a connection to the operator's network when connected through unprotected communication channels, including the internet. For security purposes the traffic between the mobile device and the ePDG is encapsulated in an IPSec tunnel and encrypted. After association with a Wi-Fi network and obtaining an IP address, the mobile device identifies the IP address of the cellular operator's ePDG gateway serving the SIM card. It uses a special kind of FQDN (domain name) regulated by 3GPP standards. Each cellular operator has a unique PLMN-Id (Public Land Mobile Network – identifier). This identifier includes the country code (Mobile Country Code, MCC) and the operator's network code (Mobile Network Code, MNC). These codes are unique, and for each operator the FQDN of the ePDG gateway will look like this:
The links contain lists of MCCs of different countries and MNCs of RF operators, and at the end of the article there are domain names and IP addresses of ePDG gateways of the largest RF operators. DNS response to this format address request contains one or more IP addresses of the ePDG gateway. If your smartphone has SIM cards of several operators that support VoWiFi, DNS requests are sent for each operator.
Next, the mobile device initiates an IPSec tunnel to the gateway at the address received from the DNS response. Below is a screenshot from Wireshark showing an example of establishing an IPSec tunnel between a smartphone and an ePDG. Host 192.a.b.c is the smartphone (VoWiFi client) and host 213.d.e.f is the cellular operator's ePDG gateway.
What is Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a special way of transmitting information wirelessly within the boundaries of a local network, which is possible through the use of special devices made according to the IEEE 802.11 standard.
This is the scientific concept of wi-fi. In layman's terms, Wifi is the ability to transmit information without the use of cables, through the air, thanks to an invisible wave. The closest analogue of the technology can be called mobile communication, radio or Bluetooth. Before this network became available to users, the Internet could only be carried by wires.
By the way, the Wi-Fi system was developed in 1990 to make it possible to link cash registers.
How it works and how to use it
The principle of operation of the considered technology of data transmission over a wireless network is as follows:
- Access points – in other words, transmitters, on which there are already 2-3 antennas, are installed in a certain place.
- The built-in antennas receive a current, which is an electromagnetic wave. In this way, a certain type of radiation is formed, similar to the radiation from the operation of a microwave oven.
- The radiation generated spreads out to the sides, overcoming concrete and metal obstacles. It can be jammed, but it still reaches users' gadgets and PCs.
- Personal computers, too, have wi-fi devices that are able to trap the caught radiation with their antennas, extract the signal from there, and transmit the response over the radio.
- Devices in the same location can catch any wireless signals and select exactly what should be coming to a particular gadget.
The principle of operation of the technology is similar to a conversation in a noisy place: a person's ears pick up all neighboring conversations, but are able to distinguish the speech of the person with whom he is communicating at the moment.
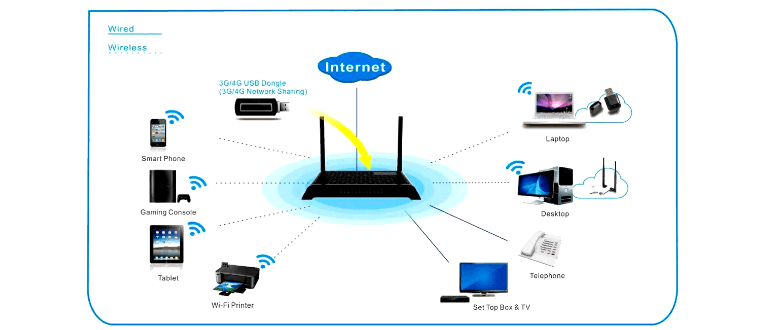
How a router works
A router, otherwise known as a router, is used when you want to create access points to a wireless network. It is not a device through which you can simply access the Internet. A modem or a special cable that attaches to the router is responsible for this.
It should initially be understood that a router and a modem are completely different devices. But today the difference between them is somewhat reduced, which is why modems are commonly built into the router during its manufacture. With the connection, the router itself becomes the access point and the network. All gadgets or personal computers that have access to such a network can work with the Internet.
Read More: