A slightly different approach to the Wifi frequency range is used for 5 GHz. Unlike the last variant, more "higher" channels are used here – from 34 to 180 (some of the channels drop out of the list). Each variant is characterized by its own range – from 5.17 to 5.905. In Russia, indoors, 5150 to 5350 MHz is used.

Wi-Fi signal frequency – what wavelength
Wi-Fi technology involves wireless and high-speed data transmission, based on the principles of electromagnetic technology. Wi-Fi signal is a radio wave, the features of which will be discussed below.
Data transmission is carried out by ordinary data coding, which flows to the transmitter. That in turn reformats the electronic signal into a radio wave.

Note! Radio waves are used in television, mobile networks, and microwave ovens for heating food.
A radio wave has three characteristics: length, frequency, and height or amplitude. Frequency determines the data channel, which affects speed.
At what frequency does wi-fi work
Many users wonder how to find out what frequency Wi-Fi works. At the moment, network equipment operates in only two bands – 2.4 and 5.
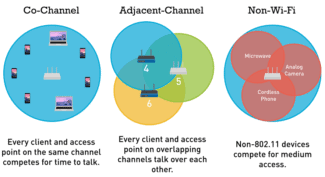
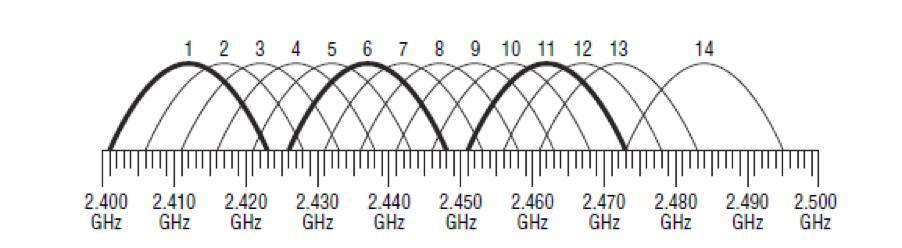
In the vast majority of cases, the 2.4 GHz frequency is used, since it appeared first. Each remote access point on this frequency functions on channels from the first to the thirteenth inclusive.
As a rule, problems with Internet connection occur if there is a working router nearby. Thus, on the same channel they simply share the speed between them. By default, network equipment automatically connects to the most free channel, so in case of Internet problems it is recommended to reboot the router.
Pay attention! Such manipulation is not able to unload the range even a little bit. That is why experts strongly recommend buying dual-band routers, which will allow you to use the second wave length of 5 GHz, which is more free because it is new.
Now it is worth familiarizing yourself with the principle of setting a particular frequency when operating network equipment.
2.4 GHz.
The Wi-Fi signal frequency is set quite simply in the router's web interface. After logging into the system the user has to go to the "Wireless 2.4 GHz" section. Then the sequence of actions looks like this:
- Go to "Wireless Setting" and specify the name of the wireless network.
- Among available parameters it is necessary to pay attention to the used channel, by default it should be set to "Auto" mode.
- Set Mode 11 b/g/n mixed.
- Set the channel width to "Auto".
- For the changes to take effect, you must "Save" them.
Number of antennas
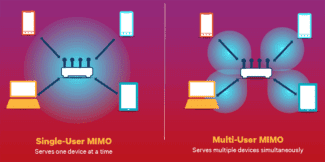
The number of antennas in a WiFi hotspot – is this important for choosing wireless devices? Can it be used to determine which access point or router will give a faster wireless connection than its counterparts?
Some people believe there is a direct correlation between the bandwidth of a WiFi access point and the number of antennas it has: the more antennas, the higher the bandwidth.
The maximum throughput of a wireless access point is not directly related to the number of antennas in it. Although, of course, a greater number of antennas has a positive value:
- the sensitivity of the device increases,
- more effectively realized spatial multiplexing, due to the simultaneous transmission of data through multiple transmitting and multiple receiving antennas.
As a result, throughput does improve, but, as we have said, not directly proportional to the number of antennas.
In addition, the parameter "number of antennas" is a fuzzy concept:
- First, a device can physically have 3 antennas, but still support MIMO 2×2 operation, that is, have the functionality of 2 transmitting and 2 receiving antennas. In this case, the third antenna serves as both transmitting and receiving, dynamically switching to different modes.
- Secondly, to determine, for example, in what mode MIMO works wireless access point (in recent years, manufacturers are increasingly not specified this characteristic), you need to know not the total number of WiFi antennas, and a separate number of transmitting and receiving antennas. In order to determine that the device is MIMO 1X2, you need to know that it has 1 transmitting and 2 receiving antennas.
Perhaps that is why the data on the number of antennas is often not specified at all in the specifications of the equipment, due to the uselessness of this information.
Chain
Chain is sometimes translated as "chain", "transmit/receive channel" or is not translated at all and is simply transliterated as "chain". This term refers to a complex channel, a transmit/receive circuit including the antenna. It directly describes the implementation of MIMO in the device and is used in two ways:
1. Chain quantity refers to the "aggregate" number of MIMO receive/transmit channels. For example, a MIMO 2×2 access point specifies a dual chain, while a MIMO 3×3 device specifies a triple chain.
If the MIMO is 2 × 2 or 3 × 3 , in which case the number of chains usually equals the number of transmitting antennas.
2. The number of chains means separately the number of channels of reception and the number of MIMO transmission channels. This is most often used when recording wireless characteristics in the form: nTnR, where nT is the number of transmit circuits, nR is the number of receive circuits. For example: 2T3R – two transmit chains, three receive chains), 1T1R – one transmit chain, one receive chain, etc.). This designation is relatively less common.
Chain and bandwidth
Again, many people use the number of chains to calculate the maximum throughput of a wireless device. So, it is assumed that if an 802.11n access point has the "dual chain" or MIMO 2×2 designation then its maximum throughput will be 300 Mbps (150*2). Often it does turn out to be true, but only because of a simple coincidence.
In fact, calculating the maximum throughput based on the number of chains is a wrong approach.
Two chains and MIMO 2×2 for 802.11n devices does not guarantee a channel speed of 300 Mbit/sec, and MIMO 3×3 with three transmit/receive circuits does not mean that the maximum throughput of the device – 450 Mbit/sec.
How the signal is amplified
In more expensive models, a MIMO circuit is used. That is, the data is transmitted in multiple streams at once. When used, the data is divided into a number of parts of the MIMO circuit and sent to the receiver at the same time. But the receiver must also support this technology.
For example, in this way you can reach speeds of 7 Gbit / s, if you use a scheme 8xMU-MIMO. That is, the router must have up to 8 antennas or more. Each antenna will send a different signal and at the end they will add up.
At home, it is most common to use broad antennas. They have less gain, but the beam itself has a larger radius. It is clearer if you look at the picture below. When you increase the dB the beam becomes narrower. That is why high-powered wi-fi routers use several high-powered antennas at once to increase coverage.

What does signal frequency affect?
WiFi signal frequency is a parameter involved in the formula for calculating the wavelength and affects its index. In addition, a number of signal properties depend on this parameter:
- Absorption. The higher the WiFi frequency, the higher its penetration capability. The greatest impediment to the wave has reinforced concrete pavement, concrete floors and ceilings, interior partitions, etc. In addition, in rainy weather there is a slight deterioration in signal quality, which is common.
- The ability to bypass obstacles. According to the laws of physics, the shorter the wave and the higher the frequency, the harder it is to overcome various obstacles in its path. That is why 2.4 GHz is more suitable for normal apartments and homes, and 0.9 GHz is the most effective from this position.
- Natural attenuation. Like any other parameter, WiFi signal tends to attenuate. The higher the frequency, the more active this process is.
- Reflection. WiFi signal tends to bounce off surfaces or pass through them (all or just part of them). Either way, signal strength decreases.
- Information density. The higher the frequency range of WiFi, the more data you can transmit in a given amount of time.
Against the background of the information received, it is easier to make a decision. In normal mode, you can set it to 2.4 GHz. If you live in an apartment building, where all channels are heavily overloaded, you can switch to 5 GHz, but to do this you need to buy special equipment and know how to change the frequency of the router. Universal option when the device supports two modes at once. In that case, you can set up both networks in parallel and work with the one that gives the best WiFi signal quality.
Read More: