Barrier in the form of a wall some 10-20 centimeters thick due to such a sharp angle can be impenetrable several meters of reinforced concrete. Mirrors may also severely impair the signal due to their metallized coating. Massive safes, located between the point and the client, can also nullify the signal, even at a short distance.

- Wi-Fi – what is it, how it works, how to use, all about the wireless network wi-fi
- Where it all began
- Origin of the word
- Pronunciation
- History
- How does it work?
- Ten years later
- Yay, new technologies
- Something about Wi-Fi
- How does it work and how do you use it?
- Basic functions, or what is Wi-Fi for?
- Standards
- How does Wi-fi work?
- How do I connect Wi-fi at home?
- How does wi-fi work
- History of the emergence of wi-fi
- Standards for the physical layer of Wi-Fi
- Signal representation
- Channels in the 2.4 GHz band
- Speed Adaptation
Wi-Fi – what is it, how it works, how to use, all about the wireless network wi-fi
In today's world, Wi-Fi is well included in the lives of ordinary people, and very few people do not use it in everyday life. But even now not every person will be able to intelligibly and reliably answer the question of what is Wi-Fi, when was Wi-Fi created, explain on what principles this system works, or how to connect it yourself. Let's consider the basic concepts concerning this popular wireless technology.
The acronym WiFi, used for the wireless Internet technology used by most modern devices, grew out of the slogan "The Standard for Wireless Fidelity," promoted by the developers when it was first created. After a while, the name of the technology was shortened to two words, "Wireless Fidelity," then four known letters remained. The abbreviation "HiFi" (High Fidelity) was involved in the history of the name.
Where it all began
Wi-Fi digital technology was invented by the Australian engineer John O'Sullivan in 1998. In its characteristics, it has similarities to Bluetooth, IR modules, radio transmissions, and mobile networks. A device that emits a wi-fi signal creates a wireless network connection, functions in a set range of radio frequencies that covers a certain area. All gadgets within the area can join the network (provided they support wireless communication).

The Wi-Fi brand name was invented by Alliance members when developing this invention. Wi Fi routers operate according to the IEEE 802.11n communications standards specification.
Origin of the word
Not everyone knows the definition of the term Wi-Fi, but it is encoded in the word itself. It comes from the first two letters of the words Wireless Fidelity which means "wireless fidelity," in Russian. It's a brand name coined by Alliance Corporation for the Internet technology they promote.
Pronunciation
The word Wi-Fi has a simple pronunciation. It reads as "wi-fi".It is pronounced quickly without separation or with a slight pause. Pronunciation "wi fi." is fundamentally wrong.
History
Let's not go on a journey of half a century or more, bypassing all the prototypes and developments. The "father" of Wi-Fi is thought to be John O'Sullivan, an engineer at the Australian Astronomy Laboratory. Under his leadership, between 1997 and 1998, the Wi-Fi was developed by the Australian Astronomy Laboratory. there was something that almost the whole world uses. Two years later the first IEEE 802.11a standard was registered, which is still widespread today.
Because of the high level of wave interference, IEEE 802.11b was quickly developed, but it did not solve the main problem. The waves were also scattering and overlapping. However, this was corrected by dividing the operating frequency range into channels.
After 10 years of development, the standard IEEE 802.22 appeared, which supports data transmission over distances of up to 100 km in a straight line. As of 2019, 18 IEEE 802.11 standards have been developed with different bandwidths and operating frequencies.
The term "Wi-Fi" is a hint of Hi-Fi, and is not deciphered in any way. However, it is commonly believed that the word comes from Wireless Fidelity.
About the work of wireless technology in a video format:
How does it work?

Wi-Fi is a wireless data transmission technology, a wireless local area network (WLAN). The principle of Wi-Fi is based on the transmission of encrypted signals through microwave waves (ultrahigh-frequency waves) over short (tens of meters) distances. A network scheme consists of at least two elements: an access point and a client.
There are client-client schemes – without the use of access points.
The access point broadcasts the identifier (SSID, network name) through special data packets 10 times per second at 100 Kbps. This is theoretically the lowest bandwidth wireless channel.
How does a Wi-Fi network work? When in range and detecting a signal the client device makes a conclusion about the possibility to connect to it (the difference in technology can be a hindrance). The transmitter may not transmit its ID, then the network will be invisible to clients. You can connect to it only by entering the SSID and password, if it is protected.
If there are 2-3 networks with identical SSIDs in the same area, the receiver device connects to the one with the better signal.
The access point in home Wi-Fi networks is mainly a wireless router – a router. It and the clients must work in the same mode (frequency, signal modulation). Let's take the example of Internet distribution in a private house.
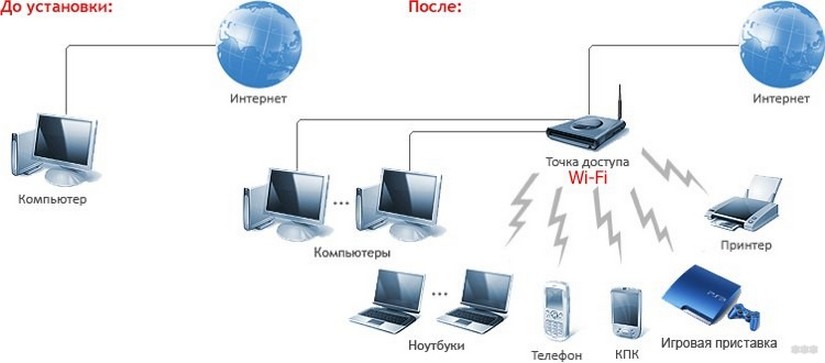
The router gets the traffic through the network cable, converts it into radio waves and broadcasts them "through the air" in the form of very high frequency radio signals with certain parameters. The receiver "catches" these waves and decodes them (decodes, extracts information from them, which is encoded by the carrier frequency).
Ten years later
Yes, during ten years the technology was developing, but not very fast – the bandwidth was quite enough for the needs of the users of that time. But then it became clear that it could not go on like that – we needed a new standard that would allow us to transmit more data per unit of time.
The main reason is that the quality of photos and videos has increased, and very significantly, compared to the end of the 20th century. One only has to look at photos from the early 2000s, comparing them with digital content from earlier times, and everything becomes clear.
In general, technology has been around for a long time, in 2003 for instance there was the 802.11g specification. But it was not something fundamentally new – the developers took advantage of the 5 GHz band technology, adapting it for the 2.4 GHz band. By the way, the number of WiFi Alliance members also began to grow by leaps and bounds. By 2003, there were more than 100 of them. Correspondingly, more and more companies were developing equipment compatible with the WiFI wireless standard.
Yay, new technologies
In 2009, the WiFi Alliance Development Team adopted a new standard, 802.11n. This was already a new generation of WiFi, without cloning the data transfer mechanism from one band to another. At the same time, the data transfer rate increased many times over – up to 600 Mbit/s.

This dramatic increase in throughput was achieved by using MIMO multithreading instead of SISO. Multistreaming made it possible to use multiple data streams directed by different antennas. In the beginning, the standard allowed for 4 streams, each providing 150 Mbps of throughput.
At the same time the technology was "smart" – the signals were processed and then combined into one, which made it possible to achieve a throughput of 600 Mbit / s, at least in theory. Basically, MIMO was the beginning of the development of modern WiFi – fast, reliable and long range.
Something about Wi-Fi
I recently attended a conference on "Building Wireless Networks". Despite the fact that I have been an administrator for a long time, it is not every day that I have to deploy wireless networks. I am hastening to share with you some of the nuances. I invite all interested readers under the hood.
Wi-Fi does not have a clear boundary of propagation.
That means that without proper evaluation no one can give you a guarantee that the connection will work even within one office or room.
There were cases when in the office once a day the connection was lost for about half an hour. A tech-support staff member of the access point manufacturer was very experienced, therefore after finding out the time when the connection was down most often (which usually happened from 12-00 to 14-00), suggested that the blame lies in the microwave oven. In this office there was no microwave, but it was in the next, just behind the wall to which was screwed access point.
Here we should also remember all kinds of Wi-Fi jammers, which can be used by your competitors and pay your neighbors to turn it on from time to time.
Because of this, it is not recommended to use wireless networks as a substitute for a corporate LAN with twisted pair or fiber. Or do it as a last resort when laying cable is not possible. For example, if you need to connect two nearby offices out of town.
Wireless network is best seen as a wonderful addition to the "traditional" networks. For example, to organize guest access for their customers.
You should also keep in mind that Wi-Fi networks may not work equally well with different transport layer protocols. So, for example, TCP and UDP may work fine, but IPX is out of hand.
In order to understand exactly how to build a network and to try to determine the possible cause of the failure it is necessary to understand a little bit about the existing standards and their vulnerabilities.
At this point I think it makes sense to look at 802.11g and 802.11n.
How does it work and how do you use it?
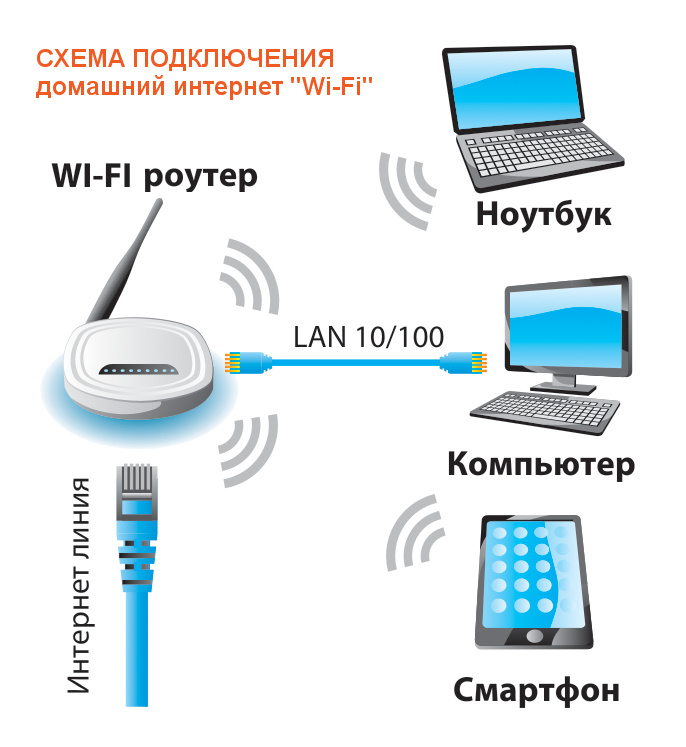
Let me outline how the Internet via Wi-Fi is delivered to your end consumer – laptop, smartphone, tablet. Yes, you can connect it through adapters and to a desktop computer, but usually the latter is still connected by wire.
To connect a PC to Wi-Fi you can always buy an adapter – a good device can be found under $10.
But for mobile equipment at home this is already a standard. So, let's see.
- You connect the Internet service from your Internet provider (Rostelekom, or whatever).
- The provider usually already has a cable into your house and even the entrance. When connecting, the master only leads it from the switchboard to your apartment.
- Your apartment now has a cable that connects to the device (the same router).
- The router activates the function of creating a Wi-Fi network. Through which it distributes the Internet to all.
- All devices connect to it and use the Internet.
Another possible scheme is based on the use of networks of mobile operators and their modems:
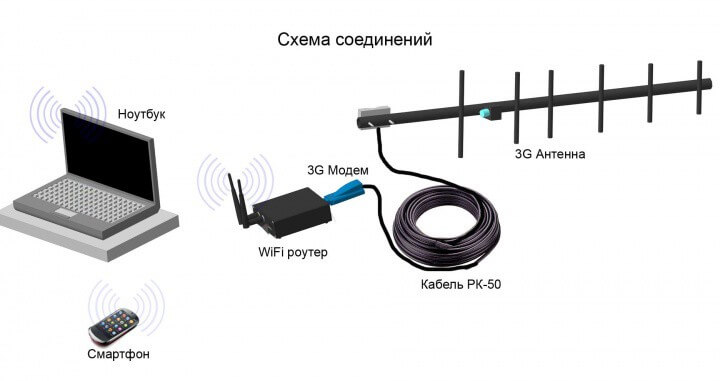
- You buy a SIM card of a mobile operator with a special Internet tariff.
- "The SIM card is inserted into the modem.
- The modem creates an Internet connection via the SIM card and gives out wi-fi.
Bottom line: WIFI creates a special device that works as an "Access Point":
Read More:In public places, cafes, hotels, usually everything is already done for you – there are usually good powerful routers. All you have to do is find the right network on your device, enter the password and enjoy free Internet (sometimes paid – it depends on your luck). Another name for public hotspots is hotspots.
Basic functions, or what is Wi-Fi for?
To summarize, there are now two main functions of Wi-Fi devices:
- Connect to the Internet – and visit your favorite sites and services from there.
- Creation of local network – all devices connected to one access point can see each other and transfer the same files directly.
- An extension of the previous point – connecting wireless devices. Printer, joysticks, TV remote, refrigerator – you can't imagine everything.
Historical background. The technology was invented in 1991 and was used just for the cash register equipment.
Standards
There are now many different standards for 802.11 wireless LANs. Some are much more popular such as 802.11n and 802.11ac. In addition, today's devices work in multiple modes (802.11 b/g/n).
The standards have a lot in common. The most important similarity is the use of the airwaves to transmit data. Interestingly, the very first 802.11 standard also used infrared radiation. Today it is used in remote controls (such as a TV remote control). Since the second generation of the standard only radio waves are used. All of the physical layer variants work with the same medium access algorithm, CSMA/CA. Link layer frame structures of all standards are identical.
The differences in the specifications lie in the frequency band used, the coding methods, and, as a result, the data rate. Some MAC layer timing parameters may also differ.
The most popular IEEE 802.11 standards
Since 1999, the OFDM multiplexing method replaced the DSSS and FHSS methods of the first versions. Another 10 years later the standard was extended to support MIMO. Let's highlight the common properties of the IEEE 802.11 family of standards:
- The same topology.
- All standards support either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, or both, as an operating frequency band. 802.11ax may include additional frequency bands in the 1 to 7 GHz bands as they become available.
- The same method of accessing the CSMA/CA shared medium is the carrier frequency listening method with multiple accesses and collision avoidance.
- The same frame structure of the data link layer.
- All standards have an adaptive mechanism for changing the transmission rate depending on the distance to the receiver. Adaptation can occur by changing the method of coding signal – for example, to increase the data rate the access point can switch from 16-QAM coding to 64-QAM coding.
- When using OFDM technique, the access point can, along with a change in the coding method, increase the number of frequency subchannels, allocated to the user.
How does Wi-fi work?
Moving on to the interesting and very important, understanding how wi-fi networks work you will be able to intelligently formulate your thoughts about internet connections. So, in order for you to have a Wi-fi network at home you first need to wire the internet to your home.
After, the Internet cable must be connected to special equipment – a router.
Router – a device which receives signals from the Internet, converts them into a so-called wi-fi network and transmits them to specific devices (phone, computer, TV).
How do I connect Wi-fi at home?
As I said earlier, the first thing you need to do is to install the Internet in the house, apartment, office, the process is not complicated, you need to find out what providers work with your house, call them or visit the office, where they will accept the application for laying the Internet cable in your apartment.
You can find a suitable Internet provider through the service Inetme – just select the city, house and street to find out all the current offers for connection. All tariffs are up to date, so you only need to compare them and make a choice.
As a rule, you will be given several dates to choose from, you choose the most convenient for you, when you can be at home, at the appointed time will come and install the internet cable in the place you need.
By the way, for laying cable no money are taken, the company you choose does it at its own expense, you pay only the selected rate internet connections, usually from 300 to 1000 rubles per month.
The monthly fee (tariff) will depend on the connection speed you choose.
For comfortable access choose the speed of 30 Mbps, about 400-500 rubles/month.Once you have the cable, you can connect it to your computer and use the Internet, but our goal is to create a wi-fi network, so we move on. It is necessary to buy a router (some companies provide their routers), it is to him you will then connect the Internet cable, after that router will create an active wi-fi network, and already to it you can connect without any wires if only from a laptop or phone and here it is comfortable access to the Internet from anywhere in your apartment or house.
Tip 1: When you discuss the terms of connection to the Internet cable, you should ask what kind of router you should buy, because the choice in our stores is quite large. The right advice on buying the right router will save you time and money.
Tip 2: When connecting the router will need to configure (once), if you do not have the slightest idea how to do it, I recommend to ask the master, who will come to lay the Internet cable. Let him configure everything for you at once (may require an additional fee for setup, about 500 rubles).
How does wi-fi work
Wi-fi is a method of transmitting digital data over radio waves at a range up to 150 meters at high speed comparable with the speed of the cable network.
Today, wi-fi is in every home, café, hotel. Most modern devices can give out and receive wi-fi, the radio network for digital data transmission has become more than accessible. A huge number of users can connect to the network at the same time, and the quality of communication is not reduced.
Around the world, the number of Wi-Fi hotspots is increasing rapidly. Who invented this network, which means so much to the modern world, can be understood simply by tracing the history of its creation from the beginning.
It is one of the most currently in-demand and promising areas for the development of local and global networks.
History of the emergence of wi-fi
So who invented wi-fi? The original prototype of modern wi-fi was a wireless network created in the Netherlands under the leadership of Vic Hayes in order to optimize the work of cash registers in supermarkets. The speed of the protocol was about 2 Mbit per second.
And engineer John O'Sullivan is considered to be the author of the wireless data protocol. In 1991 the first network, which can already be called an analogue of modern wi-fi, was created in the laboratory of radio communication under his command.
In 1997 a unified standard for data transfer was adopted, and by 1999 the data transfer rate through the protocol was already about 11 Mbit per second.
So why is there a rumor that wi-fi was invented by a woman. Who is really behind it?
Standards for the physical layer of Wi-Fi
There are several different implementations of wi-fi, and they are described in 6 standards. The very first 802.11 standard was adopted in 1997 and had a speed of 1 or 2 Mbps, Ethernet at that time could transmit at 10 Mbps. The current standard wifi 802.11as was adopted in 2014, the maximum transmission speed, more than 6 Gb/s.
Now wifi is used to transmit data – electromagnetic radiation or radio ether, but the first version of wifi used infrared radiation, now this method is used in TV remotes.
But since the second generation of 802.11b only electromagnetic radiation is used. Two frequencies are used, 2.4 and 5 GHz. Frequencies in this range can be used without licensing. However, other devices operate in the same range, such as a microwave oven, and this interferes with the Wi-Fi signal.
Signal representation
Modern wi-fi standards use orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFMD) to transmit data. Data is transmitted in parallel at different frequencies. Although the frequencies overlap in the picture, the OFMD method allows the signals to be recognized reliably.
Channels in the 2.4 GHz band
The channels in the 2.4 GHz band uses 14 channels for data transmission, the picture lists their frequencies. The channels are slightly shifted in relation to each other, but still partially overlap.
Thus the number of Wi-Fi networks which are in the same place is limited by the number of channels there cannot be more than 14. If more than 14 networks are operating in the same area, they will not have enough channels. This situation is known as a "wi-fi jungle" and it is quite common, for example in apartment buildings where there is a wi-fi router for Internet access in each apartment.
Speed Adaptation
With Ethernet the speed of the equipment is fixed, it will be the same for all devices on the network. Wi-Fi allows you to change the speed depending on the quality of the signal. If the signal quality is high, the speed will be increased, if it is low, the speed will be decreased. In order to increase or decrease the speed, the wifi varies several parameters:
- You can use different channel widths from 20 MHz to 160 MHz.
- Supports a variety of modulations that allow you to transmit data at different speeds and reliability
- It is possible to change the data interval between the characters that are transmitted via wifi.
A table that shows the different speed options for one spatial wi-fi stream. The lowest speed of 6.5 MB / s is obtained by using a binary phase modulation BPSK channel 20 MHz and the interval between the characters 800 ns. The highest speed of 866 Mb/s is obtained by using quadrature amplitude modulation which has 256 states, the channel width of 160 MHz and the interval between the characters 400 ns.
The data provided is for one spatial stream, if your access point and your station have multiple antennas, then you can use multiple spatial streams and at the expense of this even further increase the transmission speed.















