Using a wifi extender is another great way to boost your router's signal in a remote part of the house.

- Powerful wifi router
- Powerful Wi-Fi router
- Expanding the signal coverage area by technical means
- Improving your network coverage with the right installation
- Does it really reduce the speed?
- How many devices can be connected for normal Wi-Fi work?
- Wi-Fi signal range.
- Router's age
- Router location
- Outdated firmware
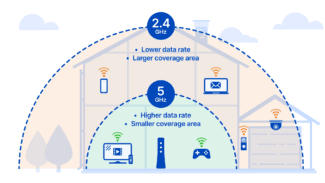
- WiFi network coverage
- What the range can be
- Getting your router set up correctly
- Methodology for calculating effective distance
- Effective distance without obstacles
- Results of practical observations
- Maximum range, good reception
- What not to do
Powerful wifi router
The range of a wifi router depends on the type of router or access point you use. Factors that determine the range of the router (access point) are:
- total transmitter power;
- The type of 802.11 protocol used;
- The length and attenuation of the cables connected to the antenna;
- Obstacles and interference in the signal path in a given room;
- the gain of the router's antennas.
Range wifi router standard 802.11g, with the regular antenna (gain about 2dBi) is approximately 150m in the open and indoors – 50 m. But brick walls and metal structures can reduce this range by 25% or more. 802.11a uses higher frequencies than 802.11b/g, so it is more sensitive to various obstacles. In addition, the range of 802.11b or 802.11g Wi-Fi networks is greatly affected by interference from microwave ovens. Tree foliage is also a strong obstacle because it contains water, which absorbs the microwave radiation of the band in use. For example, heavy rain weakens the signal in the 2.4GHz band to 0.05 dB/km, thick fog – 0.02 dB/km, and the forest (dense foliage, branches) – up to 0.5 dB/meter.
Choosing a Wi-Fi router, the range can be roughly calculated using a special calculator, which is slightly below, it is designed for D-Link equipment, but the formulas and methodology used there will be suitable for any other.
If creating a radio bridge between two networks, it must be taken into account that the space around the straight line drawn from the receiver to the transmitter must be free of
absorbing and reflecting obstacles in a radius equal to 0.6 of the radius of the first Fresnel zone. The size of this zone can be calculated by the following formula:
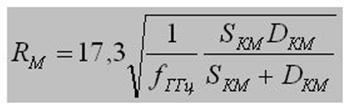
Powerful Wi-Fi router
If you choose a powerful router, its range and reception quality should satisfy your requirements.
The power of a wifi router is largely determined by the power of the signal boosters in it.
A powerful router on the Realtek 8187L chipset has not only a high power of 1 watt, but also large-scale support. Drivers for this chipset are supported by all operating systems. If you use an external optional antenna, the distance can reach up to 5 km.

Rasprostranenye brands Alfa, NEtsys, Senao EnGenius EUB Ext High-Power, Wifly city 8G , 20G , AIRLIVE, G-Sky GS-27USB-50, KASENS.

Amped Wireless has released its most powerful router, the R20000G High Power Wireless-N, which features 600 mW of 2.4 GHz signal amplification.
The R20000G is capable of two networks: 5000 MHz and 2400 MHz. Router provides indoor coverage up to 930 square meters. Two powerful antennas with 5 dB/inch of gain are connected to the router, but they can be replaced with more powerful ones.
Expanding the signal coverage area by technical means
Method #1 – use a long-range wi-fi router to extend the signal range. Router with about 1 watt with the possible connection of antennas is able to provide wi-fi propagation already in kilometers. Recall that officially it is forbidden to use routers with a power of more than 100 mW without a license. However, you can find them on sale.

Method #2 – organize a system of several routers or by using repeaters. You don't have to look for forbidden devices or install antennas. But it is also not always possible to install an additional access point, even a wireless one, on the desired path.
There is another disadvantage – it is the quality of the repeatable signal. First, it will be twice as bad if you use additional router points. Secondly, regardless of the device, the subsidiary networks will only work properly when the air is free.

Method #3 to increase the range of the router by installing an effective antenna. This is an option to increase the signal strength without buying a forbidden router. It is worth looking at the specifications of the antenna. The market offers options with a gain of up to 13 dB.

This will increase the coverage area, but there will be "dead zones". The plus side is that the router is also good at picking up signals from devices. This will be needed wherever a wi-fi camera is connected, the range of which is also amplified. Not only can a more powerful antenna improve the connection, but multiple antennas on a single router can.
Another type of router that covers a larger area is the 5 GHz dual-band. It benefits from operating on a free frequency. But in addition to being expensive, it doesn't fit all gadgets, cameras and other devices.
Improving your network coverage with the right installation
Sometimes you can achieve the coverage you need without the cost of long-range wi-fi transmitters, antennas, and repeaters.
- vertical antenna position. In a tilted position, the signal is spent spreading into the floor and ceiling. This is more of an installation optimization, but will work for a small expansion of coverage;
- optimal location of the access point. The latter should be located as close as possible to the receiver or equidistant to several;
- minimal interference between the router and the devices. Either remove serious obstacles, or place the devices so that there is no interference between them. This is difficult to arrange;
- Changing the router mode. The new 802.11n mode has better propagation and signal quality. The inconvenience is the inability to connect to equipment with 802.11 B/G;
- changing the channel of the router. This is done in the settings. In fact, this method is a special case of the third point. It will only help against interference from neighboring networks;
- increase the power. It is again about the settings. Often only 75% of the possible power is set. But by changing the setting to the maximum, there is a risk of signal quality degradation;
- blocking the signal from propagating in the wrong direction. This is where metal-containing materials that do not allow the signal to pass through can help.

Some of these ways are difficult to do in practice. If the mirror can still be re-hung, then the reinforced concrete wall is nowhere to go. Finding a suitable access point location is easy, but it is not certain that there will be an outlet. In addition, these means are not very effective, but not too expensive and solve some problems. In any case, the method must be chosen according to the purpose. Next, consider the configuration of the network in the organization of video surveillance.
Does it really reduce the speed?

Yes, the number of connected devices slows down your Wi-Fi.
In this context, "slowdown" means that the router is not able to simultaneously exchange data with all the devices in the network.
The router must "share" the frequency with each device; there can be a lot of traffic on the same frequency, because other devices are also trying to send their data packets through it.
However, this has nothing to do with internet speed. You may well have a good, fast connection provided by your ISP and a slow wireless connection.
Typically, the network slows down when four or more devices are connected to the network, although this largely depends on the router being used. The slowdown occurs because the router cannot communicate with more than one device at a time.
Thus, the more connected devices, the slower the Wi-Fi is.
The decrease in Internet speed depends not only on the number of connected devices, but also on how much data they use. However, it is worth noting here that a slight slowdown is quite normal.
How many devices can be connected for normal Wi-Fi work?

We recommend connecting no more than five devices at the same time. In this case, the bandwidth will not be affected by the slowdown due to the simultaneous connection of too many devices.
On the other hand, you can have up to 25 devices connected to public Wi-Fi before you notice a speed drop (again, depending on the router).
Here are a few other factors that can affect your network connection speed:
Wi-Fi signal range.
The Wi-Fi signal sent by the router is key to how many devices you can connect. If the signal is weak, the wireless speed will definitely drop when you connect multiple devices.
Here it is recommended to test the signal, so that you can determine its range and, if necessary, use a Wi-Fi repeater (extender).
Router's age
Older routers produce low speeds and are unable to support the same number of devices as newer models. Buying a new router with better features is another way to speed up your Wi-Fi connection.
Router location
If your router is in one room and your connected devices are in another room, the Wi-Fi signal is bound to weaken if there are walls in the way. It's best to place the router in the center of the room, or move your connected devices closer.
Outdated firmware
The firmware installed on the router controls all the basic functions of the router: it monitors the quality and power of signals, adjusts their power, handles channel allocation, etc.
If there is any error in the firmware, it can cause problems with your Wi-Fi connection, which ultimately slows down your wireless connection speed.
WiFi network coverage
As practice shows, such parameter as the range of the wifi router plays an important role when choosing a router. After all, the further operation of your wireless network will depend on it.
Imagine, it is not very pleasant if the WiFi signal does not reach some point of your home, or the signal will be, but the speeds will be weak. So let's take a look at what the maximum range of your WiFi network can be and how it can be increased.
Usually, for a standard city apartment, the most common router is enough, and its signal is distributed to all corners of the dwelling. But if you want to make a unified network with your neighbor, that is where the problems may arise.
It happens that a person lives in a private house and wants to have Internet access in the garage and the summer kitchen. Here we will have to think about the distance your router will cover and how it can be increased.
What the range can be
If you make an analogy, the work of a wireless router can be compared to the work of a mobile operator tower, the only difference is that the router has a much smaller coverage area, and it communicates via WiFi. The range of a standard router is around 100-200 meters and that is if there are no obstacles, but if it has reinforced concrete walls or steel constructions on its path, the coverage area can fall down to 50 meters.
Factors that affect the range of the network:
There are a variety of ways to increase the range of your wireless network. Both the location of the router itself and its settings affect this parameter. Let's see what you can do to increase your network coverage.
Getting your router set up correctly
Your wireless coverage area can be drastically reduced due to interference from your neighbor's WiFi devices, microwave ovens, or even your typical baby monitor.
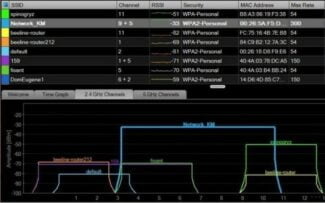
To avoid this, you should pay attention to which channel your router is operating on. If the channels are the same as a nearby router, there may be network problems and a significant reduction in range. So go into your router's settings and see what channel it is operating on.
Methodology for calculating effective distance
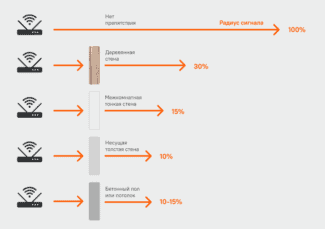
Let's say the wireless connection works when the distance between the access point and the smartphone is N meters with no obstacles in the signal path. A table from which you can find out how many times the intensity decreases when passing this or that obstacle, there are several sites (such as ZyXEL). At the same time, it is known that reducing the intensity by 2 times (by 3 decibels) is equivalent to reducing the effective distance N by the root of two times. It's simple – the square of the distance is inversely proportional to the intensity.
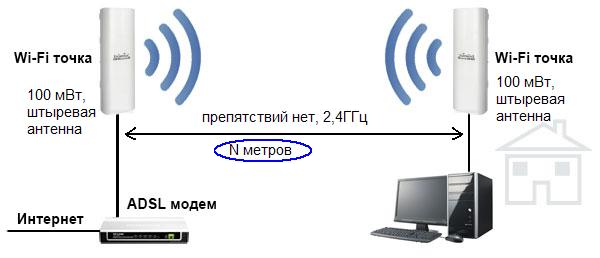
When the signal passes through a glass window, the intensity is reduced by just 3 dB, which means that the effective distance is reduced by the root of two times. Using this technique, you can calculate at what distance the Wi-Fi connection will still work in this or that situation:
- Glass window – reduces intensity by 3 dB (2x)
- Tinted window – 6 dB (4 times)
- Wood wall – 9 dB (8 times)
- Interior panel wall, concrete floor – 15-20 dB (32 times or more).
The coefficient by which you divide the distance value is equal to the square root of the intensity reduction factor. Consider an example.
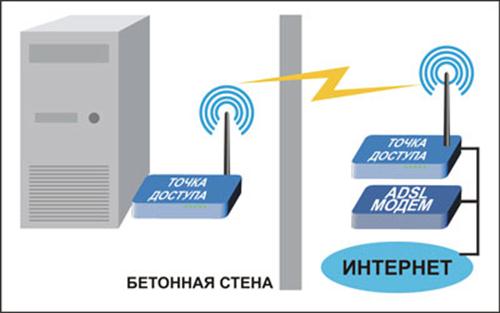
Suppose that N is 400 m. Now we "put" one panel wall and one wall of wood between the router and the smartphone. Adding up the decibels (15+9 dB), we get 24 decibels. On a logarithmic scale it is 24, and on a linear scale it is equivalent to a 251-fold decrease in intensity. Now, calculate what the root of 251 equals (it's 15.84). Dividing 400 meters by 16, we get 25 meters. As you can see, everything is simple and seems to be true.
Effective distance without obstacles
The reader is probably wondering what the value of N in the total absence of obstacles is, depending on the choice of Wi-Fi range. If the router's transmitter power is 40 mW, and its antenna "amplifies" the signal in the horizontal plane by 3 dB (it's multi-link), then according to ZyXEL, the N value is 400 meters. See: the router has a less powerful transmitter than the smartphone, but it uses a multilink antenna. Bottom line: the connection between two Wi-Fi devices with a transmitter power of 100 mW and an ordinary pin antenna is confidently maintained at a distance of up to 400 m. Here we were talking about the 2.4 GHz band.
Results of practical observations
Let's evaluate the "penetration capability" of Wi-Fi in practice. For this purpose we will take a set of access points supporting communication in the range of 2.4 GHz: this is TEW-411BRP+ from TRENDnet, DWL-2100AP from D-Link, and USR 805450 from US Robotics. As the subscriber device we will use a smartphone with 100 mW transmitter power. At the access points will install regular antennas, and they will be located on the fifth floor of a panel building.
Maximum range, good reception
There is no Wi-Fi network on the third floor of the building where our equipment is installed. The wave overcame 2 reinforced concrete slabs, so we lost 30 dB and that's it, no connection. In fact, consider that 35 decibels are lost when going through two slabs. You have to add the attenuation depending on the length of the distance, then we get about 36-38 dB. So, this is the attenuation for 100 milliwatts that is critical.

Let's try to catch the signal on the street. At a distance of 150-180 meters you can notice the presence of the network, but this is true if you are opposite the window of the room where the equipment is installed. And the connection remains stable at a distance of 100 meters. As you can see, the theory corresponds to practice with a sufficient level of reliability. For reliability, theoretically obtained result (one window -> 200 meters) is better to divide by 2.
What not to do
It is clear to everybody that it is hardly worth increasing the power of one of the transmitters when the second, i.e. the "subscriber" transmitter, remains unchanged. The same can be said of the use of antennas which allow increasing the intensity of the wave, but narrowing the diagram. However, the use of sectorial and multi-link antennas will still be effective, and here's why. Routers and other radio wave emitters may not only be in your apartment, but also the neighbors, etc. And by narrowing the capture sector, you can rid your router of extraneous radio frequency noise.
Read More: