This word in computing is commonly used for WiFi or wireless LAN connections , but it actually covers a lot more than we think. Because of its electromagnetic nature, Wireless applies to all types of communication for which no physical means are required.

- Learning Objective
- Example
- Wireless Communication Technology: What It Is
- Wireless communications
- The basic principles of digital wireless communication. Licence
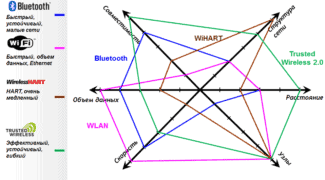
- Bluetooth .
- Wi-Fi
- Wireless and wired: which is better and how do they differ?
- What are all types of wireless networks currently implemented?
- Wireless Personal Area Network-WPAN.
- Wired LAN WLAN.
- WMAN Wireless Urban Network.
- WWAN Wireless Global Area Network.
- Wireless communication standards
Learning Objective
- Wireless operations allow you to organize communication over long distances.
- The most common options use electromagnetic wireless telecommunications, like radio.
- There are also options using light, sound, magnetic, and electric fields.
- Telecommunication – the use of electrical, electronic and electromagnetic pulses in communication science and technology.
- Conductor – a material with moving electrical charges.
- Radio wave – electromagnetic rays whose wavelength is 0.5 cm to 30,000 m.
Example
The most famous example of wireless communication technology is the cell phone. The technology uses radio waves, through which users can communicate around the world.
Wireless communication is the transportation of information between several sources that are not connected by an electrical conductor. It is most often used in telecommunications. Data is transmitted over short and long distances. Wireless operations provide communication services over significant distances that would not be guaranteed when using wires.
Electromagnetic wireless communications, like radio or IR signals, are most commonly used in this type of technology. IR enables short-range transmissions and radio enables long-range transmissions. The wide range of applications covers radios, radios, mobile communications, wireless networks, etc. It also includes garage door remotes, GPS devices, computer mice, keyboards and headsets, headphones, satellite TV, and more.
Perhaps the most striking example would still be the cell phone. There are approximately 4.6 billion subscribers worldwide (as of 2010). The technology uses radio waves to communicate with all corners of the planet. Of course, there is a communication range where special equipment is installed to receive and transmit radio signals.
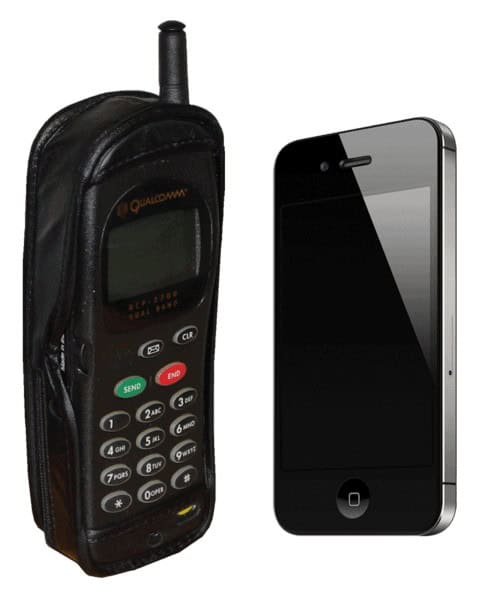

Qualcomm QCP-2700 – monoblock style phone in the mid-1990s and the iPhone 4S – modern use
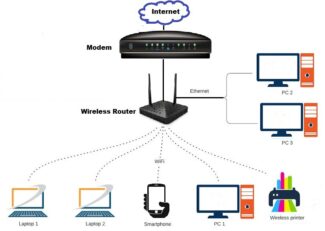
To make the device available to handle multiple connections, a VPN is used to create a single secure network. The most popular local area network technology is Wi-Fi. It is the standard for use in homes, offices and public places. Some companies charge a monthly fee for use, while others provide the service for free.
Cellular services set up coverage within 10 to 15 miles of a cellular point. Of course, the speed and range have increased with the advent of GSM, CDMA, GPRS and 3G networks. Satellite communications are important for aviation, transportation, maritime and military applications.
Wireless Communication Technology: What It Is
You can understand what wireless communication technologies are by their name. Any type of connection which does not require a cable connection is called wireless. In the early days of mobile technology, infrared ports were popular. Now they are only left in remote controls. Wireless technology uses radio frequencies. The following standards are the most common and we see them every day:
- Mobile Communications (APN). . This is the mobile Internet, which is provided by the service provider. It can be found and changed in the phone settings, but more often it is set automatically when you insert a SIM card, and the operator sends SMS settings. The plus is that this technology of wireless data transmission is widespread. The disadvantage is that it is difficult to control the speed and stability, and in addition such communication is paid, and the operator can determine different limits, packages, etc.
- Mobile Internet 4G (LTE-A technology). This is one of the data transmission technologies, which is available after connecting the phone to the APN. It is the fastest at the moment: it should provide speeds of about 100 Mbps – 1 Gbps. A plus is the speed and availability of the network. Various wireless means of communication, communication: modems, phones, etc. can connect to it, and then they provide fast Internet for the whole network. The minuses – the device must support this technology, and in addition, you must know your tariff plan, so as not to overpay for extra megabytes.
- NFC technology ("Near Field Communication"). This technology allows you to connect and exchange data in a second. At the same time, the range is extremely small: up to 10 cm. In the beginning, NFC was used in payment systems, for contactless payment, as "smart" passes. Now NFC wireless systems are built into smartphones, tablets and other devices, which is very convenient. The plus is the speed and accuracy, the minus is the small range, although it turns into a plus for the exchange of confidential data. By the way, you will also find a list of phones with NFC on the pages of our website.
Wireless communications
Nowadays, most technologies use radio waves to create a connection. The range of frequencies and the accuracy of the data transfer allows for many devices to be connected without slowing down. Some devices use their own wireless types of communication. For example, mice and headphones can be equipped with Bluetooth, or they can have a separate radio module. Of course, if you install a dozen of these gadgets at the same time, it can start to malfunction.
When absolute accuracy of data transfer and the highest speeds are important, then I advise connecting by wire. In other cases, wireless communication between devices is the most convenient way to transfer information, connect gadgets and share the Internet. And Wi-Fi is the most successful option for this purpose.
The basic principles of digital wireless communication. Licence

Hello all. In this article I would like to talk a little about the basic techniques and ideas of modern digital wireless communication – using the standard IEEE 802.11. Nowadays, very often people live at rather high levels of abstraction, poorly aware of how exactly the things around us work. Well – I will try to bring the light of enlightenment to the masses. This article will use the things and terminology explained in this article. So it is recommended that people who are not familiar with radio engineering read it first.
DANGER: there is a matan in the article – do not press this button for the particularly impressionable:
Analog Signals

Before the development of computers, analog signals were usually transmitted via radio waves – i.e. signals whose many values were continuous..

For example – sound – Pressure vs. time. The signal (voltage) received from the receiver goes to an amplifier of sound frequency and makes the speaker oscillate.

Or the video signal for a kinescope. The level of the signal determines the power value of the beam running on the screen, which at the right moments of time illuminates the phosphor, forming an image on the screen
The main disadvantage of this way of transmitting information is low noise immunity – the transmitting medium always includes some random component in our signal – a change in the shape of the video signal changes the color of individual pixels (we all remember the noise of the radio and the ripples on the TV screen).
Digital signals
Digital signals – i.e. signals with a discrete set of values – are much better than analog signals because we are not directly interested in the value of the signal, but in range in which this value is located and we are not afraid of interference (for example in the range of voltages 0V – 1.6V we consider that it is log 0, and in the range of 3.3V – 5V log 1). The payoff for this is an increase in the required speed of transmission and information processing.
Bluetooth .
Access point, as in the case of Wi-Fi, can be any device equipped with a special controller which forms a piconet around itself. This piconet may include several devices, if desired, they can be combined into bridges for data transmission.
Some computers and laptops already have a built-in Bluetooth controller, if this function is not available, then USB adapters are used which are connected to the machine and give it the ability to transfer data wirelessly.

Bluetooth uses a frequency of 2.4 GHz, while consuming as little power as possible. It is this indicator has allowed the technology to occupy its niche in the field of information technology. The low power consumption is due to the weak transmitter power, the short range and the low data transfer rate. Despite this, these characteristics were enough to connect and operate various kinds of peripheral equipment. Bluetooth technology has given us a wide variety of wireless accessories: headphones, speakers, computer mice, keyboards, and more.
- Grade 1. The range of wireless synchronization can reach up to 100 m. Devices of this type are usually used on an industrial scale.
- 2nd class. Radius of action is 10 m. Devices of this class are the most common. Most wireless accessories belong to this category.
- 3rd class. Range is 1 meter. Such receivers are put in game consoles or in some headsets, when there is no sense to distance the transmitter and receiver from each other.
Wireless data transmission system based on Bluetooth technology is very convenient for communication devices. The cost of chips is quite low, so equipping equipment with wireless connectivity is not too much of an increase in its price.
Wi-Fi
Along with Bluetooth, Wi-Fi technology is as ubiquitous in the field of wireless communications technology. However, it did not become popular right away. The development of Wi-Fi technology began back in the 80s, but the final version was introduced only in 1997. Apple decided to use the new option on its laptops. Thus appeared the first network cards in the iBook.
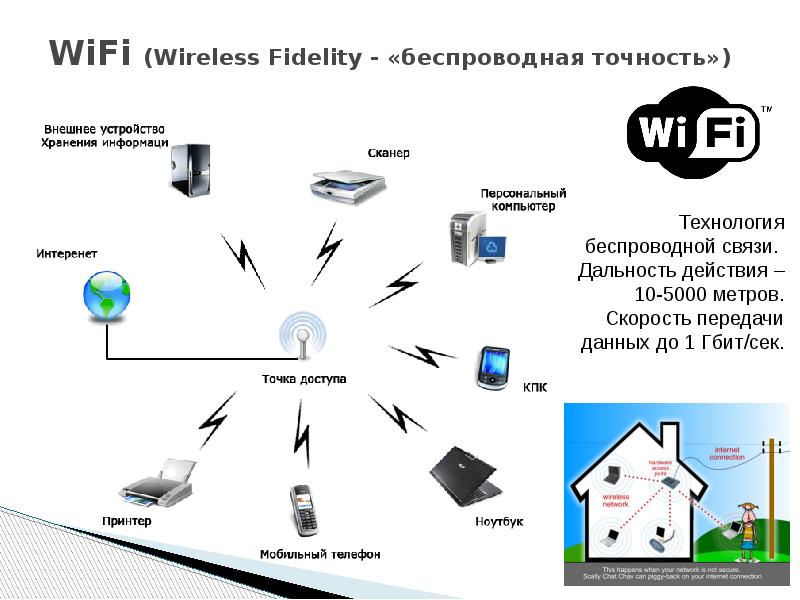
The principle of operation of the Wi-Fi technology is as follows: a chip is built into the device which can provide reliable wireless synchronization with another such chip. If there are more than two devices, then it is necessary to use an access point.
A Wi-Fi access point is the wireless equivalent of a fixed router. Unlike the latter, the connection is made without wires, by means of radio waves. At the same time there is an opportunity to connect multiple devices at once. Do not forget that when using a large number of devices, the data transfer rate will be significantly reduced. To protect the data, Wi-Fi access points are protected by encryption. Without entering a password, it will not be possible to connect to such a data source.
The first Wi-Fi standard was adopted in 1997, but it did not become widespread because the data transfer rate was too low. Later 802.11a and 802.11b standards appeared. The first gave transmission speeds of 54 Mbps, but worked at 5 GHz, which is not allowed everywhere. The second allowed networks to transmit at a maximum of 11 Mbps, which was not good enough. That's when 802.11g was born. This combined the previous two standards, allowing for a very fast network speed at 2.4 GHz. Standard 802.11y is an analog of 802.11g and has a longer range (up to 5 km in the open space).
Wireless and wired: which is better and how do they differ?

Before we begin, we must emphasize that since wireless refers to a wireless or wired connection, Wired was the opposite and refers to a wired or wired connection.
Now to say which one is better depends on the use, because Wireless Is more convenient and practical, it has Has its own limitations when transferring data.
For example, WiFi, which most people currently use and which is considered common, does not allow you to exceed 350 MB/s when it comes to network connection, so the Demons of one exalts the other, it all depends on the needs of its use.
There are many factors that we have to evaluate when it comes to these two forms of network connection. For this, we will take as an example a large office where we have many computers to connect to the Internet.

From the beginning, on the economic side. we find that it is much more convenient to buy internet service with Wireless because, since it is a lot of computers, to use a wired connection we need to make a great investment in a few meters of network cable.
If we evaluate the comfort , we will find that it is much more convenient to have a Wireless connection because it makes it easier for the team to work without being tied to a cable. In addition, Wireless connection makes it possible to connect other devices, such as cell phones, printers and scanners.
In terms of navigation speed it is possible that with a wired connection we can get a bigger advantage, because all the potential reaches the equipment through the cable, and there is no possibility of interference due to obstacles. p>
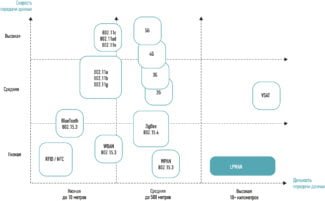
What are all types of wireless networks currently implemented?
Wireless networks are classified according to bandwidth, and we can find 4 that are the most implemented:
Wireless Personal Area Network-WPAN.
This is the smallest known wireless connection with a distance 10 meters or less. Note that all Bluetooth connections work with this protocol.
It is used for small and high speed data transfers, you see it very often on cell phones, mice, keyboards and wireless printers.
Wired LAN WLAN.
This is the popular WiFi, it has a wide range of coverage of more than 15 kilometers of radio. It works through Network adapters and access points on computers, cell phones, and routers.
WMAN Wireless Urban Network.
Works around the world with microwaves and is much more powerful than WiFi in terms of bandwidth and throughput.
WWAN Wireless Global Area Network.
This is the networking technology that cell phones use to transmit data. Known as Universal Mobile Telecommunications Systems or its acronym UMTS, it includes all connections GPRS, EDGE, GSM, HSPA, 3G, 4G, etc.
Wireless communication standards
The most commonly used and commercially available frequencies for connecting to Wi-Fi networks:
- 802.11a : approved in 1999, it combines the original set of protocols of the standard operating in the 5 GHz band. The maximum speed is 54 Mbps, although in practice the speed is usually around 20 Mbps.
- 802.11b : in this case also ratified in 1999. With a bandwidth of 2.4 GHz, the bandwidth is quite widespread and used. The maximum transmission speed is 11 Mbit/s, although in practice it is about 5.9 Mbit/s.
- 802.11g : This is an evolution of the previous one, using the same bandwidth, but with a theoretical maximum speed of 54 Mbps, as in the case of 802.11a. As usual, the average speed in practice or the actual speed is usually down to 22 Mbps. In addition, there is a variant called 802.11g+, which can reach 108 Mbps.
- 802.11n : This appeared in 2004 as a new revision of the standard. The actual speed in this case reaches 600 Mbps, so it represents an important performance leap over the previous ones. In addition, it can operate at both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, so it is compatible with all devices from previous editions.
- 802.11ac. : This is the standard that we typically find in most modern electronic devices and one that works with the 5 GHz band. This standard supports speeds of up to 3.46 Gbps, which provides data rates that are much faster than Wi-Fi N.