To prevent anyone but the administrator from accessing the Wi-Fi hotspot settings, you must set a password. There is no password by default.

- Notes of IT specialist
- Wireless Station Modes in Mikrotik
- How to configure your Asus router in the wireless network client mode (Wirelss ISP)?
- TP-Link router as a wifi wireless signal adapter (WISP)
- What is a WLAN port?
- The connection between WLAN and Wi-Fi
- Quick Internet Setup with QuickSet.
- Let's set up the WiFi.
- Bridge mode configuration
Notes of IT specialist
Wireless client mode is used in Mikrotik much less frequently than access point mode, but administrators often encounter all sorts of difficulties when they need it. This is largely due to a lack of understanding of the peculiarities of wireless equipment in this mode. Therefore, in this article we have decided to acquaint readers with the theory and practice of using routers of this manufacturer as a wireless station and to answer frequently asked questions.
You can learn how to configure MikroTik from scratch or systematize your existing knowledge in an in-depth course on MikroTik administration. The author of the course, certified MikroTik trainer Dmitry Skoromnov, personally checks the lab work and monitors the progress of each of his students. Three times as much information as in the vendor's MTCNA program, more than 20 hours of practice, and access forever.
To begin with, wireless equipment is far from straightforward. There is a set of standards IEEE 802.11better known as Wi-Fi, which specifies the requirements for wireless data networks and its support guarantees interoperability between devices from different vendors. To put it simply, if your access point and client devices both say that they support 802.11nstandard, then they work together, otherwise they don't.
In fact, devices support not just one, but a whole group of standards for backward compatibility purposes, so it is safe to say that any device purchased with the declared Wi-Fi support will work with another similar device under 802.11 protocols.
But in addition to the obligatory support of the standard many manufacturers implement their own proprietary solutions for wireless devices, and we won't even touch such protocols as Nstream и NV2It should be understood that such features are only supported by certain vendor's equipment and will work with other devices. This is neither good nor bad but you should always be clear which of the features provided by the equipment are 802.11 compliant and which are added by the manufacturer.
Wireless Station Modes in Mikrotik
Mikrotik equipment provides a fairly rich set of modes for the wireless station, some of them are standard, the other part contains proprietary extensions, so we have prepared a small compatibility table that allows you to quickly assess the applicability of one or another mode.
The 802.11 column shows the ability of the wireless station to work with the standard equipment from other vendors, RouterOS shows the compatibility with Mikrotik access points in normal mode, and CAPsMAN shows the compatibility with the software controller mode. Compatibility with Nstream and NV2 protocols is not considered by us, as it is far beyond the scope of this article.
How to configure your Asus router in the wireless network client mode (Wirelss ISP)?
And now I want to show in detail, how exactly to configure the router as a wifi receiver in client mode on the example of the model from Asus. Surprisingly, manufacturers still haven't decided what to call the WISP mode of the router as a wireless adapter. Each company has a different name – WISP, WDS, Bridge, Bridge.
This is especially noticeable in Asus, where it may have a different name for each model. For instance, on Asus EA-N66 it is called "Wireless Network Adapter". To activate it you have to go to the "Administration" section, the "Working Mode" tab and check the necessary item.
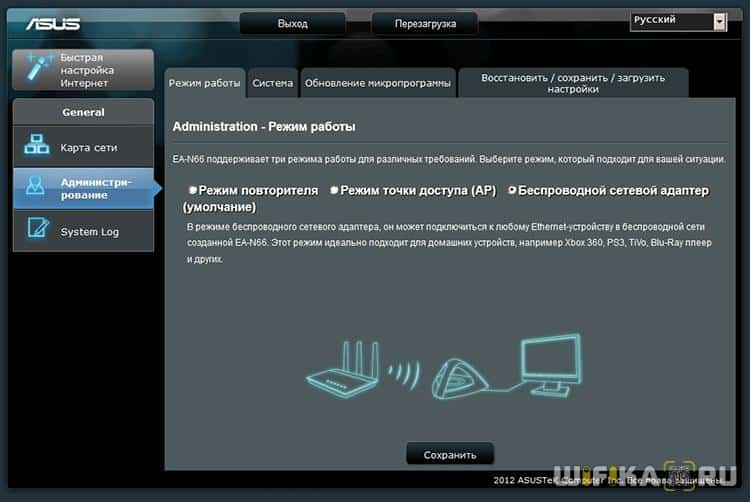
The WISP client mode in very many cases is not available in official firmware installed on routers from the factory. For example, like on my home Asus RT-N10U – this mode doesn't exist officially. So if you are planning to use this type of connection, make sure that the model you buy has a client mode – usually it is indicated as "Client mode".

But if you have already bought it and it turned out that the router has no WISP function, all is not lost – you can use unofficial firmware, for example, mine came from the DD-WRT group, which opened this possibility.


TP-Link router as a wifi wireless signal adapter (WISP)
In the range of TP-Link routers the client mode of the WISP adapter for receiving wifi signal is called "WDS Bridge". For the example I took the TL-WR1043ND. Its admin panel is located at 192.168.0.1 – here we enter the menu "Wireless Mode – Settings" and check "Enable WDS Bridge" – additional fields for settings will open.

Here we do the same as with other routers – prescribe SSID, password and other data from the main network wifi, and then save the settings.
The video on how to set TP Link client mode as a wireless network receiver shows it more clearly
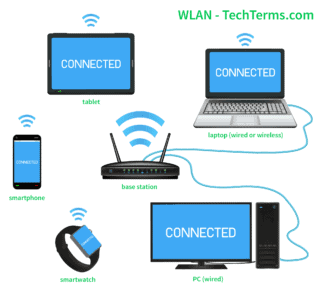
What is a WLAN port?
A Wireless Local Access Network (WLAN) is a limited local area wireless network. A WLAN port is a device that allows computers to connect to the WLAN. Essentially, a WLAN port is a type of router. The difference between these devices and a standard router is usually the ports. Most routers for standard network connections have at least two wired ports, while a WLAN port usually has none. The only way to connect to one of these devices is through a wireless connection. To understand what a WLAN port is and isn't, you need to know a few networking terms. Local Access Network (LAN) – This is the network that exists in your home or office, to which all computing devices are connected. A wide area network (WAN) is a network outside the local area network, in general often just the Internet. The router allows the user's computer devices to connect to the network; it is basically the center of the system as well. Finally, a wireless router for physically connecting devices contains both ports, such as computers and game consoles, and wireless systems, such as laptops and some cell phones.

In most cases, a wireless or wired router will have at least two wired ports, but can have many more. As computer devices move more and more to wireless connections, these ports are used less. Some router companies have begun to create routers that have no wired ports at all; they only allow you to connect wireless systems. These devices have several names, one of which is the WLAN port.
In general, a WLAN port is exactly the same as a standard router, except for the wired connections. It will perform all routing functions and provide a basic firewall, just as the user expects from a standard router. The biggest difference is the initial connection. Many standard routers require a wired connection to perform the initial setup processes; since this is not possible in this case, it is not required.
The connection between WLAN and Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a cell with a diameter of up to 100 meters, within which a wireless LAN connects many different gadgets and computers.
The range of the Wi-Fi signal depends on the environment through which it spreads. The maximum range is achieved in open spaces, such as within a room, cafe halls, etc.
When passing through walls and ceilings, the signal is weakened, as well as if its path meets Powerful sources of electromagnetic radiation – microwave ovens, etc.
Quick Internet Setup with QuickSet.

In the Quick Setup Wizard "Quick SetThe "QuickSet" wizard provides several modes of operation for the router:
- CAP .CAP: A controlled access point which is controlled by a CAPsMAN server
- CPEClient mode which connects to an AP.
- Home AP.: The Home AP. This mode is suitable for simplified Internet access configuration.
- PTP Bridge AP.: Creates an access point for a remote PTP Br > client to connect to.
Select Home AP mode and proceed to configure the router as a regular Internet access point, which can be used for a small office or home.
Let's set up the WiFi.

Network NameName of the network. This is the name that will be visible to whoever is connected to your WiFi network.
Frequency: Normally, it is best to leave it set to Auto .The router will select the optimal frequency.
Band .Bandwidth range for your home router 2GHz-only-N. If there are older 802.11b or 802.11g devices on the network, then 2GHz-B/G/N mode should be selected, but there will be a loss in connection speed.
Use Access List (ACL).: Used to limit WiFi access. Before enabling this option, it is necessary to create a list of clients who are allowed access. Select from the list of connected clients and click Copy To ACL.
Normally, it is better not to use this function, as password authentication provides sufficient restrictions.
Bridge mode configuration
Select in the section Configuration operating mode Bridge.
If you want the Wi-Fi hotspot to receive network settings from the router automatically via DHCP, then in the Bridge make the following settings:

I prefer to specify the IP address of the Wi-Fi hotspot manually, so I know exactly where to look for it later. That's why I use static network settings.
If you are using static network settings, under Bridge make the following settings:
- Address Acquisition – select Static;
- IP Address – enter the IP address of the Wi-Fi hotspot. It must be from the same subnet as the router;
- Netmask . – enter the mask 255.255.255.0;
- Gateway – Enter the gateway IP address (the IP address of your router);
- DNS Servers – Enter the addresses of the DNS servers. You can specify your router's address or Google's DNS server address 8.8.8.8.