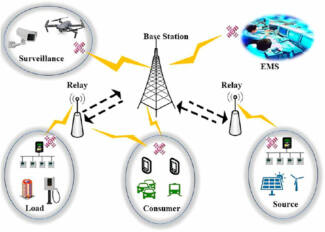
Trusted Wireless 2.0 also allows you to use devices as repeaters and, moreover, to reconnect if the signal breaks. That is, if the device loses the connection, it looks for another nearby repeater through which to transmit data. Thus, the link is restored and the data begins to be transmitted through the backup channel. It takes anywhere from milliseconds to seconds to reconnect, depending on the data rate selected. This kind of topology, where communication channels are lined up through randomly selected repeaters, is called mesh topology.
- Wi-Fi is a wireless data transmission standard
- History of wireless communications
- Reliability of data transfer
- Compatibility with other wireless networks
- Wireless transmission technologies and standards
- Bluetooth .
- Features of the wireless environment
- Radio frequency range
- Wired communication channels
- Coaxial cable
- Twisted Pair
- Wireless lines of communication
- Radio waves
- Infrared
Wi-Fi is a wireless data transmission standard
Wi-Fi is a technology for transmitting information wirelessly over a local area network using IEEE 802.11-based devices.
Around the world, the need for the ubiquitous presence of wireless networking is constantly growing, and this is especially true for the business sector. The technological capabilities of Wi-Fi are widely demanded in the telecommunications market. They are applied at organization of local networks having access to the Internet in different objects of public use, for instance in cafes, stations, airports, hotels and other places. Wireless modems act as both a receiver and transmitter, and they are used by mobile operators to organize the exchange of information over the network. Usually, to use cellular networks for communication, a SIM card must be installed in the modem. Wireless modems are included with various telemetry, dispatch and other similar equipment. A wireless modem can be used instead of a telephone modem, for example, in various automatic vending equipment, in an ATM, as well as for installation in various software and hardware systems. A wireless modem can be used wherever there is a mobile connection and a variety of computer equipment can be connected to the Internet so that it is possible to send electronic messages, carry out information exchange and the like.
History of wireless communications
It is well known that A.S. Popov was the inventor of radio, but at that time information data was sent by radio in the form of telegraphic signals. Then came the communication system based on radio telephones. Then it became possible to transmit images with the help of radio waves, and television broadcasting appeared. Further advances in telecommunications have led to the development of wireless networking technologies, categorized into the following types, which differ in the range of radio signal transmitters:
- PAN (Personal Area Network, which means personal networks). This is a network with a small coverage area (about ten meters).
- WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network, which means wireless local area network).The coverage range is about a hundred meters.
- WWAN (wide area wireless networks). This network uses wireless communication, which provides Internet access to mobile users.
- Technological technique of Wi-Fi (Wireless fidelity, i.e. wireless communication). Today, such network organization technologies are the most in demand with high demands on mobility, convenient implementation and use. This standard appeared in the ninety-seventh year of the twentieth century and is considered the standard for broadband wireless communication with the 802.11 series. Wi-Fi devices are generally used to organize wireless local computer networks, and in addition, to form a separate node for access to the Internet at increased speed.
Reliability of data transfer
The first thing that people start to question when thinking about networking using wireless technology is data transfer reliability. By reliable data transmission I would suggest that you should understand data transmission with a permanent connection and without data loss.
There are two primary causes of data loss and connection failure:
Electromagnetic interference in an industrial facility is generated primarily by frequency converters, electric drives, and other primary equipment. Such interference has a frequency range in multiples of kHz or MHz. And all of the technologies we took for comparison operate at 2.4 GHz. Interference from primary equipment simply does not reach this range. So the source of interference is other wireless systems transmitting at 2.4 GHz. There are two very different approaches to ensuring the electromagnetic compatibility of these systems:
- Using Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) broadband modulation;
- Use of Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS).

When FHSS is used, the frequency of data transmission changes in a pseudo-random order. In this case the interference will only affect one of the random frequencies, regardless of spectrum width.

FHSS
Thus, if serious electromagnetic interference occurs in the FHSS system will lose some data, and in the DSSS system data transmission will stop completely.
WiFi uses DSSS. The width of one channel is 22 MHz and, accordingly, 14 WiFi channels are available on the 2.4 GHz band. In Russia, only 13 are available, with 3 non-overlapping channels available for use. Many of you have probably observed the picture of WiFi completely going down at home. This can happen just because your neighbor's access point is operating on the same channel as your point, or on an overlapping channel.
Compatibility with other wireless networks
As mentioned above, interference can only be caused by other systems operating at the 2.4 GHz frequency. With the growing popularity of wireless networks in the industry, more and more wireless systems are being installed at facilities. As such, the question of interoperability between wireless networks is very important in order to provide a reliable and uninterrupted data stream.
The worst thing about interoperability is WiFi technology. Due to the fact that WiFi only uses DSSS as modulation, and the channel is quite wide, it is quite problematic to use it simultaneously with other wireless technologies. As mentioned above, we can only create three WiFi networks at the same time, but that only happens in an ideal world. In reality, there are many more WiFi networks in any apartment building or shopping mall and we end up with overlapping networks that worsen the connection quality and sometimes even make it impossible to connect to WiFi.
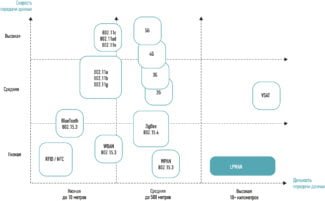
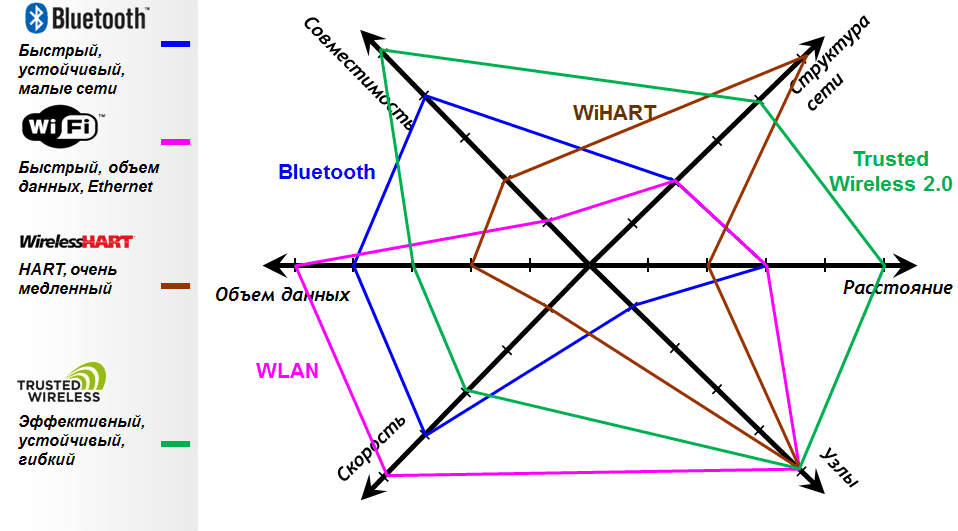
At the top of the compatibility list is Trusted Wireless. This protocol offers a "blacklisting mechanism" in addition to FHSS. This mechanism allows a range of frequencies that are used by other networks to be blacklisted. The frequencies on this list are not used by Trusted Wireless 2.0 devices, and there is no retuning to these frequencies.
Wireless HART is also not bad at compatibility – it also uses FHSS and has the ability to use "blacklists", but the small number of channels for frequency hopping does not allow it to be as flexible as Bluetooth or Trusted Wireless. In the latter two protocols, it is possible to switch to many other channels if there has been interference on a particular frequency.
Wireless transmission technologies and standards
Information technology is currently developing at a rapid pace. Information can now be transmitted using radio waves, infrared or laser radiation. This method of information exchange is much more convenient than the wired type of synchronization. The range will vary, depending on the technology.
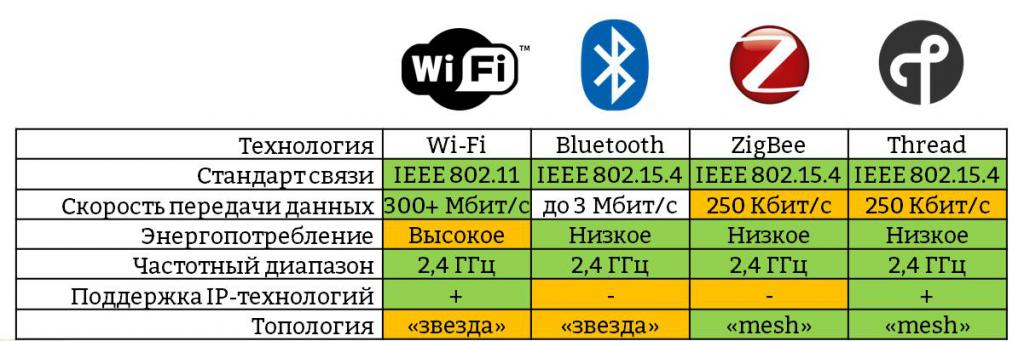
- Personal Networks (WPAN). Peripheral equipment is connected using these standards. Wireless computer mice and keyboards are much more convenient to use than their wired counterparts. The speed of wireless data transfer is quite high. Personal networks make it possible to equip smart home systems and synchronize wireless accessories with gadgets. Examples of technologies working with personal networks are Bluetooth and ZigBee.
- Local area networks (WLANs) are based on 802.11 products. The term Wi-Fi is now known to everyone. It was originally a product name given to the 802.11 series and is now used to refer to any product in the 802.11 family. WLANs are capable of creating a larger operating radius than WPANs, and the level of security has also increased.
- City Wide Area Networks (WMANs). These networks operate on the same principle as Wi-Fi. A distinctive feature of this wireless data transmission system is a wider coverage area, more receivers can connect to this network. WMAN is the same as Wi Max, a technology that provides broadband connectivity.
- Wide Area Networks (WWAN) – GPRS, EDGE, HSPA, LTE. Networks of this type can operate on a packet data basis or via circuit switching.
The differences in the technical characteristics of the networks determine their scope. If we consider the general properties of wireless networks, then we can distinguish the following categories:
Bluetooth .
Access point, as in the case of Wi-Fi, can be any device equipped with a special controller which forms a piconet around itself. This piconet may include several devices, if desired, they can be combined into bridges for data transmission.
Some computers and laptops already have a built-in Bluetooth controller, if this function is not available, then USB adapters are used which are connected to the machine and give it the ability to transfer data wirelessly.

Bluetooth uses a frequency of 2.4 GHz, while consuming as little power as possible. It is this indicator has allowed the technology to occupy its niche in the field of information technology. The low power consumption is due to the weak transmitter power, the short range and the low data transfer rate. Despite this, these characteristics were enough to connect and operate various kinds of peripheral equipment. Bluetooth technology has given us a wide variety of wireless accessories: headphones, speakers, computer mice, keyboards, and more.
- Grade 1. The range of wireless synchronization can reach up to 100 m. Devices of this type are usually used on an industrial scale.
- 2nd class. Radius of action is 10 m. Devices of this class are the most common. Most wireless accessories belong to this category.
- 3rd class. Range is 1 meter. Such receivers are put in game consoles or in some headsets, when there is no sense to distance the transmitter and receiver from each other.
Wireless data transmission system based on Bluetooth technology is very convenient for communication devices. The cost of chips is quite low, so equipping equipment with wireless connectivity is not too much of an increase in its price.
Features of the wireless environment
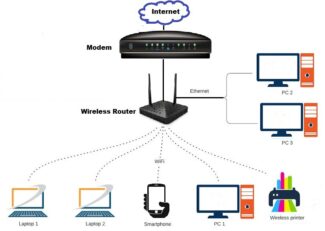
A network without wires is practically the same as an ordinary network, but the method of transmission is completely different. A network adapter installed in the user's PC or laptop communicates with an access point, which can easily be connected to a cable network. The most common method of communication without cabling is radio transmission.
In a wireless environment, the signal can be broadcast in a variety of ways. This occurs with the use of:
All system components guarantee user mobility and remove the limitation on maximum network length due to the absence of cable lines.
Radio frequency range
There are several types of RF connections without cable, depending on range and transmission distance. Systems that use radio waves have these standards:
- WPAN (ZigBee, Bluetooth) – operates in the 2.4-2.5 GHz ISM band. Devices are interconnected using a radio frequency channel, with one of the nodes acting as a coordinator. The technology helps establish communication between devices and with higher-level networks.
- WLAN (Wi-Fi) – data is broadcast on 5 and 2.4 GHz. The controller serves as the base, it controls the signal distribution to wireless equipment and is responsible for subscriber identification. It provides fast Internet access, good coverage and allows you to add additional access points to your Wi-Fi network.
- WMAN (WiMAX) is a broadband radio transmission for the scale of a metropolitan area. In most countries, 3.5 and 5 GHz bands are reserved for this purpose. Equipment the size of a conventional modem is installed both indoors and outdoors and can transmit radio pulses to objects at a distance of up to 80 km.
- WWAN (UMTS, HSDPA, CDMA, Mobitex, GSM, GPRS, CDPD) – uses cellular technology, operates within the operator's coverage area, covers a fairly large area and allows any device to connect at any time. The range of the base depends on the power of the radiation and is practically unlimited, the rate of transmission is affected by radio frequency and the distance from the distributing device.
Wired communication channels
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable Is an electrical cable consisting of a central copper wire and a metallic braid (shield), separated from each other by a layer of dielectric (inner insulation) and placed in a common outer jacket.
- Thin coaxial cable (~5 mm in diameter) has worse characteristics than the thick one, but it is easy to install, although it often breaks in the places of connector.
- Thick coaxial cable (~10mm in diameter), which provides good mechanical and electrical characteristics. However, it is difficult to install because it does not bend well.
This type of cable uses simplex mode (sometimes half-duplex). Great for use in digital and analog television broadcasting, but has not been used in computer networks for a long time.

Twisted Pair
A cable based on twisted pairs is a pair of twisted pairs of twisted pairs of insulated copper wires in a single dielectric (plastic) jacket. It is quite flexible and easy to lay. Twisting the wires minimizes inductive crosstalk between cables and reduces the influence of transients.

Twisted pair is one of the most common types of cable used in computer networks. Its standards and modifications are described in technology Ethernet .. Thus, cable types are divided into categories depending on bandwidth, number of turns, etc.

Twisted pairs (as well as many other types of twisted pairs) can be shielded и unshielded
Wireless lines of communication
Wireless lines – are communication lines that use various kinds of radiation to transmit a signal.
Unlike wired communication lines, wireless lines do not require a direct connection between devices using wires. This has both advantages and disadvantages.
Often, the radio signal spreads over short distances.
The radio signal can easily be tapped, so various encryption algorithms are used to protect the data itself.
But there is no need to lay a cable. This allows the use of various mobile devices as part of a network.
Radio waves
Radio waves – are electromagnetic waves that can transmit a signal in space. Depending on the task at hand, different frequency spectrums are used. Some of the most common network technologies that use radio waves as a transmission medium are Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LTE, cellular communications.
Radio waves use a narrowband frequency spectrum.
Infrared
Infrared uses a low frequency wave spectrum (up to 1000 GHz).
In contrast to the radio channel, infrared is not sensitive to electromagnetic interference. However, in this case, rather high transmitting power is required so that no other sources of thermal (infrared) radiation can interfere. Infrared communications also work poorly in very dusty environments. They are mostly used to communicate between computers and peripherals.
Non-directional antenna, coupled with a low-power transmitter (100 mW), limits the range of communication up to 30-50 meters.
So there is also special equipment for the organization of high-frequency infrared channels, which supports a capacity of up to 155 MBit / sec, with a range of up to 450 meters.
Read More: