The devices of this manufacturer are configured according to the following algorithm:
- Wi-Fi network mode b/g/n/ac. What is it and how to change it in the router settings?
- History
- Simplification of names
- How do I check for congestion and find the best available WiFi channel?
- Which 2.4 GHz wifi channel is best for a router?
- Setting up Wireless Router Modes of Operation over WiFi – How to Enable
- Access Point.
- Modem mode (ADSL Modem)
- Repeater
- How do I set up Asus router mode?
- Wireless Network Mode on ASUS Router
- Wireless mode on D-link.
- Protocol specifications
- Standard a
- 802.11b
- Which mode to apply
- TP-Link
- "Asus".
- Keenetic by Zyxel
- D-link
- What is the best Wi-Fi standard for your smartphone?
- TP-Link
- ASUS
- Working Frequency of Wireless Data Transmission
- Wireless Settings
- Click on "Basic Settings".
- History
- Simplification of names
- Which operating mode should I set for 5 GHz wifi – ac or ax?
Wi-Fi network mode b/g/n/ac. What is it and how to change it in the router settings?
Finally we got to the not quite known, but quite important topic – Wireless mode. Very often it is also called WiFi Mode. This name can be found in the settings of the router in the wireless network section, where in addition to the network name and password you can set this strange mod or another type. First, we need to understand what exactly it is.
Wi-Fi – in short, it is a wireless network. The transmission of information is through radio waves. It is by such waves that you receive text messages, make cell phone calls and also heat food in the "microwave". We will not go into the theory, but I think you understand the principle.
So initially it was necessary to invent a certain standard for data transmission that could be easily understood by an electronic device. In the process, the first IEEE 802.11a standard came out – the data rate was about 20 Mbps. It was that last number that denoted the so-called mode or kind of standard.
In the process a lot of different profiles came out but some of them get scrapped and only a few are currently in use and popular:
| 802.11b | Starts at 10-12Mbps and was approved in 1999. Also one of the earliest standards at 2.4 GHz |
| 802.11g | Transmission speeds are already higher, up to 50 Mbps. It was approved in 2003. |
| 802.11n | One of the most popular standards at the moment. With speeds of 150 Mbit per second at 2.4 GHz. But it can also operate safely at 5 GHz and deliver speeds up to 600 Mbps. First released to the general public in 2009. |
| 802.11ac | The standard runs at 5 GHz and speeds start at 433 Mbps. But it can be overclocked up to 6 Gbps using MU-MIMO technology. |
History
The basic Wi-Fi standard 802.11 with a transmit/receive rate of 1 Mbps dates back to 1996. The signal solved the problem of setting up special facilities, but only as a starting point for new developments. Later, when mobile devices with Internet reception came along, new types of Wi-Fi were needed.
Manufacturers of routers offer a product line – a selection of routers, the technical characteristics of which require clarification to understand the capabilities of the device.
Important! wi-fi standards b, g, n – this is a letter designation of the modes of the wireless network, each of which provides information about the speed of the signal from the router to the adapter (Mode).
The buyer's desire to use the new speed mode causes confusion, for which the manufacturer offers three in one – bgn Wi-Fi. The fact is that a tablet, computer or other device, which is used by a person, may not support the new speed mode. The specifications of the adapters on older laptops (the year of manufacture earlier than 2009) will not be able to accept the standard n, because at the time of manufacture there was no such thing.
Simplification of names
Computers, smartphones, netbooks, and other products with built-in Wi-Fi controllers use the IEEE standard alphabetic characters for labeling.
Please note: Such labeling is understandable for specialists, but not yet for all buyers.
The names have been simplified for ease of reading. Now the main Wi-Fi standards will be publicly referred to as numbers instead of letters.
The controller icon will change when the device switches between different Wi-Fi networks, the user will get information about which versions are available. The indicator with the number 6 indicates that the device is using the most advanced Wi-Fi version 6 to date.
How do I check for congestion and find the best available WiFi channel?
In order to make sure that everything works steadily and without interference, you should first check what channels are engaged on your neighbors' access points. To find the freest wifi channel and choose the best one for your specific situation, we will use a free application – wifi channel scanner for smartphone, called Home WiFi Alert. It is free for Android users, but for the iPhone I could only find paid analogues.
Install it and run it, then go to the section "TD Structure" and select here the 2.4 Ghz band with a checkbox.

Many people will have the same picture that I have – you will find a lot of parallel networks from different access points with different reception strengths. The number next to their name is the channel on which they are operating. Three on "10", three on "1", one each on "6" and "7".
Which 2.4 GHz wifi channel is best for a router?
For the best communication quality, you need to reconfigure the channel and choose a frequency that is 5 units different from the most used. In our case from the first and the tenth (there are 14 in total, by the way).
Consequently, the fifth and sixth channels will suit me best, but since "6" is already there, let's choose "5".
There is also a similar program for the laptop – Inssider. Install it, run it, and it will start scanning the air and determine the parameters of each network in the access area. We will be interested in the parameter "Channel".

For convenience, here is a detailed list of non-intersecting channels:
Did you notice I left out 12, 13, and 14? The thing is that different countries have their own laws regarding the number of allowed WiFi channels. For example, in Japan it is all 14, and in France it is only 4. In Russia and the CIS countries, 13 channels are supported. Well, if you have a router made in or for the States, it will only have 11 channels.
Once you have selected the most suitable free channel, you can move on to the settings on the router.
Setting up Wireless Router Modes of Operation over WiFi – How to Enable
The question on the agenda is how to set up a WiFi router mode? If you're going to set up a wireless network in your home, I recommend choosing a router over an access point, modem, repeater, or anything else for this purpose. Why? Because it is a multifunctional device and it takes the place of all of these things. In this article, we will look at its main modes of operation and see how they are configured using the Asus model as an example.
First of all, we need to understand the concepts. There are a total of four basic modes in a router:
Access Point.
In Access Point mode, or as it is called by foreigners "Access Point", a router works as a device that converts a cable signal into a wireless signal. The main difference between a router in Access Point mode and another network device, which is actually called "access point", is that not only does it distribute WiFi, which means it turns a wired Internet signal into a radio signal, but it also has functionality for distributing IP addresses and port forwarding, which is the main function of a router.

Modem mode (ADSL Modem)
In pure video, the modem is a device that is designed to work with providers who provide access to the World Wide Web via a telephone cable using ADSL technology. And for nothing else – the modem itself in router mode or simply can not work. But a router in the modem mode with ADSL support can not only receive the Internet via the telephone cord, but also retransmit it wirelessly and assign IP to other clients.

Repeater
Generally speaking, a "repeater" is a wireless signal extender or repeater, which extends the signal from the wifi sharing point to some distance to connect computers in the area of uncertain reception to the Internet. If our favorite wifi router has repeater mode, it means it can do the same thing – extend the wireless signal, thereby extending the reception area. In addition, repeater mode is useful if you need to bypass some obstacle when creating a wireless bridge, when there is no line of sight between the two access points. Then we put the router in repeater mode within line of sight of both access points and transmit the signal through it.
How do I set up Asus router mode?
The router mode is set up differently in different models. We will need to connect to some existing wifi, which is distributed by some other router, and distribute it already in our apartment. I will show you by the example of Asus RT-N10U B in the new firmware.
Go to Admin (http://192.168.1.1), point "Administration", tab "Mode" (red) or just click on "Wireless Router" at the very top of the settings page (green).

At the moment, "Wireless Router" mode is activated by default. You'll find its settings in this article, and we'll put a check mark on the second-to-last one, repeater mode. And we press the "Save" button.
A page will open displaying all wireless networks within range of the router. Choose the one to connect to and enter the access key, if it is password-protected.

Press connect. After connecting to a third-party router, you can make another interesting setting: either use the data to access the existing network, which we are extending. Or set your own – then we connect to ours with one data (SSID and password), and to the second one, in which the Internet cable is directly inserted and whose signal we are extending, – with others.

Then it's a matter of waiting until all these settings are applied, and you disconnect from the network. Then in the list of available wireless connections appears the new one you just created. Connect to it and go forward to the open spaces of Runet!
Wireless Network Mode on ASUS Router
Go to the settings of the router ASUS by the address 192.168.1.1. Then open the "Wireless Network" section. On this page is the setting we need.

- "Auto" is b/g/n. Maximum compatibility.
- "N Onle" – work only in n mode, maximum performance. Without support for legacy devices.
- "Legacy" is when devices can connect over b/g/n, but the standardf 802.11n speed will be limited to 54 Mbps. I do not recommend this option.
In the same way, change the settings for the other band. By selecting in the menu "Frequency range" – "5GHz". But there I advise to leave "Auto".
Wireless mode on D-link.
Open the control panel of the router D-link at 192.168.1.1 (more details in this article), or see how to enter the settings of the router D-Link.
Since they have many versions of the web interface, let's look at a few of them. If your case is a light web interface like the one in the screenshot below, then open the "Wi-Fi" section. There will be a "Wireless Mode" item with four options: 802.11 B/G/N mixed, and separately N/B/G.


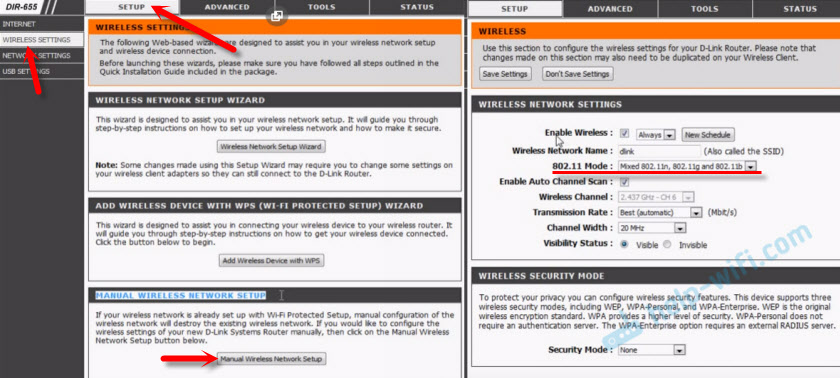
Protocol specifications
Each of the protocols at the time of its release was considered the most modern and advanced, has personal characteristics and capabilities.
Standard a
In spite of the fact that the date of its adoption is considered 1999, in practical application it entered only at the beginning of the noughties. It is used in technologically advanced countries, such as Japan and America. In domestic conditions has not reached a sufficiently large popularity. It uses a signal modulation scheme, which works on the principle of multiplexing with separation according to orthogonal frequencies.
Note! A large mass of information is divided into parallel sub-streams with low bit rate, subsequently, a certain number of carriers is used for modulation.
The protocol establishes three mandatory information exchange rates, at six, twelve and twenty-four Megabits per second, as well as as as many as five additional ones. It is possible to use two channels at the same time, and the speed of data exchange increases several times.
802.11b
In this particular case, the method of broadband modulation and direct spectrum expansion is applied. The range of operation is fourteen channels, which are distributed in increments of 25 Megahertz. This is done so that there is no interference and crossing of signals. When one channel works, information is not transmitted through the others. Three channels can be applied at the same time.
The maximum Wi-Fi speed will depend on the amount of interference and the distance between devices.
The protocol introduces the highest possible transmission speed of 11 Megabits per second, which is comparable to a 10 BaseT Ethernet wired network. This speed occurs only when information is transmitted by a single WLAN device. If an increased number of subscriber stations is applied at one time, the data is distributed evenly among subscribers, which leads to a reduction in the speed of a particular device.
Which mode to apply
Basic router settings have already been configured. Often, 802.11b/g/n mixed, or 802.11n/ac mixed is chosen. This means that the standard is of the mixed category. It is used so that the router can connect to a very old device as well as to the most modern one.
Each router has its own interface which allows it to change the protocol at the user's discretion. This is done to increase the bandwidth.
TP-Link
Important! If the device can work in two bands, you can also change the frequency.
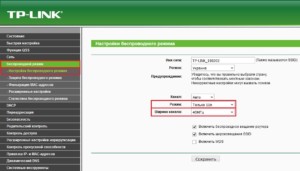
"Asus".
In devices of this manufacturer, it is necessary to follow the following order:
- Open the web interface of the router by going to 192.168.1.1;
- enter the "Wireless Network" section, where the necessary menu is located;
- select from three formats: "Auto", which corresponds to b/g/n. Maximum compatibility. "N Only", the ability to work only in n mode, maximum performance. No support for legacy devices. "Legacy", meaning devices can connect according to b/g/n, however, the speed of 802.11n will be limited to 54 Mbps. It is not recommended to use this option.
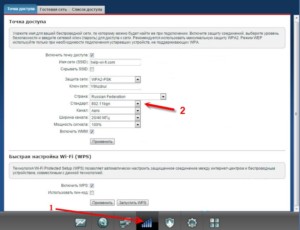
Keenetic by Zyxel
It is necessary to enter the interface of the router and find the "Wi-Fi network" section. There will be a menu on the right side of the screen called "Standard". It is necessary to save the changes, when the desired standard is set, otherwise the changes will not be saved.
D-link
There are several variants of interfaces on the devices of the represented manufacturer. However, there are not many differences in them. It is necessary to find the section with the name similar to "Wireless standard" and set one of the four proposed options in the menu.
What is the best Wi-Fi standard for your smartphone?
What the choice of standard wi-fi connection for your smartphone can mean, you can consider, having analyzed the characteristics:
Smartphones support all compatible modes. Running a mobile device at 5MHz and using the 11ac standard will give a stable connection, provide high-speed content transfer and protection from interference. However, there is still a disadvantage – at 5 MHz, the waves overcome obstacles worse. The second nuance – what router mode for a smartphone is better to choose. Of course, the devices must be compatible and the router is needed with the same standard. Adaptive antenna is able to transmit a directional signal to the user.

Other router standards will provide speeds of no more than 150 Mbps.
Thus, if the user has a technique with a wi-fi module, it is not difficult to choose a standard that will provide access to the Internet. All that is needed is to understand the difference in standards, and check the settings of the wireless router.

Podgornov Ilya Vladimirovich All articles on our site are audited by a technical consultant. If you still have questions, you can always ask them on his page.

How to connect and configure the Wi-Fi network on the laptop. Use of new technologies wireless networks – has long become a habit. But with the rapid technical development of the user can have various difficulties and questions.
TP-Link
First, you need to go into the TP-Link router settings, or use the TP-Link Tether app to control it from your phone (if your router supports this function).
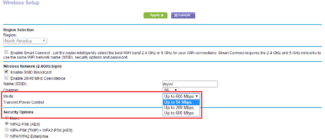
On routers with the new web interface, the 5 GHz band settings are under Advanced Settings – Wireless Mode – Wireless Mode Settings. There is a tab "5 GHz" where you can disable or enable the Wi-Fi network by unchecking/unchecking "Enable Wireless Broadcasting". You can change the network name, password, set the transmitter power, etc. If the network works fast and stable, I do not recommend to change the factory settings (except the name and password) .
There may also be Smart Connect settings. If it is enabled, the devices will see the same network and choose the range to connect to. The network name and password will be set the same for both bands.

On some TP-Link router models, the 5 GHz band settings look like this:

And on routers with the old web interface, these settings are under "Wireless Mode – 5 GHz":

And you can disable or enable the network on a certain frequency in the "Select operating frequency" section.
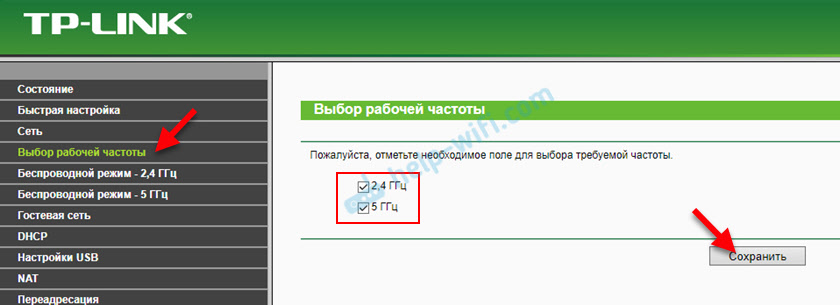
Just uncheck/check the box next to the desired frequency and save the settings. Don't forget to save the router settings after changing the parameters!
ASUS
It is possible to change the settings of the 5 GHz Wi-Fi network on the ASUS router in the web interface, in the "Wireless Network" section. There, in the drop-down menu, you need to select the frequency range "5GHz", set the necessary parameters and save the settings. If you don't know how to enter the settings of your ASUS router – see this article.
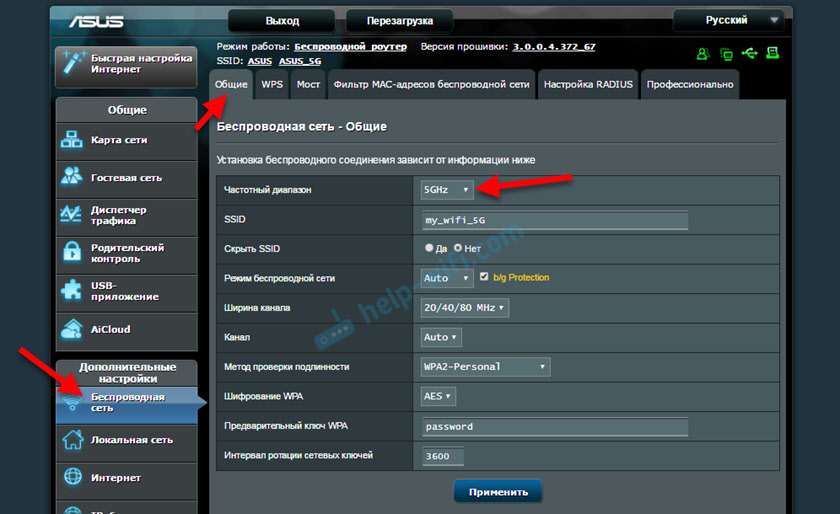
You can disable or enable 5GHz on the tab "Professional". Select the desired range and below near the item "Enable Radio Module" put "Yes" or "No".

Working Frequency of Wireless Data Transmission
If you don't need any network, you can go to the "Select Operating Frequency" tab, and disable the network at that frequency. Uncheck the box next to the unwanted network and save the settings.

But, you can keep both networks. For example, connect older devices to 2.4 GHz, and those that support it to 5 GHz Wi-Fi.
The primary difference between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz wireless frequencies is the range of the signal. When using the 2.4 GHz frequency, the signal is transmitted over a longer distance compared to the 5 GHz frequency. This is due to the basic characteristics of the waves and occurs as a result of the fact that at a high frequency the waves decay faster. That is, if you are more concerned about signal coverage, you should choose the 2.4 GHz frequency.
The second difference is the number of devices operating on these frequencies. The 2.4 GHz wireless signal is more susceptible to interference than the 5 GHz frequency. This is because many of the devices around us also operate at 2.4 GHz. Most of these devices are microwave ovens and cordless phones (or other devices). These devices interfere with the frequency environment, which further reduces the speed of your wireless network connection.
In both cases, choosing the 5 GHz frequency is the best option because you have more channels at your disposal to isolate your network from other networks and there are fewer sources of interference on that frequency.
To be brief, if your room has a lot of interference and your devices support the 5 GHz frequency, it is recommended that you use the 5 GHz wireless network. Otherwise, it is better to use the 2.4 GHz frequency.
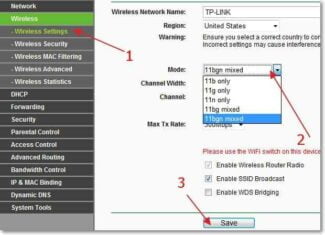
Wireless Settings
Click on "Basic Settings".
Next, go to the tab of the Wi-Fi network you want to configure. For example, as in my case. "Wireless Mode – 2.4 GHz.".
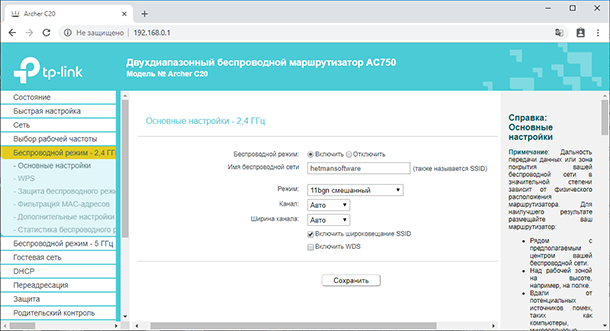
Turn on wireless mode (if it's off), and set "Wireless Name" network in the menu "Basic Settings.". The name can be anything you like.
- 11b – operates in the 2.4 GHz band. Speed up to 11 Mbps.
- 11g – Operates in the 2.4 GHz band. Speed up to 54 Mbps.
- 11n – speeds up to 150 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band and up to 600 Mbps in the 5 GHz band.
- 11ac is a new standard that only works in the 5 GHz band. Data rates up to 6.77 Gbps.
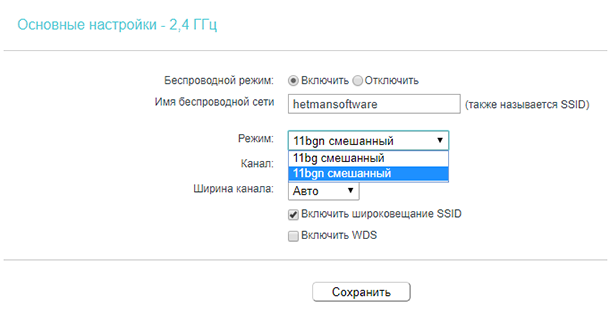
Newer modes are compatible with older modes, but not vice versa.
Typically, the default mode is automatic "11b/g/n mixed" for a 2.4 GHz network, or "11a/n/ac mixed" for the 5 GHz network. This is for maximum compatibility. So that both older and newer devices can be connected to the router.
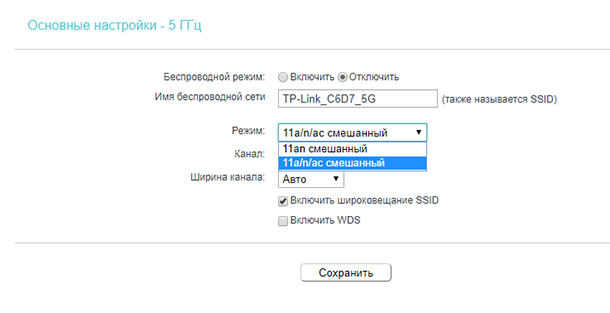
I recommend checking and setting the most complete and compatible mode present in the menu.
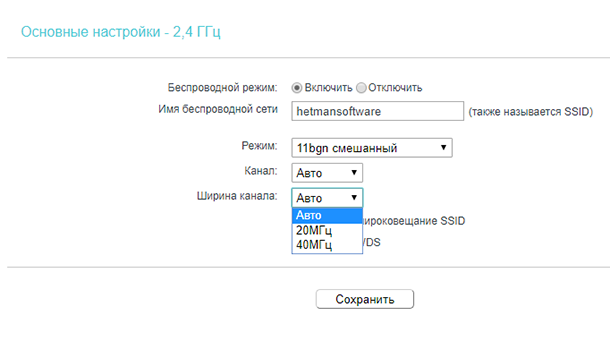
The Channel and Channel Width field is where you set the operating frequency that the router will use in wireless mode. The wireless channel should only be changed if you observe problems related to interference caused by another access point located near your equipment. If you select automatic mode, the access point will automatically select the most appropriate channel. Therefore, do not change anything here or set the automatic mode.
History
The basic Wi-Fi standard 802.11 with a reception-transmission rate of 1 Mbps dates back to 1996. The signal solved the problem of setting up special facilities, but only as a start for new developments. Later, when mobile devices with Internet reception came along, new types of Wi-Fi were needed.

Router manufacturers offer a product line – a selection of routers, the technical characteristics of which require clarification to understand the capabilities of the device.
Read also: The best portable game consoles from Aliexpress. Top 10 Handheld Consoles of 2021
Important!!! Standards wi-fi b, g, n are letter designations for wireless network modes, each of which provides information about the speed of signal transmission from the router to the adapter (Mode).
The buyer's desire to use the new speed mode causes confusion, for what the manufacturer offers three in one – bgn Wi-Fi. The thing is that a tablet, computer or other device that a person uses may not support the new speed mode. The specifications of the adapters on older laptops (the year of manufacture earlier than 2009) will not be able to accept the standard n, because at the time of manufacture there was no such thing.
Simplification of names
Computers, smartphones, netbooks, and other products with built-in Wi-Fi controllers use the IEEE standard alphabetic characters for labeling.
Please note! This labeling is understandable for experts, but not yet for all customers.
A simplification of names has been adopted for ease of reading. Now the main Wi-Fi standards will be publicly named with numbers instead of letters.

The controller icon will change when the device switches between different Wi-Fi networks, the user will get information about which versions are available. The indicator with the number 6 indicates that the device is using the most advanced Wi-Fi version 6 to date.
Which operating mode should I set for 5 GHz wifi – ac or ax?
The question of choosing a wifi operating mode for the 5 GHz frequency band is not so acute. Because it is unlikely that the average Internet user ever got his hands on a router that supports the standard "ax". The most popular today is the "ac" mode, so most models do not even offer a choice between them. Most often we see the same mixed type "802.11 A + n + ac".

If the "AX" standard is supported, then again, it is more logical to choose the mixed type for best wifi standards compatibility between all computers, laptops, smartphones and TV set-top boxes connected to the router.
Read More: