What the choice of wifi connection standard for your smartphone can mean, you can consider by analyzing the characteristics:
Wi-Fi network mode b/g/n/ac. What is it and how to change it in the router settings?
Details on what b/g Protection is in your router. Wi-Fi Legacy or N-Only mode: which one to choose and what the differences are. How it affects the speed of the Wi-Fi network.
Let's take a simple example. Here we have an iPhone 3GS, it can work in Wi-Fi only in b/g mode (if the specifications are true). That is, in the new, high-speed mode n it can not work, it simply does not support it.
And if you have the router, as the wireless mode will be nIf you will have n mode on your router, without any mixed, you will not be able to connect the phone to Wi-Fi, and you will have to bang your head against the wall here :).
But it does not necessarily have to be a phone, much less an iPhone. Such incompatibility with the new standard can also be observed on laptops, tablets, Wi-Fi receivers, etc.
A few times already noticed that when there are a variety of problems with the connection of phones, or tablets to Wi-Fi – it helps to change the mode of Wi-Fi.
If you want to see what modes your device supports, then look in its specifications. Usually the supported modes are listed next to the "Wi-Fi 802.11" mark.
You can also find the modes that your router can operate in on its package (or on the Internet).
Here is an example of the supported modes that are printed on the box of the TP-LINK TL-WN721N:

Basic Concepts
Before we begin, let's review the basic terms used in this article:
- Authentication – Authenticating a user when connecting to an access point. Most often this is done by entering a password, but there are also other ways, such as filtering by MAC address.
- MAC Address – The physical address of the device that is tied to its network module.
- SSID – The wireless network identifier, its name used for detection by other devices. SSID broadcasting can be turned off, then you will need to enter it manually to connect to Wi-Fi.
- BSSID – MAC address of the access point.
Wireless Network Modes
By far the most common modes are:
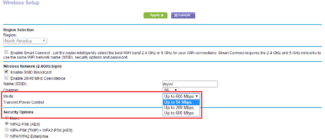
- 802.11b with transmission speeds up to 11 Mbps;
- 802.11g with data rates up to 54 Mbps;
- 802.11n has speeds up to 150 Mbps;
- 802.11ac with speeds up to 6.77 Gbps.
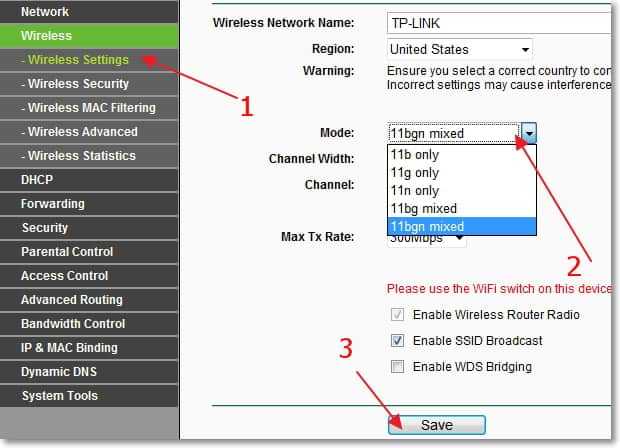
If you pay attention to the name "11bgn mixed", you can guess where the number 11 and the letters bgn come from. 11b, 11g, 11n are all names for Wi-Fi wireless modes of operation.
Without going into technical complexities, for simplicity of understanding we can say that the main difference between all these modes is their speed at which they can transfer data "over the air".
It is also worth considering that all of these modes did not appear at once, but at intervals of several years. Consequently, those devices (laptops, smartphones, tablets, TVs) which were released for example before 2009, which is the year when 802.11n mode appeared, do not have its support. They can only work with g and n modes.
It is for this reason that all routers are almost always set to wireless 11bgn mixed mode (AUTO) by default. Mixed in this case means that any device that supports at least one of the b,g or n modes can connect to the router via Wi-Fi.
Which is the best mode to set?
In order to avoid problems with the connection to the router, it is best to leave exactly 11bgn Mixed mode, as it provides maximum compatibility and support for connecting all Wi-Fi devices. Moreover, even if you do not have older devices that work with Wi-Fi, although it is in such cases, many advise to set 11n only (11n only) allegedly this in theory should increase the speed and stability of the wireless connection.
It is worth mentioning that this value (11n only) has a downside. Cases when devices stop seeing your Wi-Fi network or when you get a "Windows could not connect to …" error are very often due to setting the wrong wireless network mode.
Finally we got to the not quite well known, but quite important topic – Wireless mode. This is also often referred to as WiFi Mode. This name can be found in the settings of the router in the wireless network section, when in addition to the network name and password you can set this strange mod or under another type. To begin with, we need to understand what exactly it is.
Wi-Fi – in short, it is a wireless network. The transmission of information is through radio waves. It is by such waves that you receive text messages, make cell phone calls and also heat food in the "microwave". We will not go into the theory, but I think you understand the principle.
Initially it was necessary to invent a standard for data communication which could be easily understood by an electronic device. In the process, the first standard was IEEE 802.11a, which was about 20 Mbps. It was that last number that denoted the so-called mode or kind of standard.
In the process, a lot of profiles began to come out, but some were sifted out and at this time used and popular only a few:
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| 802.11b | Operates at 10-12 Mbps and was approved in 1999. Also one of the earliest standards at 2.4 GHz |
| 802.11g | Transmission speeds are already higher, up to 50 Mbps. It was approved in 2003. |
| 802.11n | One of the most popular standards at the moment. With speeds of 150 Mbit per second at 2.4 GHz. But it can also use 5GHz and reach speeds of up to 600 Mbps. It was first released to the general public in 2009. |
| 802.11ac | The standard runs at 5 GHz and speeds start at 433 Mbps. But it can be overclocked up to 6 Gbps using MU-MIMO technology. |
Configuring the wifi standard on Keenetic
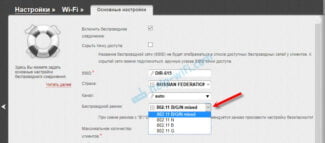
To specify wifi mode on your Keenetic router, you need to go to "Home network" in the control panel and open the "Advanced settings" link

Here, under "Standard" select "802.11bgn" and change the channel width to 40 MHz

Why change the mode of the wireless network?
It's very simple. Let's look at an example. Here we have an iPhone 3GS and it can work in Wi-Fi only in b/g mode (if the specs don't lie). That is, in the new, high-speed mode n mode, it can't work, it just doesn't support it.
And if you have the router, as the wireless mode will be nAnd if you have a router with n , without any mixed, you will not be able to connect the phone to Wi-Fi, but you will have to bang your head against the wall :).
But it does not have to be a phone and especially the iPhone. Such incompatibility with the new standard can be observed in laptops, tablets, Wi-Fi receivers, etc.
I have already noticed several times that when there are various problems with the connection of phones or tablets to Wi-Fi – it helps to change the mode of Wi-Fi.
If you want to see what modes your device supports, look in its specifications. Usually the supported modes are listed next to the "Wi-Fi 802.11" mark.
You can also check on the package (or on the Internet) to see what modes your router can operate in.
Here is an example of the supported standards which are printed in the box of the TP-LINK TL-WN721N:
Read More: