Never allow your device to automatically connect to any Wi-Fi network that you do not control.
- Understanding what Wi-Fi is – how it differs from Ethernet
- The place of Wi-Fi in the OSI model
- What is Wi-Fi and why we need it
- A brief history of wi fi technology
- How wi-fi works
- Use Wi-Fi safely
- Where is the Chicago airport Wi-Fi network here?
- Connecting Wireless Internet to Your Computer
- Windows XP
- Windows 7
- What should I do if my computer can't connect to Wi-Fi?
Understanding what Wi-Fi is – how it differs from Ethernet
Wi-Fi is now the most popular technology for transmitting data over wireless computer networks. The name Wi-Fi is a trademark belonging to the wi-fi alliance. The technical description of the technology is contained in the IEEE 802.11 standard.

Previously, wi-fi deciphered "Wireless Fidelity" wireless fidelity, but now it is believed that wi-fi does not decipher anything and just looks like a play on words Hi-Fi, that is high quality.
For a manufacturer to be able to call his equipment Wi-Fi he must submit it for inspection to the company Wi-Fi Alliance. This company checks whether the equipment meets the requirements of the IEEE 802.11 standard. And the right to use the wi-fi trademark is given after the wi-fi alliance verifies that the equipment is fully compliant with IEEE 802.11.
In comparison, for ethernet such verification is not performed, the manufacturer can create equipment which works according to the 802.3 standard and its modifications and call it an Ethernet switch
The place of Wi-Fi in the OSI model
Wi-Fi as well as Ethernet is located at the physical and data link layers, and at the data link layer two sub-layers are used, the MAC medium access control sub-layer and the LLC logical link control sub-layer.
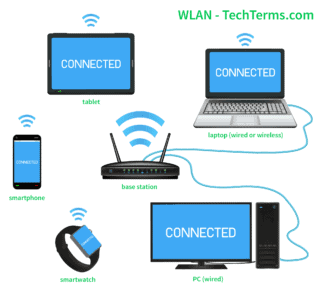
Wifi can work in two modes, wifi infrastructure mode is often used with wireless equipment, the so called access points, which are connected to a wired network and then to the Internet. Now wifi is most often used to connect to the Internet. So infrastructure mode is the most popular.

Another connection option is also possible, a peer-to-peer network, where computers communicate without any access points, directly with each other.
What is Wi-Fi and why we need it
Wi-Fi is a technology of wireless data transmission within a local area network, performed by devices based on IEEE 802.11 standards.
In simple terms, for people who are not familiar with the subject, wi-fi is a data transmission technology that uses invisible radio waves instead of wires. Similar technologies include infrared transmission, radio and Bluetooth.
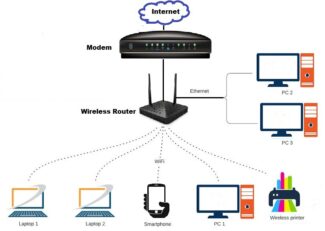
Wi-Fi is not the Internet, as many ordinary users mistakenly believe. It is a technology that creates a local network where data is exchanged between different devices (printers, cell phones, laptops) without going to the World Wide Web. Connecting to an ISP via a modem, router or access point allows devices on this network to access the Internet.
The number of devices that can be connected simultaneously depends on the technical capabilities of the router.
Wi-Fi-technology is necessary for devices that cannot be connected via cable. These include laptops, cell phones and tablets.
Technical characteristics of Wi-Fi make it possible to use it even at the scale of an industrial enterprise. The technology is convenient to use at dangerous and remote sites, as well as at the sites of secret production.
Thanks to wifi simple user becomes more mobile and does not depend on the length of the cable.
A brief history of wi fi technology
There is a widespread view that the history of Wi-Fi goes back to the early 90s of the last century. It was then that the first wireless technology in the world was created in the Netherlands. It is a kind of forerunner of modern Wi-Fi. But such a statement is a bit at odds with the reality.
In fact, the history of Wi-Fi goes back to 1985. At that time, the Federal Communications Agency of the United States approved the unlicensed use of radio frequencies by all users.
How wi-fi works
Wireless networking is based on the use of radio waves, and the exchange of information is similar to a radio negotiation:
- A wireless data adapter converts the information into a radio signal, then it is transmitted to the airwaves via an antenna.
- The wireless router receives and converts the signal back. It then transmits the data to the Internet using a cable.
- It does the same for data reception. After receiving data from the Internet, the router transforms it into a radio wave signal and uses an antenna to send it to the wireless data adapter.
Many first-time users mistakenly think that a router and a router are two different devices. In fact, both devices are the same network equipment. Router is an English word, and router is a word derived from the Russian sow "route."
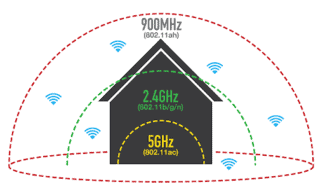
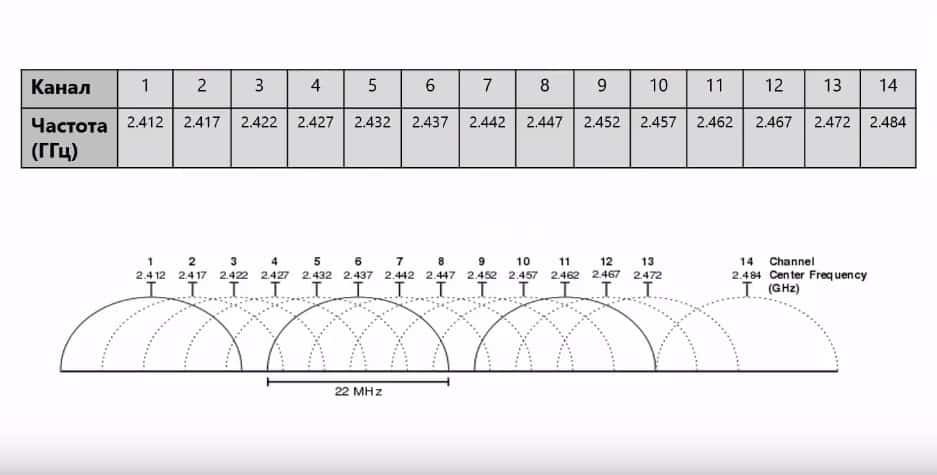
The receivers and transmitting devices used in Wi-Fi networks resemble those used in cellular phones and portable radios. They differ in that Wi-Fi devices operate on 2.4 and GHz radio frequencies. This makes it possible to transmit more information.
Use Wi-Fi safely
Even if you don't have your own network for security, you can improve your protection with the way you use Wi-Fi networks.
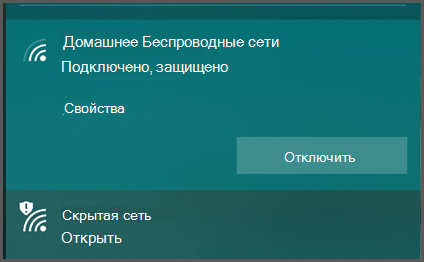
If you need to connect to a public Wi-Fi network, choose an encrypted network. Yes, it takes a little more work to connect because you usually have to find and enter a password, but it's important to have that level of security, especially in a public location.
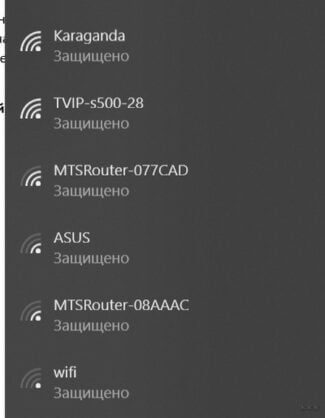
You can usually identify encrypted networks by the message "secure" or similar, and by an icon indicating that it is secure.
Open networks usually say "Open" and may have an icon indicating that they are not secure.
If you're connecting to a public Wi-Fi network, don't check "Connect automatically" or "Remember this network." While this is really handy, you don't need your device to automatically connect to public Wi-Fi networks. Why? It has to do with how the "Remember this network" feature works.
Where is the Chicago airport Wi-Fi network here?
When you tell your device to remember Wi-Fi networks, it will constantly monitor that network. If you are walking down the street and your device is turned on, it is constantly looking for one of the saved networks. When a saved network appears, the device will try to connect to it automatically.
Your device sees Wi-Fi networks by their SSID, which is essentially the name of the Wi-Fi network. However, most Wi-Fi routers can be configured to broadcast any name. You can set your Wi-Fi router's SSID as "Igor's House," "Contoso Electronics," or. "Free_ORD_Wi-Fi," which is the SSID of the actual Chicago airport Wi-Fi network.
If you went through the airport, connected to the airport's free Wi-Fi, and allowed your device to "remember" that network, when your device sees the router, any router that has the same SSID that will try to connect. Once connected, it will start sending and receiving traffic through that router. It can log into social networks (passing your username and password), and your email, banking, or just about any application open on your device can start communicating on this network. Despite the fact that this network may not be a legal network.
Connecting Wireless Internet to Your Computer
As a rule, modern versions of operating systems, particularly Windows, find the necessary drivers for such devices on their own. If this does not happen, then you will have to use the installation disk, which is included with the equipment.
After that you can proceed to connecting Wi-Fi on a desktop computer.
Windows XP
This version of the operating system has a peculiarity – there is no quick access to Wi-Fi connections. In order to configure the connection to the wireless network, you need to open "Control Panel", go to "Network Connections", find the name of the access point and log in.
Further configuration is done similarly to Windows 7.
Windows 7
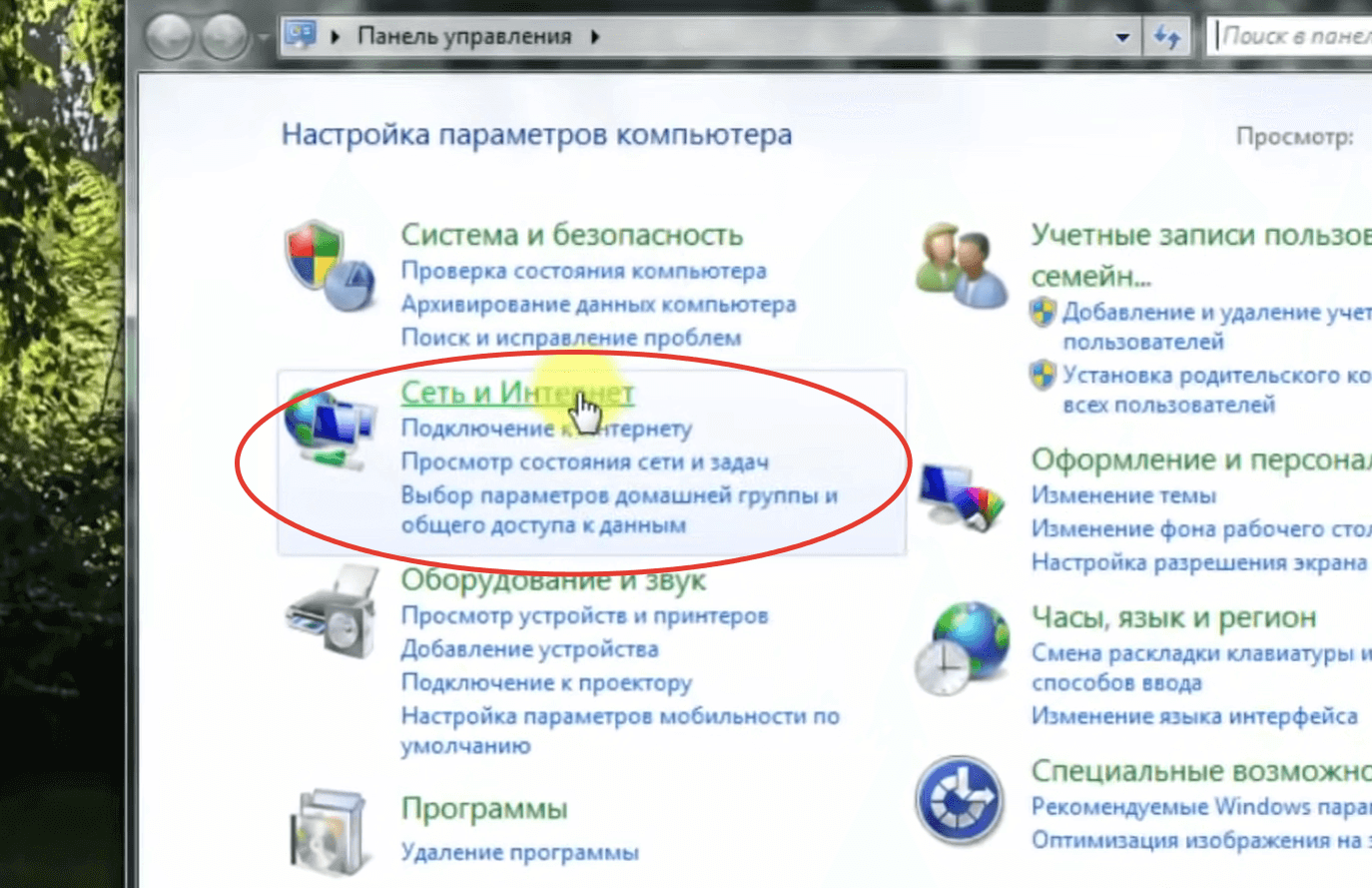
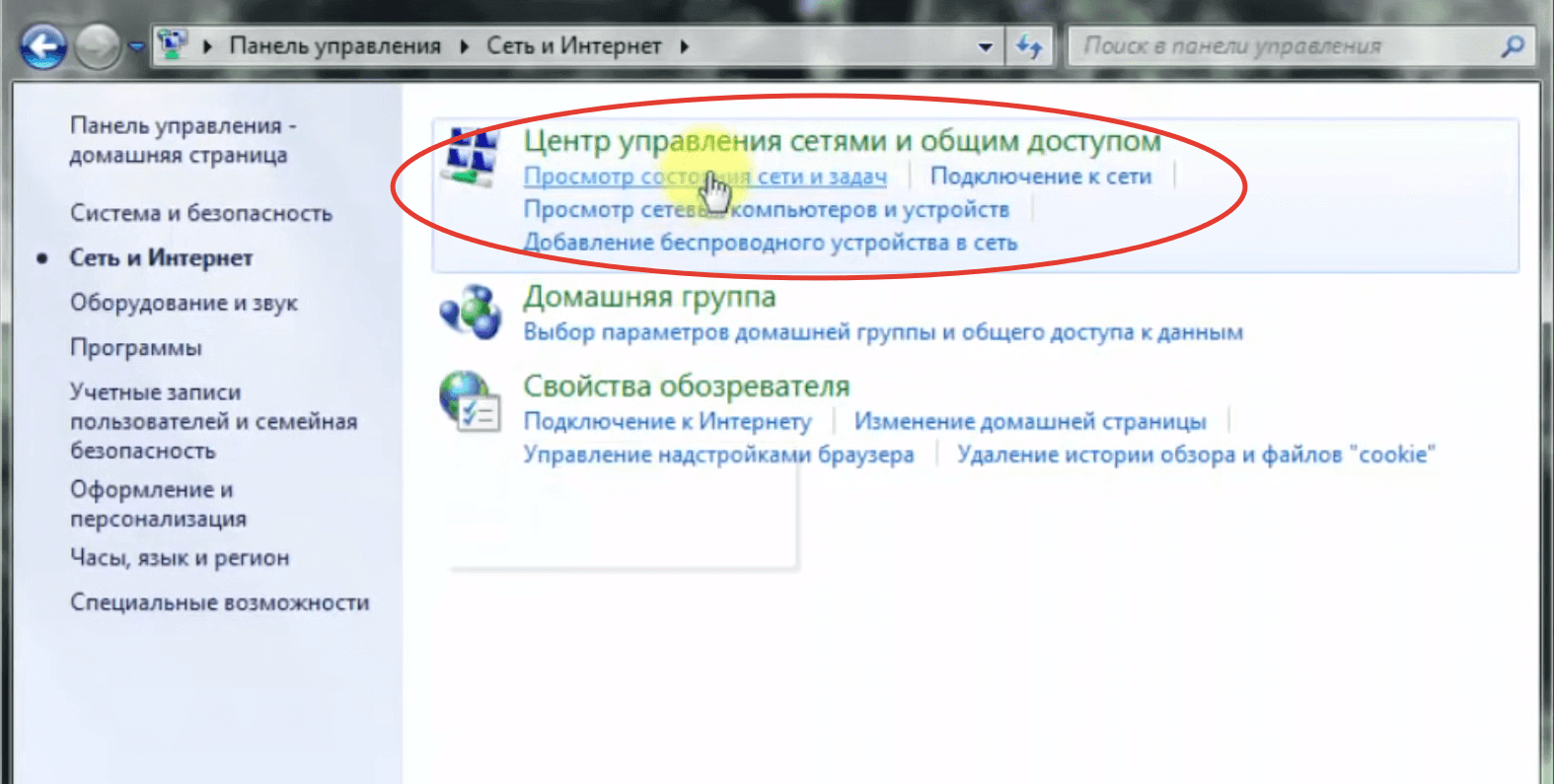
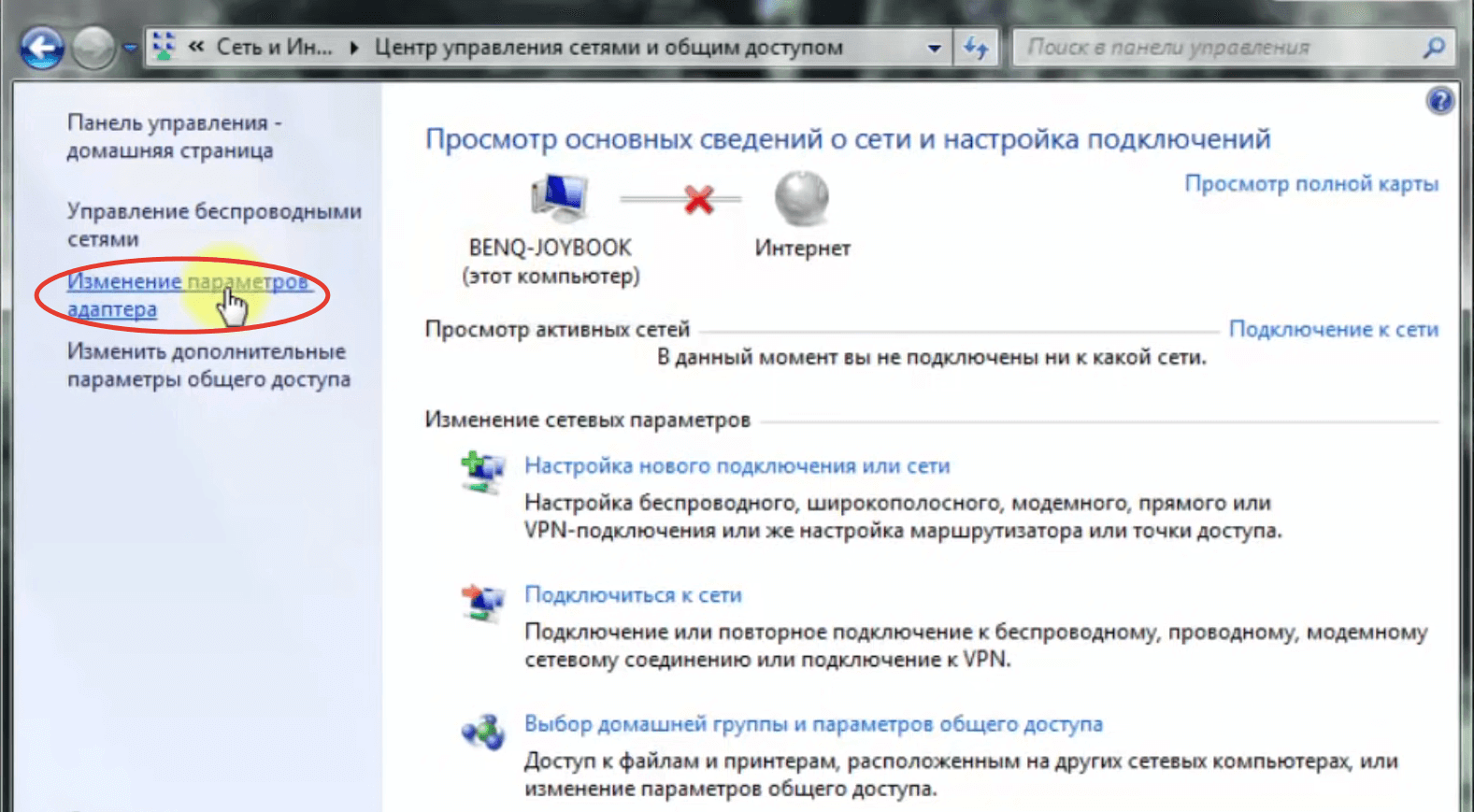
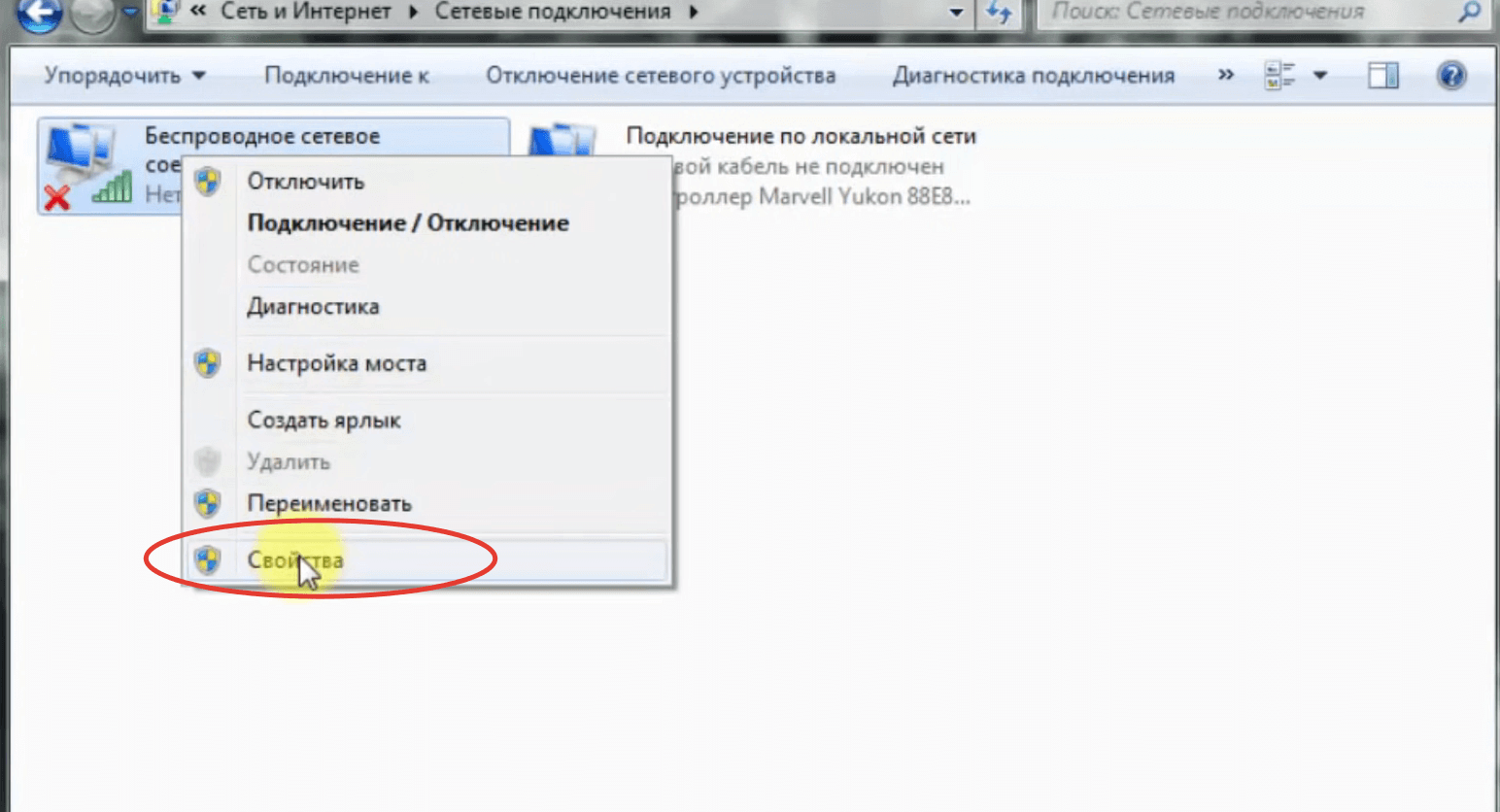
- Find in the list the line "Internet Protocol version 6 (TCP/IPv6)" and uncheck it. If there is no checkmark, go to the next step.
- Find "Internet Protocol version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" in the list and tick it. If it is already checked, skip this step.
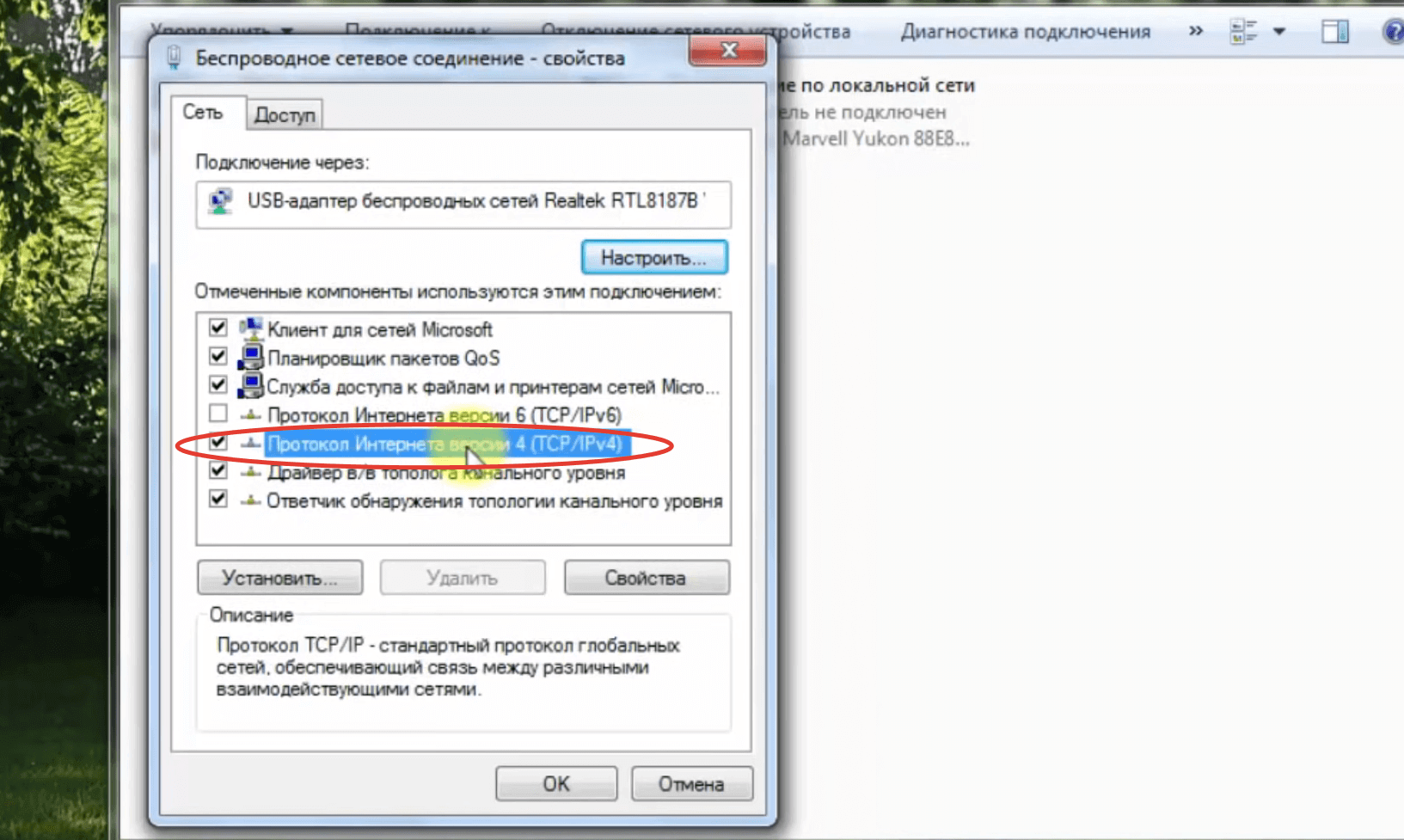
- Double-click on the "Internet Protocol version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" line – This will open the IPv4 properties.
- Mark the checkboxes "Obtain an IP address automatically" and "Obtain DNS-server address automatically" if you have a dynamic IP. If you have a static IP, you have to enter the corresponding data. You can find them out from your contract with your provider or from the technical support service.
What should I do if my computer can't connect to Wi-Fi?
First of all, make sure that you have done everything correctly. To do this, go through all the steps according to the instructions again. If no errors are found, then:
- Turn off the router for a few minutes and then turn it on again;
- reconnect the adapter to another USB connector or another PCIe bus (depending on the module type);
- make sure that you enter the correct password to connect to the access point. Maybe you are using a Russian-language layout or you have Caps Lock on;
- make sure that the router's settings are correct. Pay attention to the "Authentication methods" option (may be called "Encryption method"). Typically, home networks use WPA2-Personal;
- make sure that your computer is not on the list of banned devices. It is possible that MAC filtering is enabled in the router settings. You can check this in the network hardware web configurator;
- Reinstall the drivers by first uninstalling them. To do this, go to "Device Manager", find the block "Network adapters", expand it and double-click on the name of the module. The "Properties" window will open, where you should open the "Driver" tab, and then click on "Remove". The device name will change to "Network controller" and an exclamation mark icon in a yellow triangle will appear next to it. Next, restart your PC and install the driver from the firmware disk. If you don't have it, download the software from the manufacturer's site, using another device (laptop, smartphone or Android tablet);
- try to place the PC in close proximity to the router. Perhaps simply "not getting" the signal. If the suspicions are confirmed, then it remains only to use Wi-Fi repeater or to arrange a workplace near the modem;
- connect another router. Yes, you will have to look for it and configure it. But this is the easiest way to remove suspicion from the adapter;
- connect another receiver. Difficulties are the same, but this is the easiest way to check if the router and interfaces in the PC are working properly;
- call your ISP. Perhaps the problem is on his side – there was a malfunction or technical work is being carried out.