IEEE 802.11ac– This wlan standard further extends bandwidth and increases MIMO antennas to further increase data rate compare to 11n. refer our article on wlan 11-ac.

- RF Wireless World
- Types of WLANs
- Key Takeaways
- Comparison Table
- Сравнительная таблица
- What is a LAN?
- WAN: examples of use
- What other rare acronyms are found for networks?
- Rare but common acronyms:
- Cybernetic abbreviations:
- Other abbreviations that should be mentioned
- WLAN network establishment
- Applications of WLAN
RF Wireless World
This wireless LAN (WLAN) tutorial covers wlan basics, wlan standards and wlan features. This tutorial on wireless LAN also covers different wlan flavors viz. wlan 802.11a, 11n, 11ac, 11ad and wlan 802.11ax.
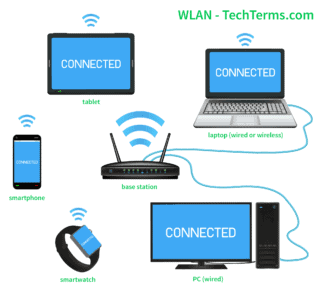
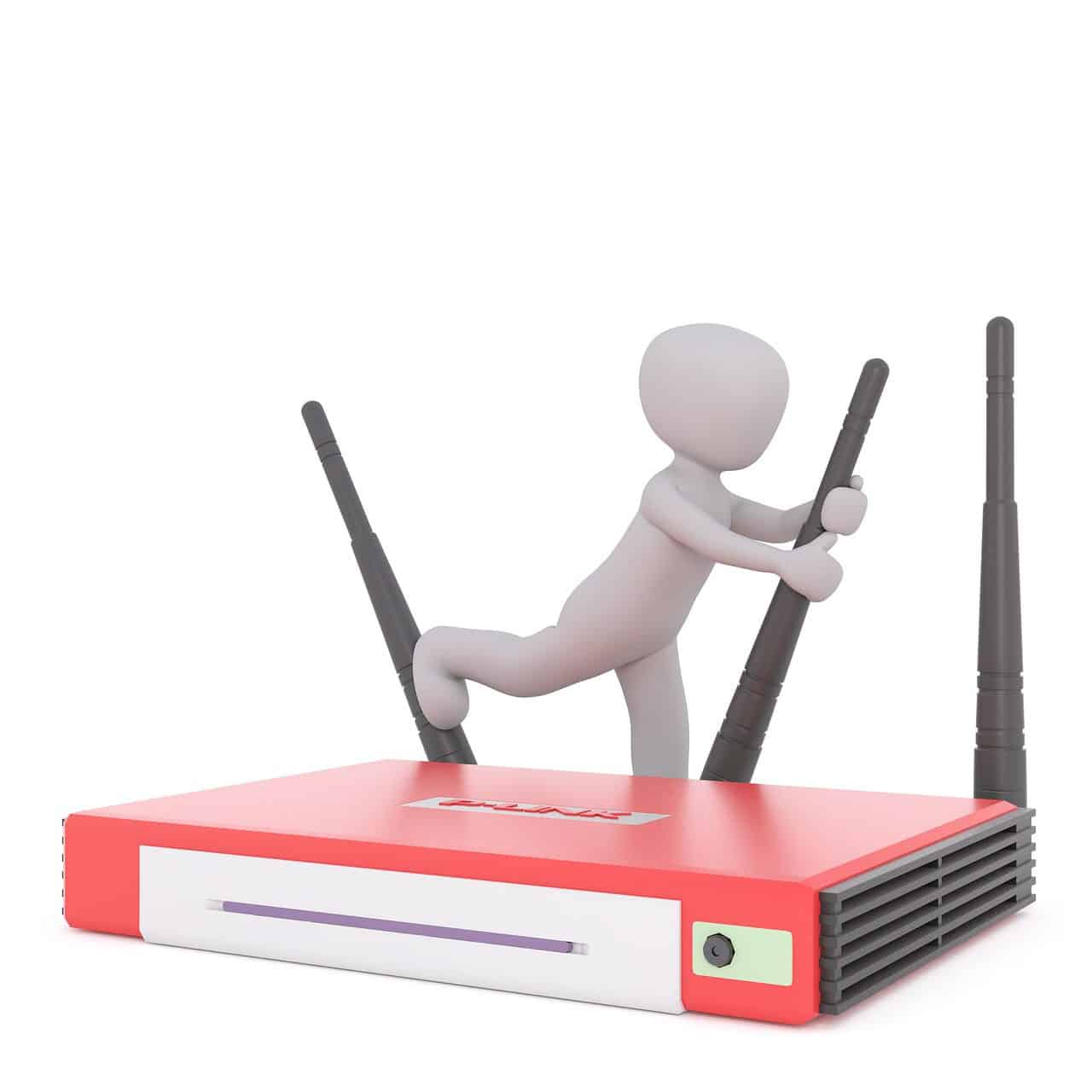
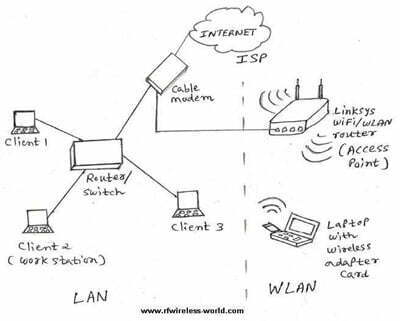
Wireless LAN is the extension of LAN which is used to connect more than one computers using ethernet cables. Also referred as WLAN. LAN was not capable of providing connectivity to wireless devices such as Laptop/PDA/ipad/Mobile. Hence wireless LAN has been developed to cater to this need. Today it has become very easy to connect such devices to the existing LAN in the company/residence with the use of WLAN routers. WLAN router connects physically with LAN and it has antennas which provides connectivity with wireless devices. This Wireless devices need to have WLAN chip with protocols to avail this service. Many WLAN hotspots or kiosks are available which provide internet facility using WLAN devices.
In WLAN there are series of standards to take care of different frequencies,data rate and range such as 11a,11b,11g,11n,11ac,11ad,11af and few are evolving. These standards define physical and MAC layers. WLAn basically connects two or more than two devices using some wireless distribution method such as spread spectrum or OFDM radio. This provides WLAN users the mobility to move around within small coverage area inside office or building premises referred as cell.
Types of WLANs
Peer to peer network permits wireless devices to directly communicate with each other. There is no central device involved in the communication or providing permission to communicate. Here all the devices communicate directly without involving any central device. This is also referred as Mesh network.
In a Bridge type of LAN, bridge connects two different networks with each other. A wireless ethernet bridge allows connection of device from a wired ethernet network to the wireless network. Here bridge acts as main interface point to the WLAN.
Key Takeaways
- WLAN stands for wireless local area network and uses radio waves to connect devices, while LAN stands for local area network and uses cables or wires.
- WLAN provides mobility and flexibility as devices can connect wirelessly, while LAN provides faster and more reliable data transfer speeds.
- WLAN is more suitable for home and small office networks, while LAN is more suitable for larger networks like enterprises or organizations.
The difference between WLAN and LAN is that WLAN stands for Wireless Local Area Network and LAN stands for Local Area Network. Both are network providers offering network services with varying costs, performance, and security levels.

Want to save this article for later? Click the heart in the bottom right corner to save to your own articles box!
WLAN stands for Wireless Local Area Network. This network type enables the transfer of data with the help of wireless transmitters and receivers. This does not use the typical data transfer done using the cables.
WLANs are used in areas that require a large number of devices to connect to the internet at the same time.
LAN stands for Local Area Network. It can be described as a collection of network devices in a specific location, and all of them are connected via switches or routers, which helps in the transmission of data. Each network device uses a cable to connect itself to the switch or router.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | WLAN | LAN |
|---|---|---|
| Stands for | Wireless Local Area Network | Local Area Network |
| Connection type | Wireless technologies | Includes both wired and wireless technologies. |
| Cost and security | Expensive to install and are less secure. | Less expensive and more secure. |
| Coverage | Large regions such as offices, buildings, stations, etc. | Large areas such as buildings. |
| Performance | High performance; performance affected by bad weather. | Good performance and it isn’t affected by the weather. |
| Interference | It can be interfered with easily. | It cannot be interfered with easily. |
| Examples | Desktops, laptops, tablets, and mobiles connected on Wi-Fi or hotspots networks. | Desktop and laptop connected to LAN in a building or an office. |
WLAN stands for “wireless local area network.” Many gadgets come pre-installed with Wi-Fi, where the users when in range of router can connect to the internet wirelessly.
WLAN connections require both an infrastructure mode and an access point. They can be concurrently used by any device and all the devices when in the range of the router.
WLANs with signal interruptions have decreased speed and link frequency. The install of WLANs is costly, but it is relatively easy to use. Nowadays, all the devices are Wi-Fi ready, so all you need to establish the connection is the hardware system.
WLAN is used in areas where a large no of devices have to be connected to network providers for the internet, but not necessarily at the same time. Nowadays, WLAN is also used at homes to connect laptops and mobile phones.
WLAN has better performance and rarely encounters interference if properly mounted. However, the distance between the device using the internet and the router has a direct impact on the connection’s speed and power.
Сравнительная таблица
| Параметры сравнения | WLAN | ЛВС |
|---|---|---|
| Стенды для | Беспроводная локальная сеть | Локальная вычислительная сеть |
| Тип соединения | Wireless Technologies | Includes both wired and wireless technologies. |
| Cost and security | Expensive to install and less secure. | Less expensive and more secure. |
| Coverage | Large areas such as offices, buildings, stations, etc. | Large areas such as buildings. |
| Performance | High performance; performance was affected by bad weather. | Good performance; not affected by weather. |
| Intervention | It can be easily interfered with. | It cannot be easily interfered with. |
| Examples | Desktops, laptops, tablets, and cell phones connected to Wi-Fi networks or hotspots. | Desktops and laptops connected to a local area network in a building or office. |
WLAN stands for "wireless local area network. Many gadgets come pre-installed with Wi-Fi, so users within reach of the router can connect to the Internet wirelessly.
WLAN connections require both infrastructure mode and access point. They can be used simultaneously by any device and all devices within range of the router.
Wireless LANs with signal interruptions have reduced speeds and connection frequencies. WLAN installations are expensive, but relatively easy to use. Nowadays, all devices are Wi-Fi ready, so all you need to establish a connection is a hardware system.
WLAN is used in areas where a large number of devices need to be connected to network providers to access the Internet, but not necessarily at the same time. Nowadays, WLAN is also used at home to connect laptops and cell phones.
What is a LAN?
Connecting to the Internet over a local area network uses Ethernet cables and adapters (mostly used in laptops and desktops). And a hub or router is also required in addition to these items. broadband routers help establish an Internet connection, simplifying the process and providing good performance results.
A LAN requires a central connection with a router and a network of cables to connect to all computers. Many of the computers on the network are connected by switches.
Switches and routers are installed using network settings. A LAN is installed in places where there are no large. computers need to be connected to the Internet at the same time, such as offices or other buildings.
The network is wired, and a standard Internet protocol is installed for proper operation of the network. Laptops have a built-in LAN port, so you only need to set up a LAN connection on your laptop to access your service provider.
LAN services are reasonably priced, which everyone can afford, making them a cost-effective and convenient way to connect to the Internet.

WAN: examples of use
WAN Encompasses the networks of an entire country or multiple nations with no geographical limitations. Global networks typically include leased telecommunications channel infrastructure.
It is believed that Internet – is a particular example of a WAN [ISBN 0-7821-4406-3].
There are also no restrictions on how networks are connected/connected on the WAN. It can be telephone lines, radio transmission, fiber-optic – anything. The main condition for the existence of a wide area network is the ability to transmit data bidirectionally (back and forth).
What other rare acronyms are found for networks?
There are not as many as you might think. They are all used in real life to classify networks.
Rare but common acronyms:
- LPWAN – Low Power Wide Area Network or "Power Efficient Wide Area Network" (Low-Power Wide-Area Network).
- IAN – a network without a physical location, an "internetified network" or "cloud network" (Internet Area Network).
- NAN – A closely broadcast network or "close-placement network" (Near Area Network), a private version of LAN (e.g., when handing out Wi-Fi from a phone).
- PAN – personal network (Ppersonal Area Network), also a particular example of LANwhere devices of the same user are combined into a network.
There is an interesting abbreviation from the IT point of view to classify computing networks. It could be referred to a futuristic and even cybernetic technology. But it is already actively used in real life for medical purposes.
Cybernetic abbreviations:
BAN (WBAN, MBAN or BSN) – A network confined to a particular person's body. It is defined as:
An example of a BAN-implant – A nail smart chip for 150 rubles.
Other abbreviations that should be mentioned
NFC – An abbreviation known to everyone. It refers to the technology of pairing two devices via a protocoled connection (a smartphone and a payment terminal, for example). It is an example of a "close field" computing network (Near-Field-Communication).
WLAN network establishment
As mentioned below there are various frames exchanged between STATION and Access Point to establish wlan network connection.
Works on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz RF center frequencies with various Channel bandwidths as shown below.
11b channels-Non overlapping (22MHz bandwidth), North America
Channel 1- 2412 MHz
Channel 6- 2437 MHz
Channel 11- 2462 MHz
11b channels-Non overlapping (22MHz bandwidth), Europe (except France and Spain)
Channel 1- 2412 MHz
Channel 7- 2442 MHz
Channel 13- 2472 MHz
11n channels-40MHz bandwidth, occupied bandwidth of 33.75 MHz
Channel 3- 2422 MHz
Channel 11- 2462 MHz
11 g/11n -20 MHz bandwidth, occupied bandwidth of about 16.25 MHz
Channel 1 – 2412 MHz
Channel 5 -2432 MHz
Channel 9 -2452 MHz
Channel 13 -2472 MHz
Applications of WLAN
It extends LAN by way of adding additional PCs(with WLAN PCI card) and other WLAN devices(laptop/ipad/tablet) using wireless connectivity.
It provides connection of two LANs housed in two nearby buildings
Wifi hot spots are available in park/coffee shop/malls, which provides visitor with wlan or wifi capable device to use internet.
Adhoc networking of devices temporarily without need of any server.Here all the devices(peers) communicate directly.
Our page on Vendors section list out WLAN devices in various categories such as equipment, semiconductor, test and measurement, channel emulator and antennas. REFER Page.
Read More: